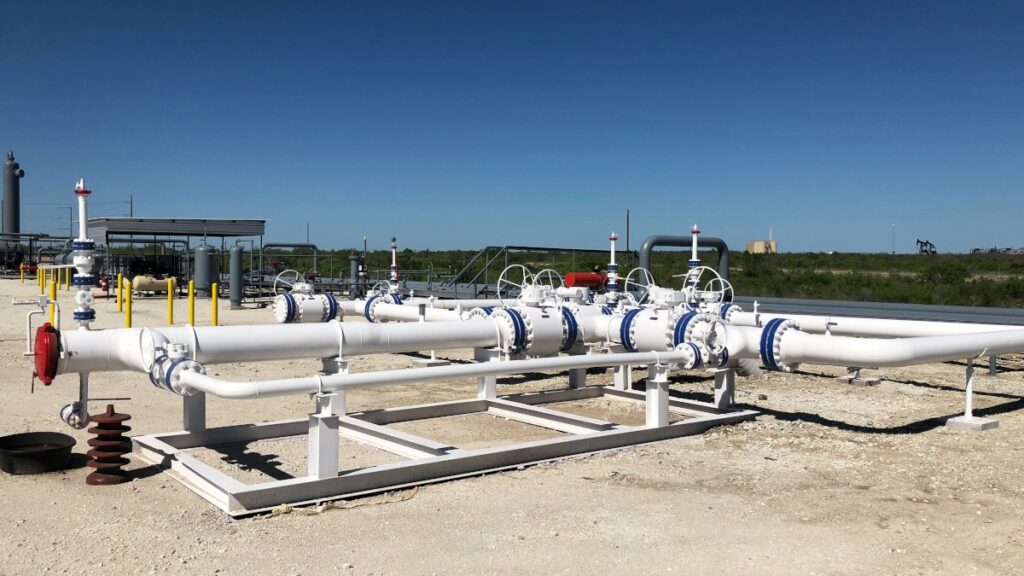

Argentina has been exploring carbon capture and utilization technologies driven by its energy sector, climate commitments, and potential for carbon utilization. The government is promoting blue hydrogen as a transition fuel, which needs carbon capture. For instance, YPF is partnering with Chevron and Shell to study the injection to boost oil production while storing emissions. This is an initiative that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions related to offshore oil and gas production. The implementation of carbon capture modules helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The modules are designed to capture CO₂ emissions from industrial processes, power plants, or directly from the atmosphere. Carbon capture modules are part of carbon capture and storage and carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies. Components like the downlead clamps stabilize vertical cables, pipes, or tubing in industrial installations.
Carbon capture and utilization technologies are crucial in the decarbonization efforts in Argentina. CO₂ injections boost declining oil output in mature fields to extend the life of Argentina’s energy reserves. Downlead clamps ensure the safe and efficient transport of CO2, power, and control systems. This is crucial in Argentina’s growing energy and industrial decarbonization projects. High-quality downlead clamps provide structural support to vertical or inclined piping to prevent vibrations, leaks, or misalignment due to thermal expansion. The clamps also organize and protect vertical cables from environmental damage in harsh industrial settings.
Importance of carbon capture and utilization in Argentina’s energy sector
Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) enables oil and gas from Vaca Muerta, cement, and steel sectors to reduce emissions. The technologies also support low-carbon hydrogen from natural gas, which positions Argentina as a future exporter. The use of carbon capture and utilization also eases carbon-neutral biofuels, supports economic and export opportunities, and expands geological storage potential. It also helps balance energy security, economic growth, and climate goals in the transition to a low-carbon future.
Carbon capture and utilization supporting decarbonization via downlead clamps
A downlead clamp is a mechanical device used to secure vertical cable runs, tubing, or instrumentation lines to a structure. The clamps guide and fix power, data, and fluid lines that support core operations. These operations include monitoring emissions, powering capture units, and transmitting CO₂ flow data. Integrating carbon capture and utilization into its energy and industrial sectors is crucial for Argentina’s transition to a low-carbon future. Download clamps enable the efficient and reliable CCU infrastructure. Here are the roles of downlead clamps in CCU technologies.
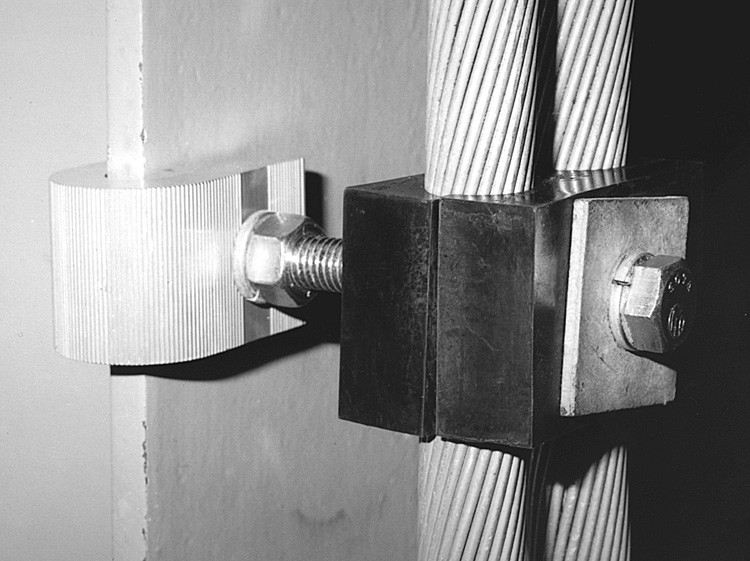
- Ensuring system integrity in harsh environments—CCU modules serve in offshore oil platforms, FPSOs, or remote industrial hubs in Argentina. Downlead clamps protect sensitive tubing and cabling from high winds, vibration, and corrosion to help extend the life and reliability of the system.
- Enabling modular and scalable design—downlead clamps enable easier assembly, disassembly, and repositioning of lines and cables during installation. This enables faster deployment in hydrocarbon hubs like Vaca Muerta.
- Supporting real-time monitoring and control—data transmission is crucial in carbon capture and utilization tech. Downlead clamps hold fiber optics or sensor wiring in place to help track CO2 volumes, temperatures, and pressures.
- Securing CO₂ transport pipelines—downlead clamps are mechanical supports used to anchor vertical or inclined pipelines transporting CO₂ from emission sources.
- Integration with renewable energy projects—CCU can mitigate residual emissions from backup gas plants to expand Argentina’s renewable energy capacity. Download clamps ensure CO₂ pipelines withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Potential for carbon capture and utilization modules in Argentina’s energy sector
Carbon capture and utilization technologies are crucial to reduce emissions in Argentina while maintaining energy security. These technologies allow Argentina to reduce emissions, enable blue hydrogen, decarbonize energy industries, and create carbon-based products. Argentina’s scaling up of renewables needs CCUs, aligning with its climate commitments under the Paris Agreement. The following are the roles of carbon capture utilization in Argentina’s energy sector.

- Decarbonizing fossil fuel-based energy—CCUS modules capture CO₂ from gas processing plants and reinject it for enhanced oil recovery or store it underground. For instance, YPF and Shell are exploring CCUS to lower the carbon footprint of Vaca Muerta’s operations.
- Enabling a low-carbon hydrogen economy—Argentina plans to produce blue hydrogen as a transition fuel before scaling up green hydrogen production. Excess renewable energy could power direct air capture modules to offset emissions.
- Supporting industrial decarbonization—the cement sector emits 8% of national CO₂. CCUS modules can capture process emissions from clinker production.