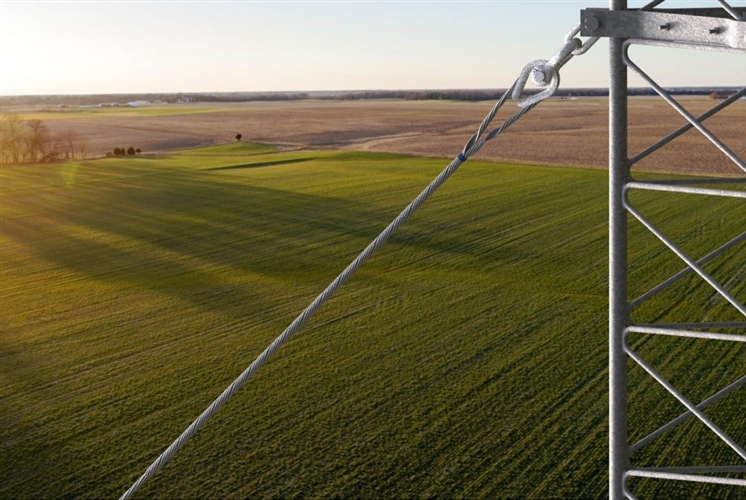

A big grip dead end is a hardware used in the construction and termination of overhead transmission lines. it also serves as a mechanical termination point for overhead conductors. This helps to provide support and anchoring to the conductor at the end of a run. A big grip dead end is also responsible for supporting the weight and tension of the conductor. It is from high-strength materials like steel to withstand the mechanical forces of overhead lines. Big grip dead ends can withstand the regions challenging environmental conditions in Southeast Asia. This helps to maintain power reliability in high-humidity coastal areas and typhoon-prone regions. The common types include full tension, semi tension, single coil and double coil dead ends. They find use in applications such as transmission lines, corner and angle structures, renewable energy, crossarms and industrial areas.
Key features of big grip dead ends
There are various features of the dead end that contribute to the reliable power delivery and structural integrity. The available features of the dead end depend on various factors. These include voltage levels, design and environmental conditions in the region. The following are the key features of the big grip dead end.

- Tension control – the dead ends provide tension control for conductors. This ensures proper maintenance at the correct levels.
- Secure anchoring – they prevent the conductors from slipping even in high tension applications.
- Gripping mechanism – they feature a reliable gripping mechanism that securely holds the conductor in place.
- Materials – they are from high-strength materials like steel and compopsite. These materials ensure durability and load-bearing capacity.
- Variety of types -they also come in various types and designs to hold different conductor sizes, tension levels and line configurations.
- Corrosion resistance – polymer big grip dead ends offer corrosion resistance. This is especially in coastal or corrosive environments in Southeast Asia.
- Environmental durability – they also withstand various environmental factors. These include high humidity, extreme temperatures and exposure to UV radiation.
- Ease of installation – proper installation is easy with clear guidelines. This is to ensure safe and efficient deployment.
- Safety – they have features that helps prevent accidents during installation and maintenance.
Selection and installation of big grip dead end
The selection process should ensure the proper functioning and reliability of transmission lines. Also, it is advisable to consult with experts for guidelines on the best big grip dead end for your application. The factors to consider include conductor size and type, tension requirements, line configuration, voltage rating, mechanical load and material among others. The installation process should ensure the reliability and safety of overhead transmission lines. the following is a basic installation process of the big grip dead end.

- Safety precautions – ensure you follow all the necessary safety protocols and verify the work area is clear of potential hazards.
- Conductor preparation – prepare the conductor end by removing any corrosion, dirt or contamination.
- Conductor attachment – place the big grip dead end on the conductor and ensure proper alignment on the dead end.
- Tightening – use the suitable tools such as wrenches and torque wrenches to tighten the dead end’s gripping mechanism securely.
- Alignment and positioning – verify that the dead-end aligns properly within the intended direction of the conductor.
- Inspection and testing – inspect for any signs of damage, misalignment or irregularities. Conduct any required testing or tension adjustments to ensure the correct tension levels.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the installation including dates, torque values and any testing results.
Maintenance and inspection of big grip dead end
Regular maintenance and inspection ensure the continued reliability, performance and safety. It also helps identify and address any issues that may lead to equipment failure or compromise. Additionally, it is advisable to follow manufacturer recommendations and adhere to industry standards and regulations. The following is a basic maintenance and inspection of big grip dead ends.

- Perform regular visual inspections of all the big grip dead ends along the transmission or distribution line. Check for signs of damage, wear or corrosion on the dead-end components.
- Check for the accumulation of contaminants on the dead ends. These may include dust, pollution or debris.
- Ensure the proper alignment of the dead-ends with the conductors and support structures.
- Evaluate the tension in the conductors near the dead ends to ensure they are within the specified range.
- Examine the dead-ends for signs of corrosion especially in coastal or corrosive environments.
- Check for loose or missing nuts, bolts or other fasteners in the dead-end assembly.
- Clean the dead-end components to remove contaminants using the approved cleaning materials and methods.
- Apply corrosion-resistant coatings or inhibitors to protect the dead-end components from deterioration.
- Replace any worn out or damaged components according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities including dates, inspections, adjustments and replacements.
Comparative analysis of big grip dead end in Southeast Asia
A comparative analysis involves evaluating different aspects of these hardware components. This is to determine their suitability for the region’s specific needs and conditions. This depends on factors such as environmental conditions, maintenance requirements, initial cost and long-term cost effectiveness. Also, it is necessary to consult with industry experts to help select the most suitable option for each application within the region. The following are the common factors to include in a comparative analysis of big grip dead ends in Southeast Asian countries.
- Material – steel dead ends offer durability and strength. This makes them suitable for high tension applications. Composite or polymer dead ends are lightweight and corrosion resistance. This makes them ideal for high pollution areas in Southeast Asia.
- Cost-effectiveness – consider the total cost of the dead ends including the initial costs and maintenance costs.
- Ease of installation – select dead ends that are lighter and easier to handle during installation and maintenance. This is to reduce labor costs and risks.
- Tension control – the choice of the dead end depends on the specific tension requirements of the transmission or distribution lines.
- Environmental resistance – big grip dead ends are from materials that resist saltwater exposure and other pollution elements in the region.
- Local manufacturing – the increased local manufacturing of composite and polymer dead-ends influences the pricing and supply.
- Renewable energy integration – increased investments in renewable energy lead to the increased demand for big grip dead ends. These help in the construction of the infrastructure that connects to the main electric grid.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
Certifications and standards help to ensure the quality, safety and reliability of hardware components in Southeast Asia. Some standards may vary by country but many countries adapt the international and regional standards. Additionally, the manufacturers should ensure their products follow the local standards and regulations. This is to ensure the equipment aligns with specific regional requirements and safety guidelines. The following are the common standards and regulations for big grip dead ends in Southeast Asia.

- IEC standards – they offer standards for compression and mechanical connectors for power cables.
- ASTM standards – these are standards for practice for salt spray apparatus, tensile properties and test methods.
- ISO standards – they offer requirements with guidance for use to enhance quality.
- Local regulations and standards – many of the southeast Asian countries have their own local standards and regulations for electrical equipment.
Regional markets for big grip dead end in Southeast Asia
The regional market for big grip dead end is volatile in Southeast Asia due to various aspects. These includes the region’s growing demand for electrical infrastructure, expansion of renewable energy projects and the need for reliable power transmission. The manufacturers and suppliers should understand the regions unique requirements and tailor their offerings accordingly required to succeed in this market. The following are the key factors that shape the regional market for big grip dead ends.
- Infrastructure development – the expansion of transmission and distribution networks drives the demand for the dead ends.
- Coastal areas – corrosion-resistant big grip dead ends are suitable for the coastal regions in Southeast Asia.
- Local manufacturing – the increased local manufacturers in the region also influence the availability, supply and prices of the dead ends.
- Renewable energy projects – the increased investments in renewable energy projects lead to the increased demand for the dead ends.
- Pollution control – pollution-resistant big grip dead ends help to maintain performance and reduce maintenance needs.
- Cost effectiveness – this may include initial costs, total cost of ownership and maintenance of the dead ends.
- Environmental conditions – the region ha diverse weather conditions that influence the demand of big grip dead ends. These include the tropical storms, typhoons and salt spray in the region.
Frequently asked questions
This is a type of hardware used in overhead transmission lines and distribution lines. It helps to secure the conductors while maintaining proper tensioning.
The dead ends are from materials such as steel, composite and polymer materials. They are able to withstand pollution, corrosion and different weather conditions.
Ensure the dead ends can handle the unique demands of connecting renewable energy sources such as wind and solar farms.