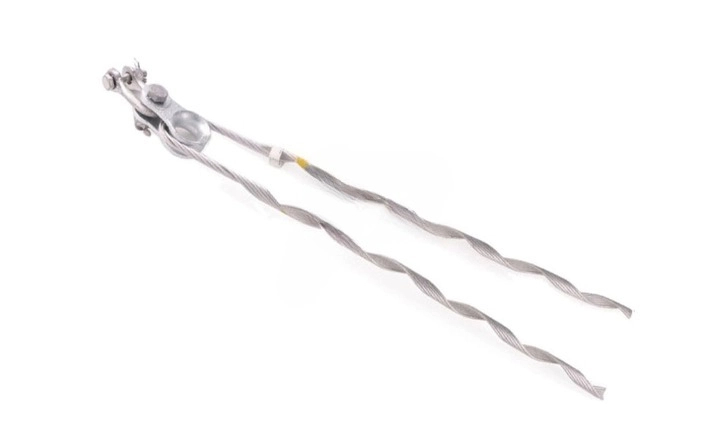
A distribution grip dead end is a component used in the installation and termination of overhead electrical distribution lines. It is also known as a dead-end grip. The dead-end grip provides a secure attachment for the overhead conductor to the pole. Its design varies depending on type and size of conductor used and tension requirements. Distribution grip dead end has designs to anchor the conductors to the structure. They also ensure they can withstand high tension and mechanical stresses. The dead-end grips are from durable materials such as steel or aluminum alloys. These materials are able to withstand the rigors of long-term exposure to environmental factors. They also come in various designs to hold different types and sizes of conductors. By doing this, the help to maintain the integrity and reliability of the electrical grid infrastructure.
What’s the design of the distribution grip dead end
The dead end has design that help ensure the secure attachment and reliable performance. The design should balance between strength, reliability and ease of installation and compatibility. The following are the key aspects of distribution grip dead end design.
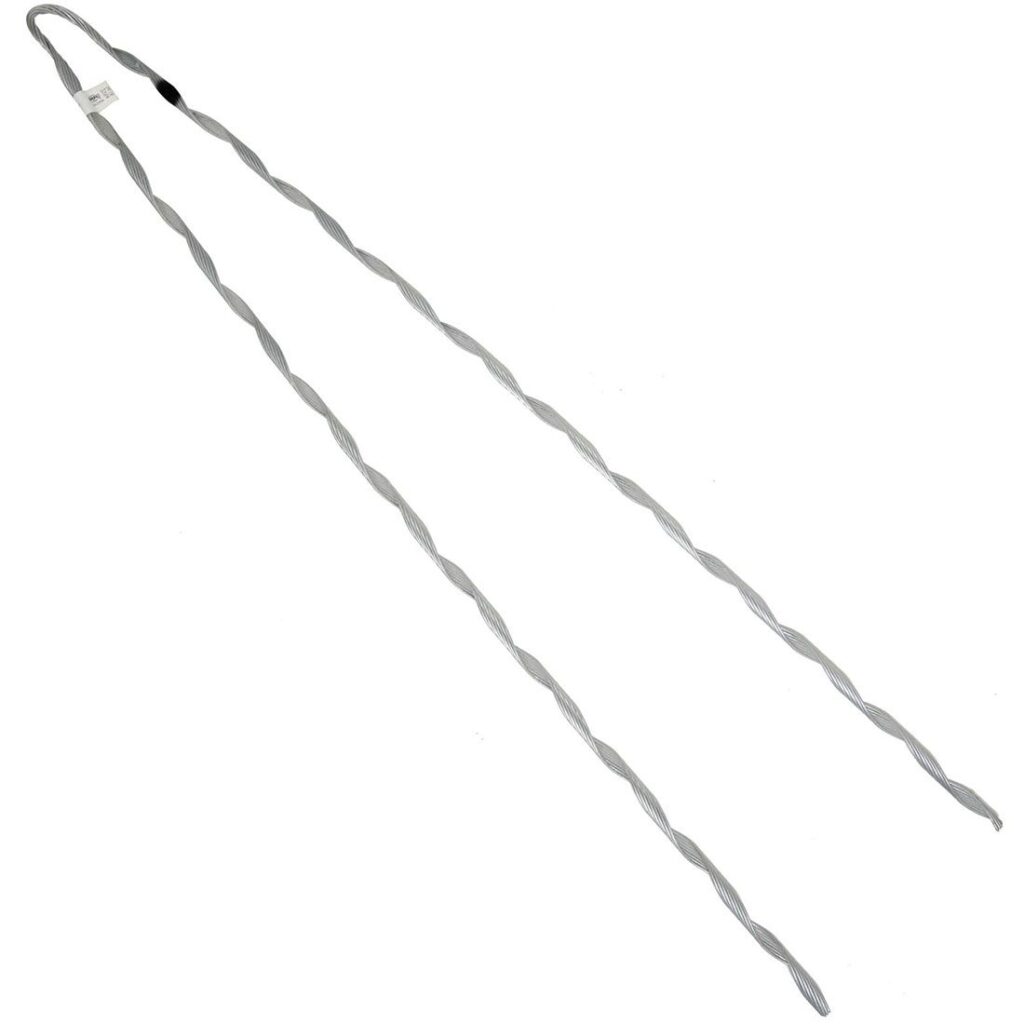

- Gripping mechanism – the dead-end grip has designs to hold the conductor in place. The grip may consist of serrated jaws, wedges of mechanisms that provide a tight hold on the conductor.
- Tension rating – distribution grip dead ends have designs to withstand specific tension levels. The design depends on wind loading, ice accumulation, conductor sag and line tension variations.
- Insulation – the dead end may include insulation to prevent electrical arcing between the conductor. The insulation helps maintain the safety and integrity of the distribution line.
- Material selection – the dead end grips are from high-strength materials. These materials include steel or aluminum alloys. The materials provide durability, corrosion resistance and ability to withstand the mechanical stresses.
- Compatibility – their design must be compatible with the size, type and configuration of the conductor used. This helps to ensure a proper fit and reliable performance under all operating conditions.
- Environmental considerations – the design should take into account the conditions where they will install. These factors include temperature extremes, UV exposure, moisture and corrosive agents.
- Ease of distribution – the dead end grips should have designs for easy installation by line workers using standard tools.
Functions and uses of distribution grip dead end
Distribution grip dead ends serve several important functions in electrical distribution systems. they help to ensure safe and reliable operation of overhead electrical distribution systems. they provide support, stability and protection for conductors and infrastructure. The following are the common functions of distribution rip dead ends.
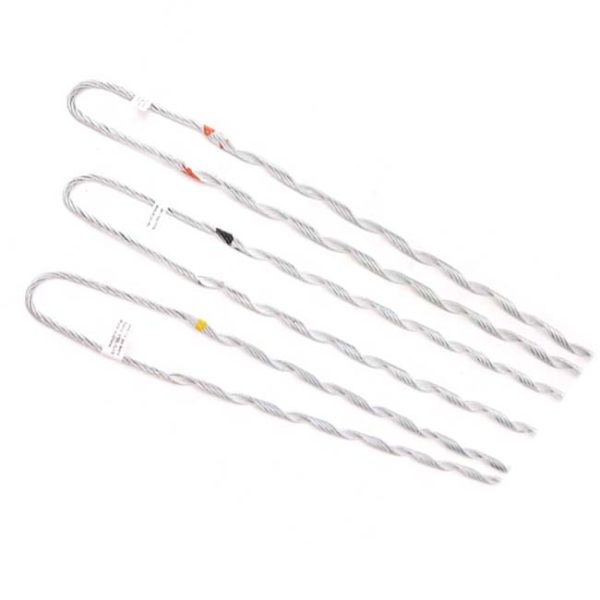
- Secure attachment – the main function of the dead ends is to provide a secure attachment point for the conductor. This ensures the conductor remains in place even under high tension.
- Tension management – dead ends assist in managing the tension applied to the conductor. The help distribute and absorb the forces reducing stress on the conductor and support structure.
- Electrical isolation – the dead-end grips may include insulation or isolation features. This is to prevent electrical arcing between the conductor. This helps maintain electrical safety and prevents damage to the distribution line components.
- Corrosion protection – dead ends are from materials that are resistant to corrosion. This helps prolong the service life of the grip and performance over time.
- Conductor support – the dead-end grips help support the weight of the conductor and prevents sagging. This is to ensure proper clearance from the ground or other objects. This is to maintain the integrity and safety of the distribution line.
- Galloping prevention – galloping is the large-amplitude oscillations that occurs in conductors. The dead-end grips have designs to dampen the oscillations and stabilize the conductor.
- Line maintenance – distribution grip dead ends have designed to allow for easy installation, removal and replacement of conductors during maintenance. This is to ensure maintenance tasks are efficient and safe.
Types of distribution grip dead ends
Distribution grip dead ends are available in different types and designs to hold different type of conductors. The selected dead-end grip depends on conductor type, installation requirements and operation considerations. Additionally, proper selection helps to ensure the reliable performance of their distribution lines. The following are the common types of distribution grip dead ends.
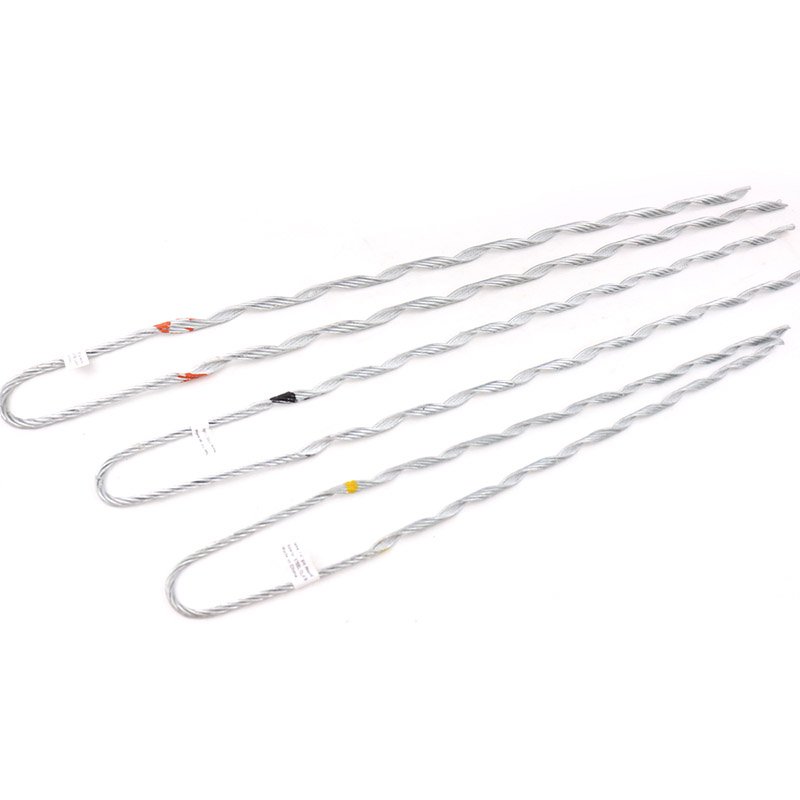

- Suspension grip dead end – these dead ends work in suspension applications where the conductor hungs from a supporting structure. They consist of a combination of grips, preformed rods, and other components that provide support and strain relief to the conductor.
- Helical grip dead end – this features a helical design that consists of a helical groove metal body that wraps around the conductor. The grip tightens using a tool wrench, providing a secure and reliable connection
- Wedge grip dead end – the dead ends use wedges to secure the conductor and a tapered opening. They are commonly used for high voltage distribution lines and can hold a wide range of conductor sizes.
- Guy grip dead end – guy grip dead ends are specifically designed for guy wires. They help to provide extra support and stability to poles or towers. They consist of grips tightened around the guy wire securing it to the structure.
- Compression dead ends – these dead ends use a compression fitting to secure the conductor in place. It works with insulated conductors and requires specialized tools to crimp the fitting onto the conductor.
- Bolted dead ends – these feature a bolt mechanism that fastens the conductor to the supporting structure. They work with bare conductors and install by tightening bolts to achieve a firm grip.
Properties of materials used for dead end grips
The dead-end grips are from materials selected for their strength, durability and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers can produce distribution grip dead ends meet the demanding performance requirements. This is to ensure safety, reliability and longevity. Additionally, the distribution grip dead ends are from materials like steel and aluminum alloy. The following are the properties of materials used for dead end grips.

- Mechanical strength – the dead-end grips face high tension forces to withstand loads without deformation. High-strength steel alloys, aluminum alloys and composite materials.
- Electrical conductivity – the materials used should not interfere with the electrical conductivity of the conductor. It is important to use materials with good electrical conductivity to reduce impedance in the distribution line.
- Temperature stability – grip dead ends face a wide range of temperatures from extreme cold to high heat. The materials should maintain their mechanical properties and performance across the temperature range.
- Ease of machining and fabrication – the materials used in the dead-end grip should be easy to machine and fabricate in the desired shapes. This allows for efficient manufacturing processes and ensures the dead ends meet the specifications.
- Corrosion resistance – dead end grips are prone to various environmental conditions that cause corrosion. Corrosion resistance materials help to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
- Weight – the weight of the dead-end grip can affect installation and maintenance procedures. Materials with high strength-to-weight rations can help reduce the weight of the dead end without compromising strength.
- Fatigue resistance – distribution grip dead end is subject to cyclic loading due to wind and conductor movement. Good fatigue resistance properties can withstand repeated stress cycles without experiencing fatigue failure.
Mounting hardware for distribution grip dead ends
The mounting hardware for distribution rip dead ends plays a crucial role in attaching the dead end to the support structure. The choice of the mounting hardware for the dead-end grip depends on several factors. This is including type of support structure, installation requirements and environmental conditions. Also, mounting hardware ensure the dead ends are securely attached and capable of withstanding the mechanical stresses. The following are the common mounting hardware for the dead-end grips.

- Bolts and nuts – bolted mounting hardware consists of bolts, nuts and washers used to secure the dead end. The bolts insert through the holes and tightened with nuts to provide a strong and secure attachment.
- Straps – mounting straps help to secure distribution grip dead ends to wooden utility poles. They wrap around the pole and fasten using bolts or screws. They help to provide a secure attachment point for the dead end.
- Welded attachment – welded attachments help to secure distribution grip dead end. Welding provides a strong and durable connection between the dead end and the support structure.
- Anchors – anchors serve as mounting hardware to provide extra support and stability to distribution grip dead ends.
- Clamps – clamping hardware uses clamps to hold the dead end in place on the support structure. The clamps may be adjustable to accommodate different sizes and types of structures.
Frequently asked questions
A distribution grip dead end is a type of hardware used to terminate the ends of conductor. They also help to attach them to support structures.
Properties such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, weight, temperature stability are important for materials.
Distribution grip dead ends serve several functions including providing a secure attachment point for conductors. They also support the weight of the conductor, managing tension and preventing galloping.