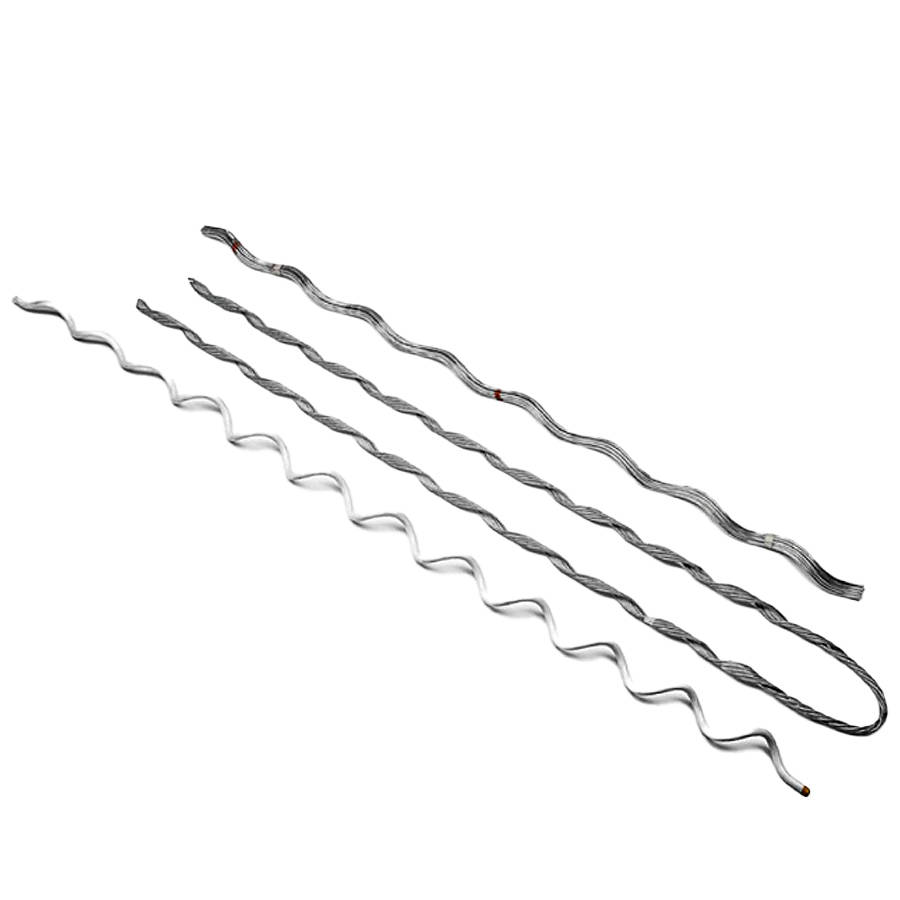

Formed wire is a specific type of conductor used to transmit electrical power from one location to another. It forms through a process of twisting multiple individual strands together in a specific pattern to achieve a desired cross-sectional area. This design provides excellent mechanical strength for withstanding tension and stresses during installation. Formed wire offers low resistance which ensures efficient power transmission over long distances. It is from materials such as aluminum and aluminum alloy that resists rust and corrosion. The material is lightweight which reduces the overall weight of the transmission line.
Components of a formed wire
The components work together to create a conductor capable of transmitting electrical power. The components are capable of carrying high voltages and long distances with minimal energy losses. Specific design of the wire varies depending on the environmental conditions and mechanical requirements of the transmission line. The following are the main components of the formed wire.
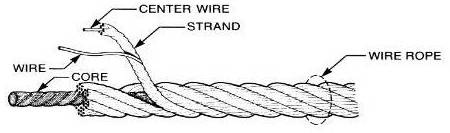
- Strands – the strands are the building blocks of the formed wires made of aluminum or aluminum alloy. The number of strands in a formed wire may be 7 strands, 19 strands or 37 strands.
- Twists – the strands twists together in a specific pattern to form a strong conductor. This forms a desired electrical and mechanical properties of the wire.
- Outer layer – formed wires have a thin layer of coat to improve their resistance to corrosion and environmental conditions.
- Core support – this is an optional component of the wire added to enhance the overall mechanical strength of the conductor. It also provides additional support during installation and tensioning of the transmission line.
Types of formed wires
There are several types of formed wire designed to meet specific electrical and mechanical requirements of the transmission lines. The selection of a specific type of formed wires depends on various factors. These include voltage level, current-carrying capacity, span length and mechanical requirements. Each design of the formed wires optimizes the performance, reliability and cost-effectiveness of the transmission system. The following are the common types of the formed wire.

- Insulator tie – this type of formed wire secures the insulators to the poles or other structures. This type of made from stainless steel or copper for corrosion resistance.
- Armor rod – this type is from materials like steel or aluminum and it helps to protect the conductors from damage. They are available in different diameters and lengths to hold different types of conductors.
- Line guard – this is from steel or aluminum and it protects the conductors from damages caused by animals or other objects.
- Conductor splice – this type of formed wires helps to splice conductors together on the transmission lines.
- Dead-end grip – this type of formed wire helps to secure the end of a conductor to a pole or other structures.
- Suspension clamp – this helps to suspend conductors from poles or other structures.
- Spiral vibration damper – This type helps to dampen the vibrations in conductors to prevent fatigue.
Applications of formed wires
Corrosion resistant formed wires is the ideal choice for industrial applications. This is because they offer long-lasting reliability. They find use in various applications in the industry due to their mechanical and electrical properties. Formed wires improves the reliability and efficiency of electrical and communication systems. The following are the common application areas of the formed wire.

- Overhead transmission lines – formed wires help to transmit electrical power over long distances. This could be from power generation stations to distribution centers and end-users.
- High-voltage power transmission – the compacted designs assist in handling higher currents and reduces energy losses.
- Railway electrification – the wires also help to power electric locomotives and trains efficiently.
- Distribution lines – the wires help deliver electricity from substations to residential, commercial and industrial areas.
- River crossings and long-span transmission lines – high strength formed wires work in river crossings and long-span transmission lines. They help to provide necessary mechanical support and prevent sagging.
- Telecommunication cables – the wires work in communication cables for support of the structures.
- Rural electrification – the wires help in rural electrification projects. This is in projects such as overhead power lines to extend power supply to remote areas.
Installation of formed wire
Proper installation ensures a safe and reliable setup of the formed wires. The installation process of the formed wire varies depending on specific project requirements, terrain and environmental conditions. Additionally, it is crucial to seek professional assistance whenever in doubt. The following is a basic step by step process for the formed wires installation.

- Identify the path, location of towers and potential obstacles to minimize environmental impacts and optimize the lines performance.
- Erect the poles or towers at specified intervals along the planned route to provide support for the overhead conductors.
- Prepare the conductors and the necessary accessories like clamps, suspension fittings and spacers.
- String the conductors using the necessary equipment such as tensioners and pulling machines to the insulators.
- Tension the conductors to the required level using tensioning equipment and ensure the conductors have the right sag.
- Splice the conductors together if necessary to form a continuous line using the necessary fittings and hardware.
- Inspect the installation to ensure all components are properly installed and secure. Conduct any necessary tests to verify the integrity and performance of the transmission line.
Selecting the best formed wire
Selecting the best formed wires may be a tough nut to crack due to the variety of options in the markets today. The selected formed wire should ensure optimal performance and reliability of your application. Ensure the selected conductor aligns with the projects requirements and contributes to the efficiency of the systems. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with the industry experts on the best formed wire to use. The following are the factors to consider when selecting the formed wires.

- Evaluate the expected lifespan of the formed wires and the required maintenance efforts. It should provide a suitable life with minimal maintenance requirements.
- Consider the skills and expertise of the installation team to ensure safety, reliability and long-term service.
- Assess the cost effectiveness of the wire and balance the quality and performance with the budget.
- Consider the environmental conditions such as humidity or extreme temperatures where the conductor will install.
- Consider the required current-carrying capacity, voltage rating and resistance of the conductor.
- Ensure the selected formed wires is compatible with the required fittings, accessories and hardware for installation.
- Evaluate the mechanical strength and tensile properties of the formed wire. It should be able to handle the tension and mechanical stresses.
- Select formed wires with steel cores or high-strength designs that offer extra support and reliability for span length and terrain.
- Verify that the formed wire meets relevant industry standards and specifications to ensure its compliance with safety and performance requirements.
Frequently asked questions
A formed wire is a specific type of conductor used to send electrical power from one location to another. It provides mechanical strength to withstand tension and stresses during installation.
There are several benefits that make formed wires a popular choice in overhead transmission lines. these include mechanical strength, efficiency, lightweight, cost effectiveness, corrosion resistance, ease of installation and reduce sag.
Formed wires have various limitations to consider before selecting for particular applications. these limitations include lower conductivity, higher sag, relaxation, handling precautions and jointing among others. These factors should help to select the best formed wire that suits your application needs.