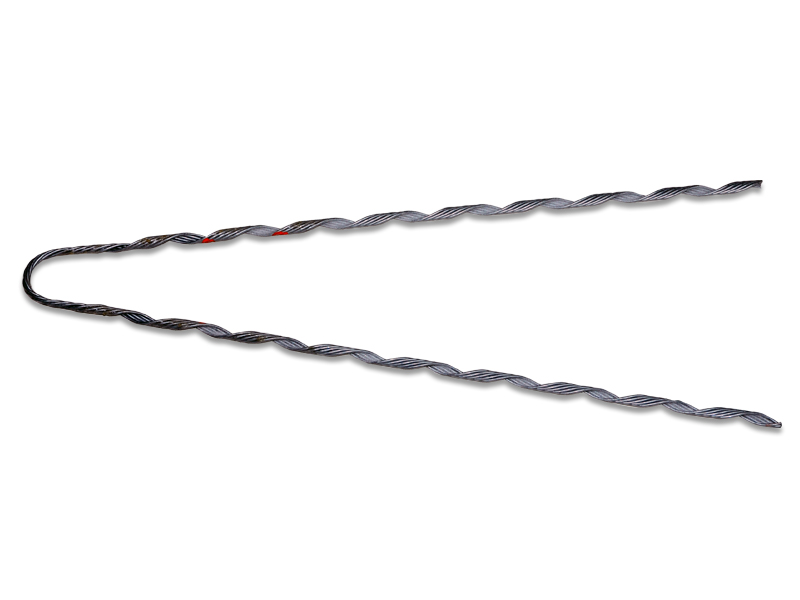

A false dead end is a structure that appears to be a dead end and allow some movement or flexibility in the line. It also provides a fixed termination point for the conductors a false dead end to absorb and accommodate certain dynamic forces. They also provide flexibility and allow for limited movement of the conductors. False dead ends help to allow the conductors to move within certain limits. This is to help absorb the effects of thermal expansion, wind-induced oscillations or dynamic forces. False dead ends also provide adaptability to thermal expansion of the conductors. Examples include ball-socket joint, slip joint and swivel link and flexible connector. They find use in applications such as wind load mitigation, seismic resilience, thermal expansion and dynamic load distribution.
Key features of false dead end
False dead ends have specific features to provide controlled movement and enhanced resilience. The following are the key features of the false dead ends.
- Flexibility – they have flexibility to respond to dynamic forces such as wind, temperature changes, or seismic events. The controlled movement helps absorb, distribute loads and prevent excessive stress.
- Environmental adaptability – they allow transmission lines to respond to changes in weather, temperature.
- Wind load mitigation -the ability to mitigate wind-induced oscillation. This helps prevent conductor galloping and sway.
- Vibration damping – the mechanisms help to mitigate vibrations in the transmission lines. This helps to prevent resonance and reducing the risk of structural fatigue.
- Articulation mechanism – this is the main feature of a false dead end which allows controlled movement of the conductor.
- Tension control – this helps to prevent the buildup of excessive tension and reduce the risk of conductor damage.
- Wind load mitigation – this feature helps prevent conductor galloping and sway. This helps to maintain the stability of transmission lines in windy conditions.
- Vibration damping – this mechanism helps to mitigate vibrations in the transmission lines.
- Materials and durability – they are from materials that provide resistance to environmental factors.
Selection and maintenance of false dead end
Proper selection of false dead ends involves careful consideration of various factors. They help to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These factors include dynamic forces, line configuration, range of movement, tension control, material and durability. The installation of false dead ends requires adherence to engineering standards. The following is a basic installation process of false dead ends.

- Site assessment – conduct a thorough site assessment to understand the terrain, environmental conditions and specific application requirements.
- Engineering design – develop a design that incorporates the false dead ends. This is to ensure the design accounts for the anticipated dynamic forces, range of movement and tension control.
- Selection of false dead ends – select false dead ends that align with specific needs of the transmission line. Consider factors such as articulation type, materials and compliance with standards.
- Pre-installation inspection – conduct a pre-installation inspection of the transmission line. This is to identify any existing or modification required to accommodate the false dead ends.
- Foundation preparation – prepare the foundations for false dead ends. This involves excavation, concrete pouring and securing anchor points.
- Assembly of false dead ends – assemble the false dead ends according to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines.
- Alignment and levelling – ensure the false dead ends align correctly with the transmission line and they are level.
- Installation on transmission line – lift and install the false dead ends onto the transmission line. Secure them in place according to the engineered design.
- Tension adjustment – adjust the tension in the transmission lines to ensure even distribution. They contribute to tension control, preventing the buildup of excessive stress on the conductors.
- Documentation – maintain detailed documentation of the installation process. This is including engineering details, types and locations.
Maintenance and inspection of false dead ends
Regular maintenance and inspection of false dead ends helps to ensure the continued reliability. It also enhances the performance and reliability of overhead transmission lines. The dead end also helps to identify and address issues extending the lifespan of false dead ends. It also helps to monitor adherence to manufacturer guidelines. This is to create an effective maintenance program. Additionally, it is important to conduct periodic professional maintenance and inspection. The following is a basic guide maintenance and inspection of the false dead ends.

- Conduct regular visual inspections looking for signs of wear, corrosion or damage to the articulate mechanisms supporting structures.
- Periodically check and adjust tension in the transmission line to ensure even distribution. This is through use of suitable tension-measuring tools to assess the tension levels accurately.
- Conduct functional test to ensure the articulation mechanisms operate as intended. Verify the dead ends allow the specified range of movement.
- Apply corrosion resistant coatings to components exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Consider the impact of weather conditions on the false dead ends. Perform extra inspections in areas prone to extreme weather events.
- Monitor the effects of temperature variations on the transmission line and adjust articulation mechanisms.
- Ensure the dead ends remain aligned with the transmission lines and check for deviations from the correct level.
- Conduct vibration analysis to identify any resonance issues. Inspect and maintain dampening systems to reduce vibrations.
- Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, inspections and manufacturers recommendations.❤
Comparative analysis of false dead ends in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis of false dead ends involves evaluating different types or models to determine their suitability for specific applications. It involves assessing and evaluating types, brands and manufacturers in South America. Additionally, it is important to consult with industry professionals for guidance in selecting the best dead end. The following are the factors to include in a comparative analysis in South America.

- Articulation mechanisms – compare the types of articulation mechanisms offered by different false dead ends. Assess the range of movement provided by each mechanism and its compatibility with the anticipated dynamic forces.
- Tension control – evaluate how well each false dead end controls and distribute tension along the transmission lines. Consider the ease of tension adjustments and the ability to adapt to varying line conditions.
- Materials and durability – compare the materials used in the construction of each false dead end. This includes considering factors such as corrosion resistance and overall durability.
- Ease of installation – assess the ease and efficiency of the installation process for each false dead end. Consider how well each model integrates with existing infrastructure.
- Vibration damping – compare the effectiveness of dampening features in mitigating vibration and quality.
- Cost-effectiveness – compare the initial costs of acquiring and the installing each false dead-end model. Consider the long-term maintenance costs, including lubrication, inspections and potential replacements.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various certifications and standards for false dead ends to ensure their compliance with safety, performance and quality requirements. it also helps to verify that the chosen product complies with the relevant certifications and standards. Also, it is important to manufacturers provide information about certifications on product datasheets. The following are the certifications and standards of false dead ends in South America.

- IEEE standards – this are standards for performance testing of sockets, connectors and bookshelf-type devices.
- IEC standards – this standard provides guidelines for direct connections between power transformers.
- ANSI standards – this includes standards for wet-process porcelain insulators for high voltage series and low and medium voltage series.
- ASTM international standards – these are standards for test methods for high voltage, low current and liquid-contaminants.
- ISO certifications – this provides guidelines for providing high quality products from the various manufacturers.
- Local electrical codes and regulations – adherence to local electrical codes and regulations specific to the region where the false dead ends install.
Regional market for false dead ends in South America
There are various factors that influence the regional demand and market for false dead ends in South America. These factors include types, competitors and regulations. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct market research and study market reports to understand the regional market. The following are the factors that shape the regional market in South America.

- Regulatory environment– understand the landscape in south American countries to comply with safety standards and environmental conditions.
- Economic trends – examine the economic conditions in the region which may influence the growth and investment in the energy sector.
- Customer needs and preferences – get to know the specific needs and preferences of customers in the region. Consider factors such as environmental conditions, durability and cost effectiveness.
- Collaboration and partnerships – investigate collaboration between local and international companies in the region.
Frequently asked questions
False dead ends define as points where the line appears to terminate but it continues in a different direction. It helps to provide access for maintenance and repairs, isolate sections of the line for testing and improve system performance.
False dead ends contribute to the resilience of transmission lines in seismic prone areas by improving isolation, stress reduction, flexibility, cost effectiveness and redundancy.