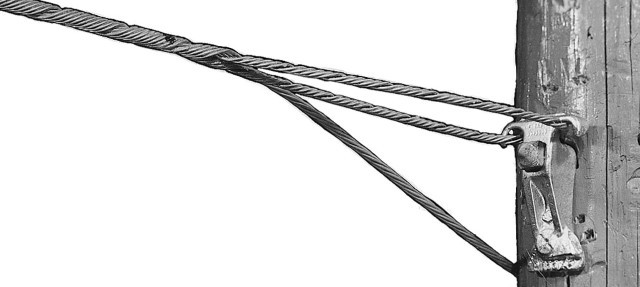
A false dead end is a structure or configuration that appears to be a dead-end. It is also known as a faux or pseudo dead ends. They help to prevent unauthorized personnel from attempting to climb the transmission tower. They also help maintain a consistent appearance along the transmission corridor. A false dead end is for visual or security purposes and do not provide the same structural support. They are from various materials such as steel, aluminum, fiberglass or concrete materials. These materials tailor to meet the unique needs of Southeast Asian environments. Common types include decorative, security, visual continuation, anti-climbing and barrier dead ends. They find use in applications such as lighting, aesthetic, security and visual continuation.
Key features of false dead ends
The features of the false dead end serve aesthetic, safety, security and visual continuity functions. They also help to fulfill specific non-structural functions in the transmission lines. the common features of the false dead ends are as discussed below.

- Safety – false dead ends design provide safety both to the public and for maintenance personnel.
- Durability – the materials help them to withstand environmental conditions.
- Compliance – they comply to regulations and standards to ensure safety and public access.
- Visual harmony – false dead ends aim to maintain visual harmony within the transmission corridor for aesthetic of the area.
- Material – the chosen material depends on desired appearance, durability and environmental compatibility.
- Security – they also enhance the security of critical infrastructure. This is by creating the appearance of a secure endpoint.
- Cost – they also provide an cheap way to improve the appearance and security of transmission lines. This is without compromising functionality.
Selection and installation of false dead ends
The selection of false dead ends involves considering several factors to meet the specific objectives. These factors include aesthetics, safety, security, purpose, environmental impacts, maintenance requirements, regulatory compliance and cost effectiveness. The installation of false dead ends varies depending on the specific design and purpose of the false dead end. The following is a basic installation process of the false dead ends.

- Safety precautions – ensure to follow all the necessary safety protocols. This includes using suitable personal protective equipment.
- Site preparation – survey the installation site to ensure it meets the intended objectives.
- False dead-end inspection – inspect the component to ensure they are free from defects or damage.
- Gather equipment – collect all the necessary equipment and tools to use for the installation. This includes climbing gear, wrenches and other mounting hardware.
- Access and climbing – access the transmission pole using approved climbing techniques and equipment.
- Positioning – position the false dead ends at the desired location on the tower. Ensure they align with the intended purpose such as security deterrence, aesthetics or visual continuity.
- Attachment – securely attach the false dead ends to the tower structure following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Wiring and integration – connect and integrate these components according to the design specifications. This is if the dead ends include lighting, signage or surveillance equipment.
- Testing – test the equipment to ensure proper functionality. This includes adjusting lighting angles or aligning cameras.
- Final inspection – conduct an inspection of the installed false dead ends. This is to verify they meet the design requirements, safety standards and aesthetic objectives.
- Documentation – keep detailed records of the installation process including photographs and equipment specifications.
Maintenance and inspection of false dead ends
Maintenance and inspection of false dead ends ensure their continued functionality, safety and aesthetics. This also helps identify and address issues before they proceed to more problems. It also helps extend the lifespan of your dead ends. This is to ensure their continued functionality. They also maintain the desired visual aesthetics of the transmission lines. The following is a basic guide to maintenance and inspection of false dead ends.

- Conduct regular visual inspections to identify any visible signs of wear, damage or deterioration. Check for rust, corrosion, loose fasteners or fading aesthetic features.
- Remove dirt, dust and debris accumulated on the false dead ends. this helps maintain their appearance and prevent corrosion.
- Apply lubricants as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent friction.
- Test and calibrate any security cameras to ensure they are operational and aligned correctly.
- Schedule periodic inspections at regular intervals depending in environmental conditions and usage.
- Conduct a more detailed examination of the false dead ends. this includes a closer inspection of structural components and connections.
- Check for signs of corrosion and clean and apply protective coatings and treatments.
- Inspect all fasteners, nuts, bolts and other hardware for tightness and integrity. Tighten all the loose fasteners following the guidelines.
- Ensure safety features such as climbing measures remain effective. They should also be compliant with safety standards.
- Maintain detailed records of all maintenance and inspection activities. This is including dates, findings and any corrective actions.
Comparative analysis of false dead end
A comparative analysis involves evaluating different types and designs of the false dead ends in the market. This helps to determine the best dead end that suits the specific requirements of a project or application. This includes creating a scoring system, weighting, data gathering, evaluation, decision-making and stakeholder input. The following are the factors to include in the analysis.

- Purpose – determine the primary purpose of the false dead ends such as aesthetics, safety, security or visual continuity.
- Aesthetics – evaluate how each dead end complements the visual landscape. This includes whether it camouflages, disguises or enhances the surroundings.
- Anti-climbing features – compare the effectiveness of anti-climbing features in deterring authorized access.
- Security and surveillance – compare the integration options and effectiveness of surveillance equipment.
- Lighting and signage integration – evaluate the integration capabilities of lighting fixtures and signage.
- Artistic expression – consider the artistic and cultural elements of each type of model.
- Maintenance requirements – compare the ease of maintenance for each type or models. This includes accessibility for cleaning, lubrication and component replacement.
- Cost effectiveness – evaluate the cost of each type of model in relation to its features, functionality and long-term benefits.
Certification and standards on Southeast Asia
Various standards and certifications for false dead ends ensure the safety, quality and functionality. Manufacturers and suppliers of the false dead ends should provide documentation. This is to indicate compliance with relevant standards and certifications. This is the assure their quality and safety of their products in Southeast Asian markets. The following are the common standards and certifications for false dead ends in Southeast Asia.

- IEC standards – these are standards that relate overhead transmission line hardware and components. This is including false dead ends with their design, materials, mechanical properties and electrical performance.
- National standards – these standards vary country by country for electrical equipment
- ASTM standards – these are references for materials and testing procedures for electrical equipment.
- ANSI standards – these are American standards for electrical equipment.
- ISO standards – these relate to quality management and product certifications. This is particularly for manufacturer’s quality control processes.
- Local regulatory authorities – each country has their own local standards. They are responsible for setting standards and certification requirements for electrical equipment.
Regional markets for false dead ends in Southeast Asia
The regional markets for false dead ends in Southeast Asia are a growing and diverse landscape. This is due to the region’s expanding power infrastructure and the need for safety, security and aesthetic solutions. They also depend factors such as climate, landscape, regulatory environment and local preferences. The markets are in countries such as Singapore, Indonesia, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Philippines and Myanmar. The following are the common factors that shape the regional market for false dead ends in southeast Asia.

- Economic conditions – the economic growth and stability in the countries influence the adoption of false dead ends.
- Infrastructure development – expansion of power grids and transmission infrastructure requires the great need for safety and aesthetic solutions.
- Environmental conditions – conditions such as coastal regions, rainforests and urban areas influence the choice of material and designs for false dead ends.
- Energy demand – there is increasing expansion of power grids requires the use of false dead ends. This is from the increased energy demand from the population growth and industrialization.
- Technological advancements – advances in materials and technologies for false dead ends influence the market trends. These include improved anti-climbing features and corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Tourisms and scenic areas – tourism hubs and scenic areas in the region demands the aesthetic aspects of power transmission lines.
- Regulatory environment – regulatory standards and safety requirements set by governments and regulatory authorities also the market.
Frequently asked questions
A false dead end is a device of structure that appears to be a dead end but not actually the physical termination point. It maintains a consistent appearance along the transmission line even beyond the apparent termination point.
False dead ends used in southeast Asian countries are from materials such as steel, aluminum, fiberglass, concrete or composite materials. These materials help o meet the specific climate conditions in the regions.
False dead ends are becoming increasingly popular due to their various benefits to the environment and safety. These include reduced environmental footprint, visual harmony, reduced impact on ecosystems, enhanced public safety, protection of infrastructure and fire prevention.