
An insulated piercing clamp (IPC) is an electrical connector used to tap into an existing power line. It does this without the need for interrupting the flow of electricity. IPC helps in making new connections to an existing power line without disrupting the power supply to consumers. It also has a clamping mechanism that allows it to securely grip onto the overhead power line. The insulated piercing clamp also provide protection from electrical shocks during installation. The IPC is from durable materials that protect them from electrical current and other factors. Common types of the IPC include inline IPC, tee IPC, parallel groove IPC, insulated piercing connector and dead-end IPC among others. They find use in various applications such as street lighting, fault detection and repair, communication and signaling among others.
Key features of the insulated piercing clamp
The IPC has various components that make working together easier for the device. These features enable safe and efficient tap connections to overhead transmission lines. These are also factors to consider when selecting the devices for your application. The following are the main features of the insulated piercing clamp.
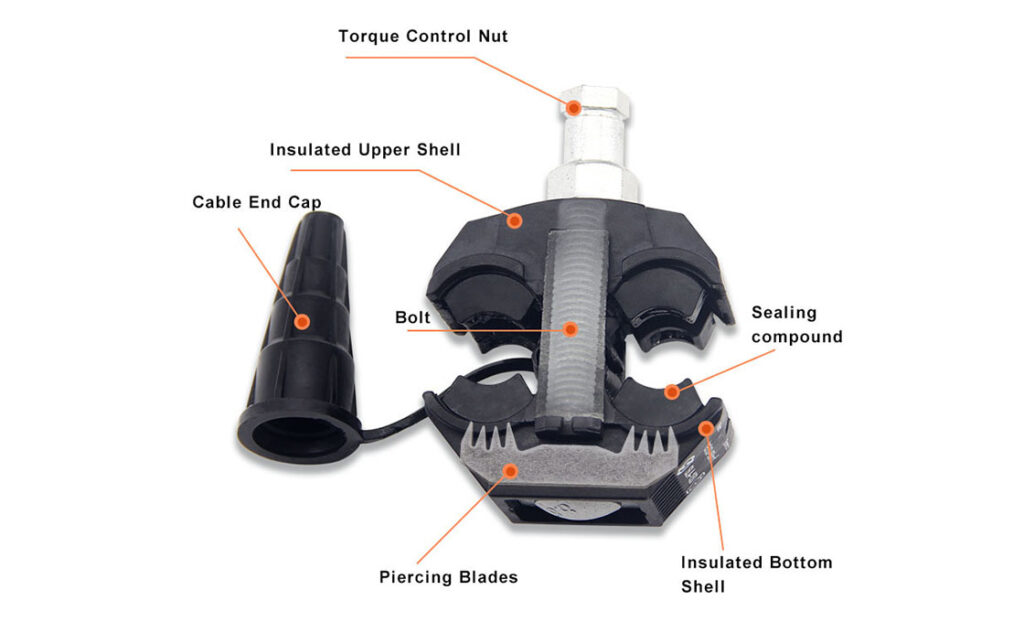
- Insulation – this is the main feature of the clamp that prevents accidental contact between the clamp and the conductor. This is to ensure the safety of installers and the public during and after installations.
- Contact blade – this is the part that penetrates the conductor’s insulation to establish electrical contact. It makes a secure and reliable connection without damaging the conductor.
- Clamping mechanism – the clamping mechanisms provides a strong grip on the conductor while avoiding damage. It securely holds the clamp in place and prevents movement that could lead to unreliable connection.
- Corrosion resistance – the insulated piercing clamp is from materials that resist conditions such as rain, humidity and extreme temperatures.
- Current rating – the IPC should handle the current load that it will encounter without causing damage.
- Voltage rating – the clamps voltage rating should match the systems voltage to ensure safety and performance.
- Ease of installation – the design of the clamp should facilitate easy and efficient installation.
Selection and installation of the insulated piercing clamp
There are various factors to consider when selecting an insulated piercing clamp for your application. They should ensure safety, reliability and efficiency of the electrical connection. These factors include system requirements, conductor size and type, application, environmental conditions, current rating, voltage rating and ease of installation. The installation of an IPC requires adherence to safety protocols and proper handling of electrical equipment. The following is a basic installation process of the insulated piercing clamp.
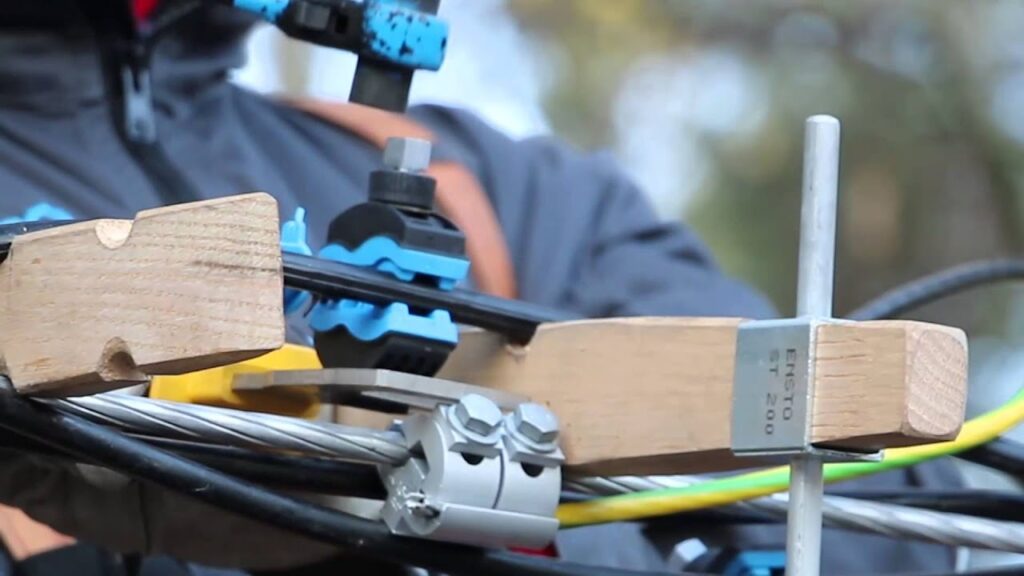

- Ensure you have the appropriate personal protective equipment including insulated gloves, safety glasses and other required gear.
- Prepare the conductor where the IPC will install which involves cleaning the surface and removing any contaminants or corrosion.
- Inspect the IPC for any visible damage or defects before installation.
- Identify the exact location on the conductor where the IPC will install and ensure proper alignment and positioning.
- Strip off a small section of the insulation from the conductor where the IPC’s contact blade will make contact.
- Open the clamp’s clamping mechanism and position it on the conductor. Ensure that the contact blade aligns with the section where the insulation was from.
- Close the clamp’s clamping mechanism securely onto the conductor and apply the specified amount of torque.
- Apply the sealing components if applicable to help protect the connection from moisture and environmental factors.
- Perform a visual inspection to ensure the IPC is securely installed, contact blade is properly positioned and sealing is intact.
- Keep records of installation including the location, date and any relevant details.
Maintenance and inspection
Maintenance and inspection of an insulated piercing ensures the ongoing reliability and safety of electrical connection in overhead transmission lines. Regular maintenance and inspection help identify potential issues early and prevent unexpected failures. Additionally, you should follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and inspection procedures specific to your IPC. The following is a basic guide on how to perform maintenance and inspection on an IPC.
- Establish a regular schedule for inspecting IPC which may vary depending on various factors. These includes environmental conditions, usage and the criticality of the installation.
- Visually inspect the IPC for signs of damage, wear or corrosion. Check for cracks, degradation, or any signs of wear that could compromise its effectiveness.
- Inspect any sealing components for integrity and ensure the seals are not cracked, deteriorated or missing.
- Verify that the contact blade is properly aligned and securely clamped onto the conductor. Ensure that the clamping mechanism functions as intended. This is to allow for secure attachment without excessive force.
- Check for any signs of corrosion on the IPC’s metal parts which can compromise the clamps conductivity and structural integrity.
- Assess the IPC’s exposure to environmental conditions. These include weather, humidity and temperature changes.
- Maintain detailed records of each inspection including date, location, observations and any actions taken.
- Clean the IPC as needed to remote dirt, debris or contaminants that could affect its performance or insulation.
- Replace any clamp with signs of wear, damage or deterioration to ensure the continued reliability.
Comparative analysis of IPC in Southeast Asia
Comparative analysis involves comparing quality, process and designs of the IPC in the market. It involves several factors to consider to ensure the safety and reliability of the overhead transmission lines. The priorities and considerations of the IPC in Southeast Asia should help to ensure the best selection of the IPC in the market. Also, consult with local experts and electrical engineers for valuable insights for a comparative analysis of IPC in Southeast Asia. The following are the factors to consider in the comparative analysis.

- Manufacturer presence – look into the manufacturers and suppliers of IPCs that operate within the south East Asia. Consider their reputations, years of experience and product offerings.
- Environmental conditions – Southeast Asia has a range of conditions such as high humidity, tropical storms and high temperatures. Consider IPCs designed to withstand these conditions without degradation.
- Conductor types and size – ensure the IPC can accommodate the range of conductor sizes used in South East Asia.
- Cost-effectiveness – consider the cost of the IPCs relative to their features and benefits. Balance the quality and cost according to your budget.
- Innovation and technology – consider whether IPC manufacturers incorporate features such as improved insulation, ease of installation or compatibility with emerging technologies.
- Local standards and regulations – different countries in South East Asia have varying electrical standards and regulations.
- Voltage levels – select IPCs suitable for different voltage levels whether low-voltage distribution or higher-voltage transmission systems.
Certifications and standards in South East Asia
Certifications and standards for insulated piercing clamps vary by country and region within Southeast Asia. These standards and regulations are essential to stay updated with the latest information from official sources. This is to ensure the insulated piercing clamp offer safety and reliability for efficiency. It is important to evaluate standards available in the region. This is by checking manufacturer documentation, certification labels, and local authorities. These certifications and standards are as discussed below.

- IEC – these standards include compression and mechanical connections for power cables.
- IEEE – these include standards for qualifying permanent connections used in substation grounding.
- Local standards and regulations – southeast Asian countries have local standards and regulations related to electrical components.
- ISO – these are standards quality management systems requirements and guidelines for use.
Regional market for insulated piercng clamp in South East Asia
There are various aspects in the south East Asia to consider when selecting IPC for your application. The market trends may change over time from a various factor in the countries. The key countries with a market for the IPC include Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia and Philippines. These factors depend on the market trends as discussed below.

- Smart grid integration – the adoption of the smart grid technologies require compatibility with modern communication and control technologies.
- Renewable energy integration – the increased adoption of renewable energy sources influences the demand of IPC in applications such as connecting solar panels to the grid.
- Energy efficiency – increasing need for energy efficiency and reduction of losses in the distribution networks leads to the adoption of advanced IPC designs.
- Local manufacturing and sourcing – South East Asian countries have strong manufacturing capabilities. This influences the production and sourcing of IPCs.
- E-commerce and online procurement – the trend towards e-commerce and online procurement could affect the distribution channels for IPCs.
- Power grid expansion – upgrading power grids to meet growing energy demand creates opportunities for IPC in new installation and upgrades of distribution networks.
- Diverse voltage levels – the Southeast Asia has a mix of low-voltage and medium-voltage distribution systems. This makes IPCs suitable for different voltage levels.
Frequently asked questions
An IPC is an electrical connector designed to tap into an existing power line without interrupting the flow of electricity.
IPCs allow for the safe and efficient connection of new power lines to existing power lines without the need for power interruption. This makes them ideal for maintenance, upgrades and new installations.