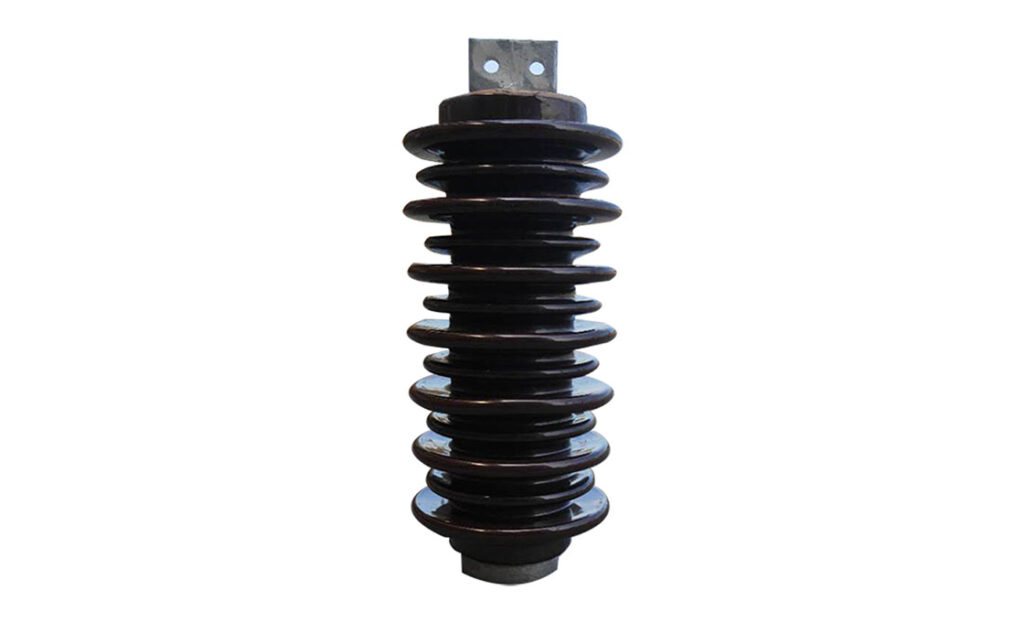

A post insulator is a device used to support the conductors and insulate them from the support structure. It is also known as a disc insulator. The structure consists of insulating discs arranged in a stack separated by metal fittings. These discs are from materials such as porcelain, glass or composite materials. Post insulators help to reduce corona discharge that can lead to power loss and radio interference. Post insulators prevent the flow of electricity from the conductor to the tower pole which could cause electrical faults. They also provide mechanical support to the conductors to withstand the stresses caused by wind and ice. Use of post insulators on transmission lines help to ensure safe and efficient transmission of electrical power.
Selecting the best post insulator
There are several factors to consider when selecting the post insulators for your application. These factors help to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the electrical system. Selecting the right post insulator helps meet the electrical, mechanical and environmental requirements. It also helps to ensure reliable and efficient operation of the transmission lines. The following are the factors to consider when selecting the post insulators.

- Voltage rating – determine the voltage level of your application and choose a post insulator with a suitable rating.
- Material – consider the material of the insulator with potential to resist environmental conditions. The materials offer electrical insulation, mechanical strength and weight.
- Mechanical strength – assess the mechanical requirements of your application. This is including conductor tension, wind loads, ice loads and seismic considerations.
- Corona performance – select an insulator with shapes and finishes to reduce corona discharge and maximize electrical efficiency.
- Environmental conditions – consider a post insulator with good pollution performance. It should also withstand the environmental conditions. These includes humidity, pollution levels and UV radiation.
- Supplier reputation – consider the reputation and track record of the manufacturer. They should have a record pf producing high-quality and reliable post insulators. Assess the availability and quality of technical support and after sales provided by the manufacturer.
- Cost effectiveness – consider the cost effectiveness of the post insulator and if they meet your application requirements. Compare upfront costs of different options and total cost of ownership.
- Maintenance needs – consider the ease of installation and maintenance when selecting the insulators. They should be easy to install and need minimal maintenance.
Applications of a post insulator
Post insulators work in various electrical applications that need insulation and mechanical support. They have design to meet specific voltage ratings, mechanical load requirements and environmental conditions. They also ensure a safe and reliable operation of electrical equipment and systems. Below are the various applications of the post insulators in detail.
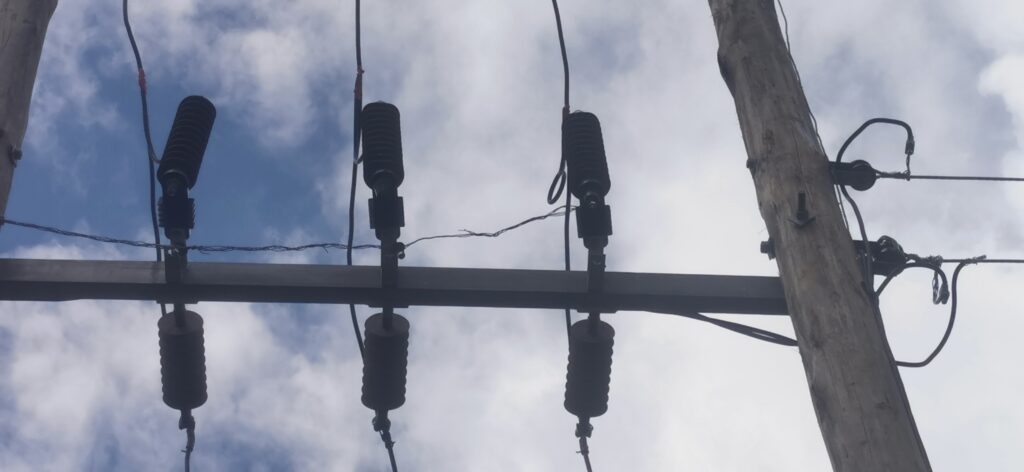

- Switchgear – post insulators work in switchgears to insulate and support switching devices. These include circuit breakers, isolators and load break switches in switchgears. They help prevent electrical breakdowns and ensure the safe and reliable operation of the switchgear.
- Power transmission and distribution – they support and insulate the conductors on transmisison lines. They also provide electrical insulation between the conductive parts of the equipment.
- Capacitor banks – post insulators work in capacitor banks to support and insulate the capacitor units.
- HVAC systems – the insulators help to support the busbars and other conductive elements within the switchyard. They provide insulation and mechanical support to maintain clearance and prevent electrical faults.
- Instrument transformers – they also work in current transformers and voltage transformers. They provide electrical insulation and mechanical support for the primary and secondary windings.
- Railway traction systems – post insulators work in electrified railways and traction systems. They help support and insulate overhead catenary wires or contact wires. They ensure efficient transmission of electrical power to the trains. This is while maintaining proper electrical insulation.
- Telecommunication towers – the insulators help to support antennas and transmission lines. they provide electrical insulation to prevent interference and ensure reliable communication signals.
- Substations – post insulators support various equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches and bus bars.
- Surge arrestors – the insulators work with surge arrestors to protect electrical equipment from voltage surges. This may be from lightning strikes or switching operations.
Installation practices for post insulators
The installation process requires professional skills and safety precautions to avoid electrocution. Proper installation helps to ensure the reliability and safety of overhead transmission lines. additionally, it is advisable to follow manufacturer guidelines and industry practices. This helps to ensure successful installation of post insulators. The following is a basic installation of post insulators.
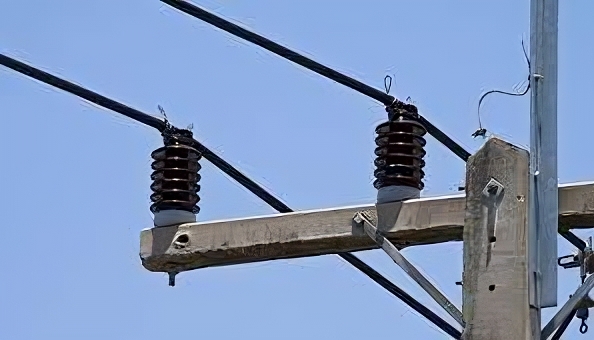
- Preparation – inspect the insulators for any visible damage before installation. Gather all equipment including post insulators, conductor hardware, fittings, tools and safety equipment.
- Safety procedures – ensure you follow all the safety protocols and guidelines established by relevant industry standards and local regulations.
- Positioning – determine the best positioning of the post insulators along the transmission line. Consider factors such as conductor sag, electrical clearance requirements and mechanical loading.
- Mounting arrangement – confirm the correct mounting arrangement for the specific type of insulator. Attach the mounting hardware to the support structure. This is including brackets, clamps or other fittings to hold the insulators in place.
- Lifting and handling – use suitable lifting equipment to handle and position the post insulator safely. Avoid damaging the insulators or support structure during the process.
- Alignment – align the insulator with the mounting structure and ensure the insulator is level and perpendicular to the conductor.
- Installation on the structure – attach the post insulator to the supporting structure using the designated mounting hardware.
- Tightening and securing – tighten all bolts, nuts and other fasteners to the torque values. Check the installation for any signs of looseness or misalignment.
- Final inspection – conduct final visual inspection of the installed insulator to verify its alignment, attachment and condition.
- Documentation -maintain detailed records of the installation. This is including insulator specifications, installation date and any observations during the process.
Maintenance actions for post insulators
Proper maintenance of post insulators in overhead and distribution systems. This is to ensure their ongoing reliability and performance of the post insulator. Additionally, regular inspections help identify potential issues early to allow for timely intervention. It also helps to prevent unexpected failures. The following is a basic maintenance guide for post insulator.

- Perform regular visual inspections of post insulators to identify any visible signs of damage, contamination or wear. Check for cracks, chips or other surface irregularities.
- Check the extent of contamination in the insulator surfaces in areas with high pollution.
- Verify that the leakage distance along the insulator surfaces is free from any foreign material. This is to ensure the specified creepage distance is maintain.
- Inspect the mechanical components of the post insulator including mounting hardware and fittings for signs of corrosion or wear.
- Check the integrity of the grounding system to ensure the grounding connection are secure and conductive. This is to provide a reliable path for fault current.
- Use thermal imaging to identify any abnormal temperature variations on the insulator surfaces.
- Apply corrosion resistant coatings to protect against environmental corrosion.
- Maintain detailed records of inspection dates, observations and any maintenance activities performed.
Testing for post insulators
Post insulators undergo various tests to ensure their proper use, performance and reliability. Some of the tests occur during manufacturing processes and during operation. They also help to ensure the post insulators meet the required standards to ensure they are in good working conditions. Additionally, conducting such tests helps to ensure the proper function and safety of post insulators. The following are the common tests for post insulators.
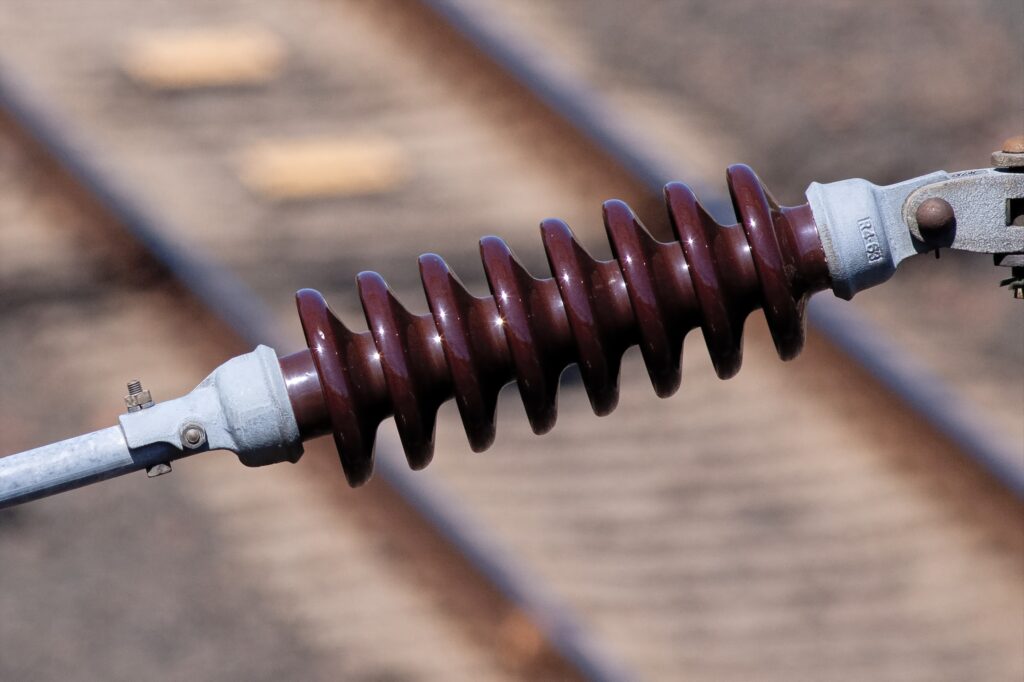

- Visual inspection – perform a visual inspection of the post insulators for any visible defects. These include cracks, chips, corrosion or surface contamination.
- Mechanical load testing – subject the post insulators to mechanical load testing. This is to verify their ability to withstand the stresses. It may involve applying a static or dynamic load to simulate real-world conditions.
- Corona testing – perform corona testing to assess the corona performance of the post insulators. Discharge can lead to power loss and interference to ensure the insulators have designs to reduce corona effects.
- Thermal testing – place the insulators to thermal testing to check their performance under temperature extremes. It involves thermal cycling to simulate the effects of temperature variations.
- Ultrasonic testing – subject the insulators to vibration testing to check their resistance to mechanical vibrations.
- Dimensional checks – measure the dimensions of the insulators to ensure they meet specified tolerances.
- Electrical insulation testing – this helps to measure the insulation resistance and dielectric strength of the post insulator.
- Porosity testing – conduct porosity testing to check for any internal defects. This includes defects that could compromise their electrical performance.
Frequently asked questions
A post insulator is a component used in electrical power systems to support and insulate conductors. Its main purpose is to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support to prevent electrical faults.
Consider factors such as voltage rating, mechanical strength, environmental conditions, corona performance and costs.
Common tests include mechanical load testing, electrical insulation testing, corona testing, porosity testing or thermal testing.