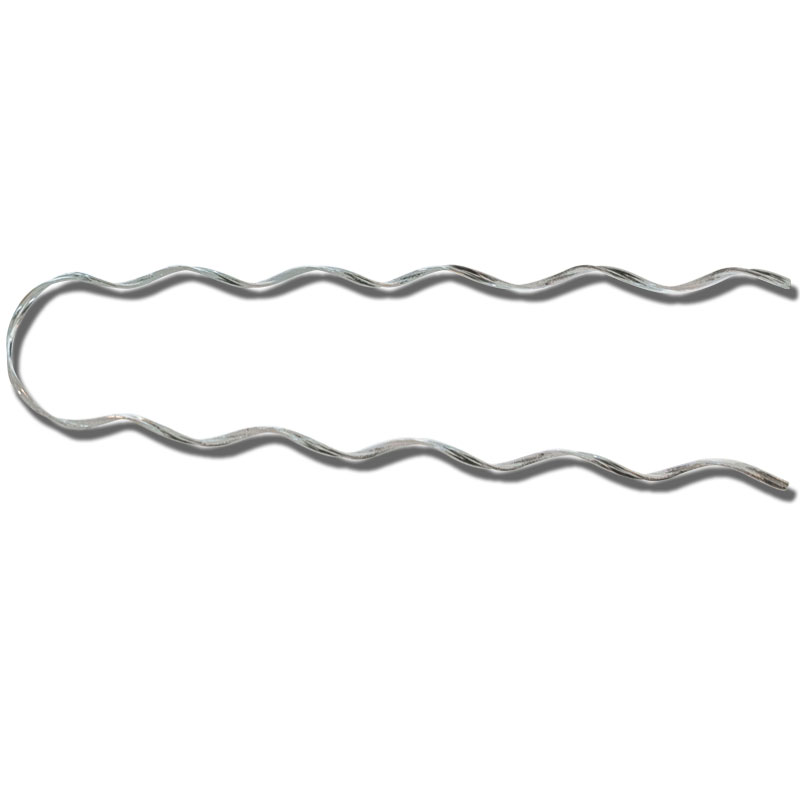

A distribution grip dead end is a device used to support and secure the conductor wires that carry electrical power. They are mostly used in lower voltage lines that distribute electricity from substations to homes, businesses and other consumers. Distribution grip dead end is also known as suspension grip or dead-end grip. The distribution grip dead end provides mechanical support and strain relief to the conductors. This is to ensure they are securely held in place. They withstand the tension and stress caused by the weight of the wires and external forces. The devices consist of a composite structure that attaches to the conductor. They distribute the tension along the length of the conductor. This prevents excessive stress at any particular point and reducing the risk of conductor breakage or damage. Distribution grip dead end are from materials like aluminum alloy, steel or both.
Components of the distribution grip dead end
Components of the distribution grip dead end work together to secure and support the conductors in power transmission lines. They vary depending on the design and manufacturer of the device. They are carefully selected and engineered to ensure the grip dead end provides reliable support, strain relief and protection to the conductors in distribution lines. the following are the main components of the distribution grip dead end.
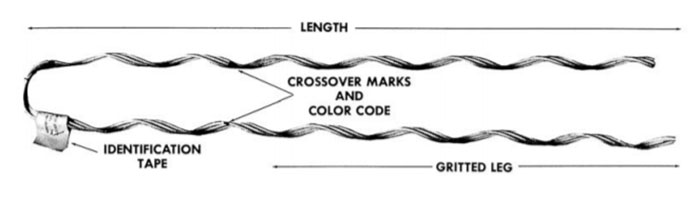
- Grips – grips are the main components of the dead end and help to hold the conductors in place. They have various designs including helical grooves, serrated jaws or clamps.
- Preformed rods – preformed rods are metallic rods or strands that help to reinforce the grip. They provide extra strength and stability to the grip dead end assembly.
- Armor rods – these are protective devices placed over the conductor and prevent damage or wear caused by the grip.
- Thimbles – thimbles are metal sleeves or loops inserted into the grip dead end assembly. They help provide a smooth surface for the conductor to pass through. This prevents the grip from directly contacting and damaging the conductor.
- Connecting links – these are connecting components used to attach the grip dead end assembly to the supporting structure. They are from strong and corrosion-resistant materials like steel.
- Cotter pins – these are small metal fasteners used to secure and lock the component of the grip dead end assembly together. They prevent the grips, preformed rods and armor rods from coming loose under the tension and stress applied to conductor.
Types of distribution grip dead end
Here are various types of distribution grip dead end. Each designmeets specific applications and conductor type. The various types are as detailed below.
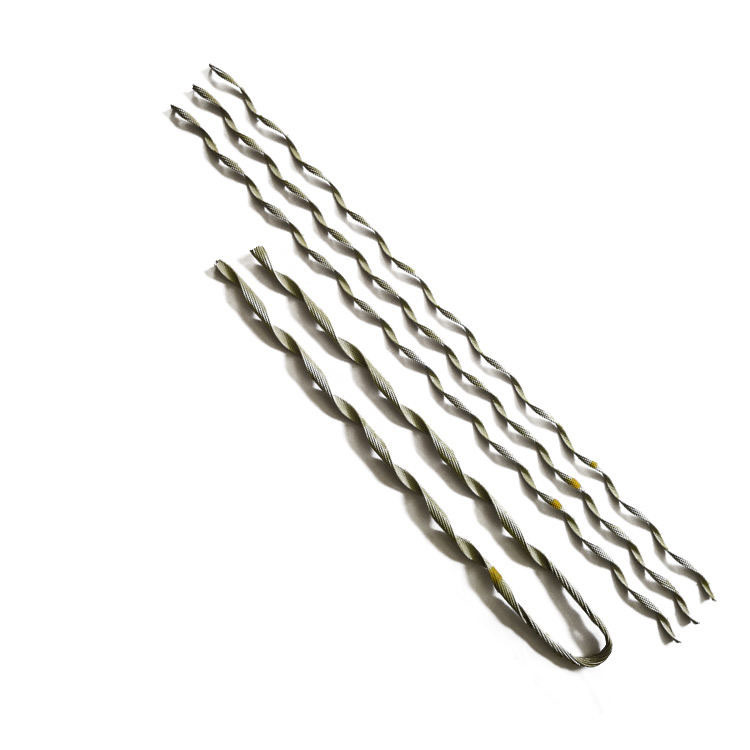

- Suspension grip dead end – suspension grip dead ends work in suspension applications where the conductor hung from a supporting structure. They consist of a combination of grips, preformed rods, and other components that provide support and strain relief to the conductor.
- Helical grip dead end – this type features a helical design that consists of a helical groove metal body that wraps around the conductor. The grip tightens using a tool wrench, providing a secure and reliable connection. They are mostly used for bare overhead conductors in distribution lines.
- Wedge grip dead end – wedge grip dead ends utilize wedges to secure the conductor and a tapered opening which the conductor inserts into. They help for high voltage distribution lines and can accommodate a wide range of conductor sizes.
- Clamp grip dead end – these types of grip use clamping mechanisms to secure the conductor where two or more clamps tighten around the conductor using fasteners. They accommodate different conductor sizes and types including bare conductor and insulated cables.
- Guy grip dead end – guy grip dead ends help for guy wires to provide additional support and stability to poles or towers. They consist of grips tightened around the guy wire securing it to the structure. They maintain the stability and integrity of distribution line infrastructure.
Applications of distribution grip dead ends
Distribution grip dead ends have an important role to play in transmission and distribution systems. They provide support, strain relief and secure connections for the conductors. The following are the various applications of the grips.
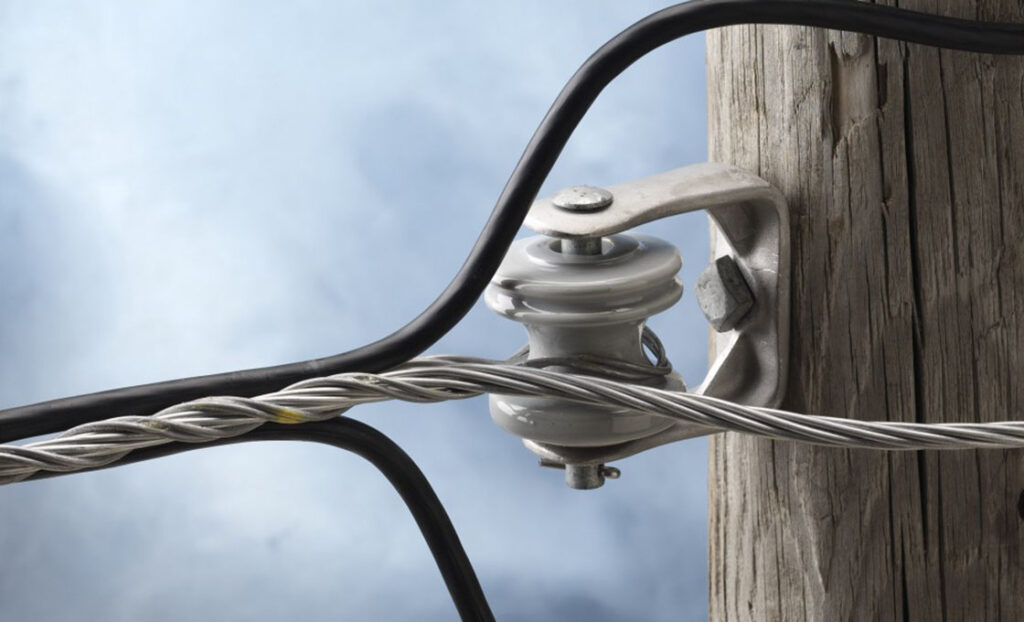

- Strain relief – grip dead ends help to provide strain relief to the conductors. They also absorb and distribute the tension or stress that occurs due to the weight of the conductors, ice or wind. This reduces the risk of conductor damage. It also ensures the longevity of the distribution systems.
- Overhead power distribution lines – the grips secure and support the conductors in overhead power distribution lines. They ensure the reliable transmission of electrical power from substations to homes, businesses and other consumers.
- Temporary power installations – grip dead ends work in temporary installations like construction sites, events or emergency power supply. They facilitate the quick and secure installation of temporary overhead power lines to provide electricity in temporary setups.
- Guy wire support – grip dead ends help to secure the guy wires or guy strands that provide extra support and stability to structures. They also ensure proper tensioning and anchoring of the guy wires. This enhances the structural integrity of the distribution infrastructure.
- Suspension of conductors – the grips suspend the conductors from supporting structures. This is to provide the necessary mechanical support to hold the conductors in place.
- Cable and wire termination – distribution grip dead ends work in cable and wire termination. They provide a secure and reliable connection between the conductors and the equipment they connect to.
Installation of the distribution grip
The installation process of the distribution grip dead ends involves several steps. They help to ensure a secure and reliable connection. The process also depends on the type of a grip dead end, conductor size and type and manufacturer’s instruction. Here is a basic process of the installation process.
- Gather all the necessary tools and equipment including the grip dead ends, preformed rods or strands, armor rods, thimbles and all the required safety equipment.
- Ensure proper safety measures are in place like wearing appropriate personal protective equipment like gloves, safety glasses and protective clothing.
- Determine the attachment points where the grip dead ends will install.
- Prepare the conductor by cleaning the surface to ensure a clean and smooth contact area for the grip dead end. Remove any dirt, debris or oxidation using appropriate cleaning methods.
- Install thimbles onto the conductor at the attachment points where the grip dead ends will install. This is because they provide a smooth surface and prevent direct contact between the conductor and the grip reducing the risk of damage.
- Assemble the grip dead end components according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It involves attaching the grips, preformed rods and strands, armor rods and other necessary components.
- Position the grip dead end assembly over the conductor ensuring the thimbles are within the grip body. Align the grip dead end with the attachment points on the conductor and the supporting structure.
- Tighten the grip dead end securing the conductor following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific type of grip dead end to install.
- Contact the grip dead end to the supporting structure using shackles or connecting links. This ensures the connection is secure and tight to provide adequate support.
- Secure all the components by inserting cotter pins. This helps prevent the grip dead end assembly from coming loose.
Choosing the best distribution grip dead ends
Selecting the best distribution grip dead ends can sometimes be a tedious task as it involves various factors to consider. It is advisable to consult with industry experts, engineers, or the manufacturer for guidance in the selection process. It is also dependable on the type of application to work in. The following are the various factors to consider when selecting the devices.
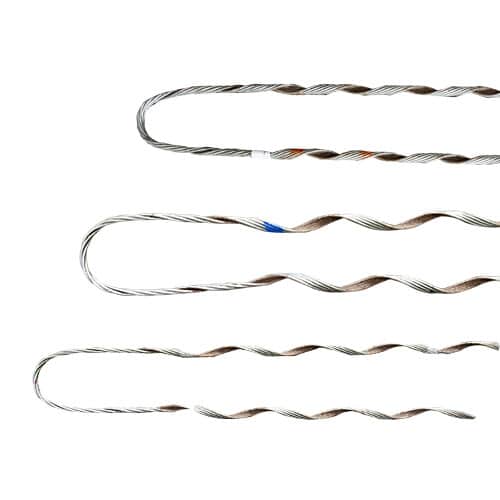

- Assess the cost-effectiveness of the grip dead end considering factors like initial purchase cost, long-term durability, maintenance requirements and the value provided by the product.
- Evaluate the ease of installation and maintenance requirements of the grip dead end.
- The grip dead end should be compatible with the overall system design and integration requirements.
- Choose grip dead ends from reputable manufacturers that comply with relevant industry standards and regulations.
- Evaluate the pros and cons of each grip mechanism and select the one that best suits your needs.
- Determine the specific requirements of the application. Consider factors like voltage level, environmental conditions, mechanical stresses and the weight of the conductor.
- Consider the type of conductor you will be working with like bare conductors, insulated cable or guy wire. Ensure the grip dead end is compatible with the conductor’s diameter, configuration and construction.
Frequently asked questions
Distribution grip dead ends are devices used to support and secure the conductors carrying electrical power. They also provide mechanical strength and strain relief to the conductors.
There are various types and designs of the frip dead ends to select from. These include helical grip dead ends, clamps grip dead end, suspension grip dead end, guy grip dead end and wedge grip dead end.
Distribution grip dead ends offer various benefits to that transmission lines. They include mechanical support, strain relief, secure connection, flexibility and adaptability, enhanced safety, easy installation and maintenance and cost effectiveness.
They also have various limitations to consider when planning a purchase. They include accommodates specific conductor types and sizes, complex installation procedures, maintenance requirements, environmental limitations and limited load capacity.