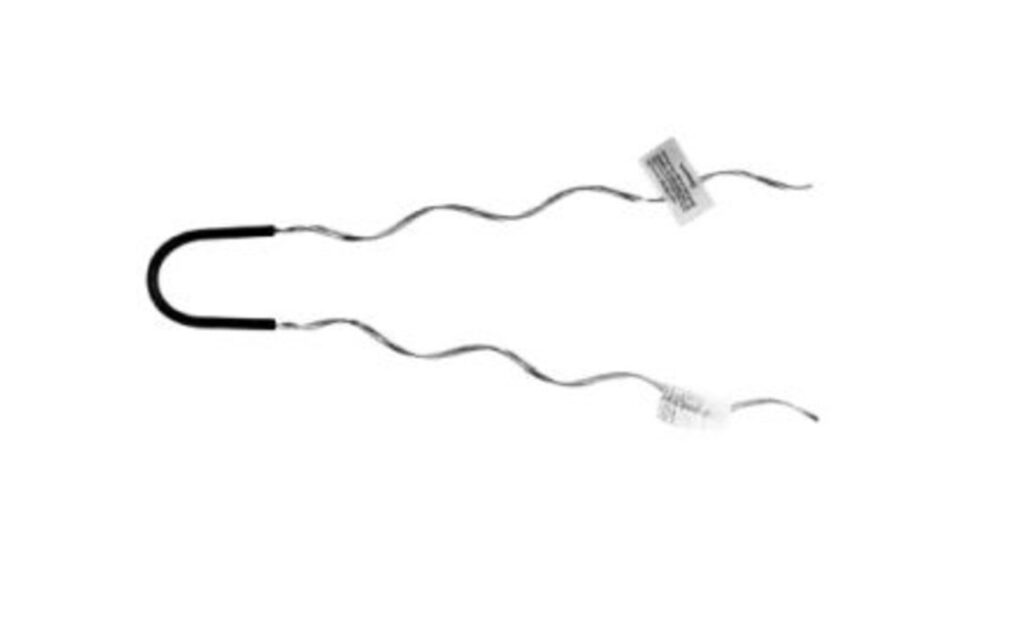
Slack span dead ends are specific arrangement used to terminate or anchor a section of the transmission lines. This is where the conductors are intentionally left with some slack or sag. This design helps them accommodate thermal expansion, reduce mechanical stresses and provide flexibility to the line. They are from materials that resist rust, corrosion and UV radiation. This makes them suitable for applications in Southeast Asian diverse climates. Common types include expansion loops, swing dead ends, sagging dead ends and pendant dead ends. They help in mechanical stress reduction, thermal contraction and expansion management, galvanic corrosion mitigation and preventing over-tensioning.
Key features of slack span dead end
The features help to address specific engineering and operational needs. The available features vary depending on the requirements of the transmission line, environmental conditions and engineering considerations. They contribute to the safe and reliable operation of overhead transmission lines. The following are the key features of the slack span dead end.
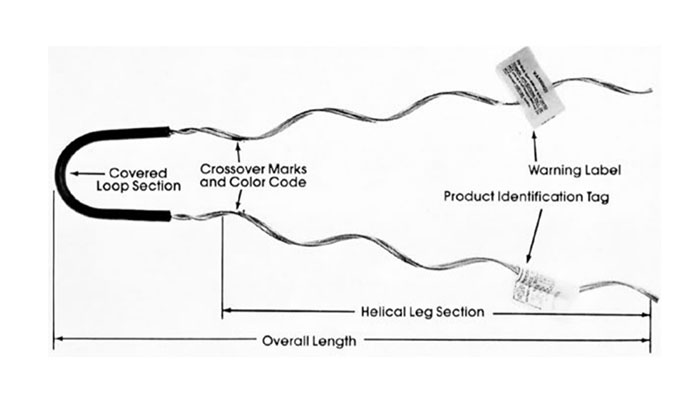
- Flexibility – they offer flexibility to accommodate conductor movement in regions with diverse weather conditions.
- Thermal expansion management – they also help manage the thermal expansion and contraction of conductors.
- Mechanical stress reduction – the dead ends also help reduce mechanical stresses on conductors. This is by allowing for movement and absorption of mechanical forces.
- Corrosion mitigation – they also help mitigate galvanic corrosion by allowing for differential movement between materials.
- Wind and ice load tolerance – slack span dead-ends provide some flexibility. This is by allowing the transmission lines to withstand extra weight.
- Compatibility – the design allows them to be compatible with various conductor types and sizes. This is to support the versatility in transmission lines.
- Maintenance and repair – the devices make it easier for maintenance crews to access and work on the transmission line. They provide flexibility for adjustment and repairs without the need for excessive tensioning.
- Seismic load mitigation – they also help absorb and mitigate the impact of ground movements on the transmission line.
Selection and installation of slack span dead end
The selection of the dead end involves several factors to consider. This helps to ensure the chosen dead-end meets the specific requirements. These factors include conductor type and size, environmental conditions, thermal expansion, corrosion resistance, costs, future expansion and safety. The installation process requires careful planning and adherence to safety and engineering guidelines. The following is an installation guide for the slack span dead end.
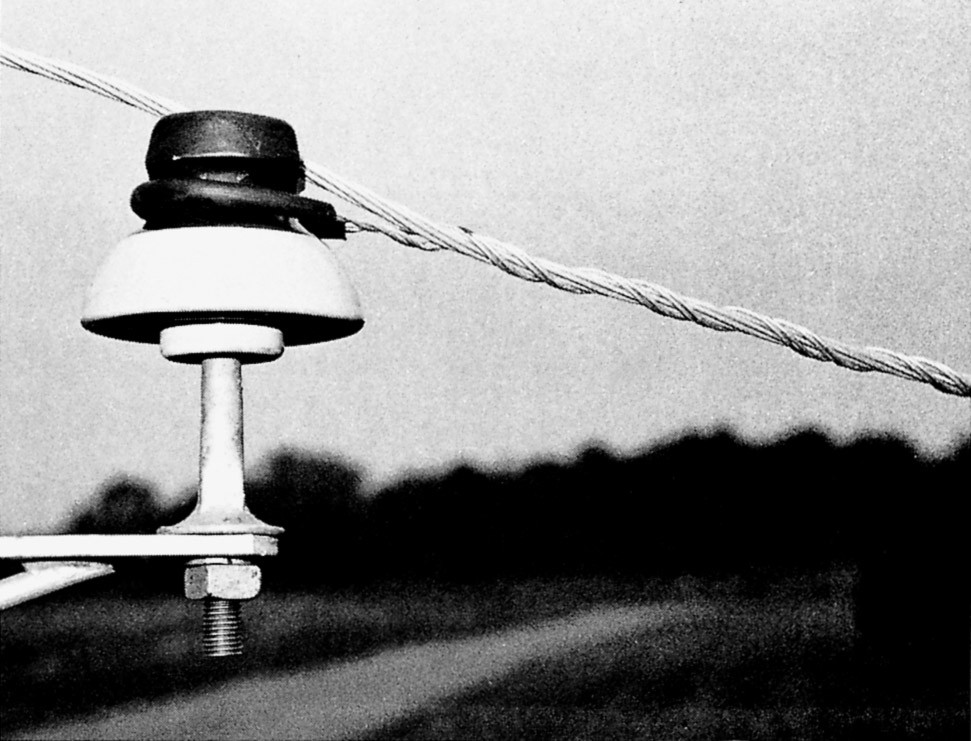
- Safety precautions – ensure all the personnel involved in the installation are properly trained and equipped with suitable safety gear.
- Conductor preparation – ensure the conductor is properly prepared and cleaned. This helps to remove any contaminants or debris from the conductor’s surface.
- Inspection – inspect all the dead-end components including the clamps, fittings and any associated hardware. This is to ensure they are in good condition and free from debris.
- Positioning – position the dead-end components on the conductor at the desired location.
- Clamp installation – install the clamps on the conductors according to the specifications.
- Tensioning – tension the conductor to the desired level following the engineering and tensioning guidelines specific to the project.
- Dead-end attachment – attach the dead-end components to the conductor. This may involve threading the conductor through the dead-end fitting.
- Attachment – follow the manufacturer’s instructions for attaching the dead-end to the structure.
- Tension adjustment – make the necessary tension adjustments to achieve the desired conductor tension and sag.
- Alignment – verify the installation maintains the required conductor alignment and clearances as specified.
- Torque verification – confirm all bolts, nuts and fasteners have the proper torque. This is to ensure the integrity of the installation.
- Inspection – conduct a final inspection to ensure all components are correctly installed, conductor tension is within acceptable limits and maintained clearance.
- Documentation – maintain records of the installation process including tension levels, clearances and any adjustments made.
Maintenance and inspection of slack span dead end
Conduct maintenance and inspection of the dead ends in the challenging environmental conditions. This is due to the humidity and potential exposure to salt in coastal areas. This helps to ensure the reliability and safety of overhead transmission lines. This also helps reduce the risk of unplanned outages and ensuring safety of the electrical infrastructure. The following is a basic guide for the maintenance and inspection of the slack span dead end.

- Conduct regular visual inspections of slack span dead ends to check for signs of wear, corrosion, loose components or damage. Check for signs of rust, cracks or any unusual changes in appearance.
- Ensure the dead-end components are from corrosion-resistant materials. Consider applying anti-corrosion coatings as needed.
- Check the tenson of conductors to ensure they are within the recommended range to maintain proper sag and clearances.
- Verify the dead-end installation maintains the required conductor alignment and clearances specified.
- Inspect all fasteners for proper torque and security to maintain the integrity of the installation.
- Conduct galloping and vibration analysis to assess the performance of the dead-end. It should control vibrations and prevent galloping.
- Evaluate the potential environmental impact of the dead-end materials and coatings used. Ensure the coatings are eco-friendly and do not harm the local ecosystem.
- Assess the structural integrity of these support structures to ensure they can safely bear the loads imposed by the dead ends.
- Keep detailed maintenance records including dates, findings and any maintenance performed.
Comparative analysis of slack span dead end
The comparative analysis for the dead ends involves assessing different types and designs. This also depends on their suitability for specific applications, environmental conditions, load bearing capacity and installation requirements. There are various factors to consider to ensure the best selection of the most suitable option. The following are the common factors to include in the analysis.
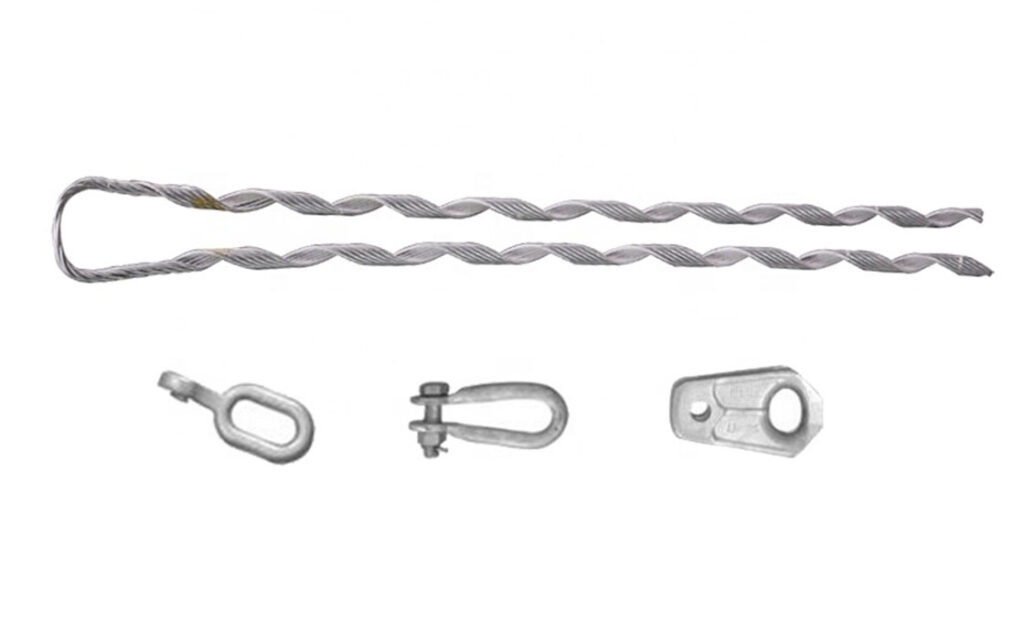

- Type of slack span dead end – each type and design of the slack span dead end has various benefits and limitations. Consider the suitability, environmental considerations and load capacity of each type of dead end.
- Environmental conditions – Consider the suitability of materials for resisting corrosion. Common materials include stainless steel or corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Load bearing capacity – evaluate the load bearing capacity of the dead end in relation to the expected mechanical loads.
- Installation and maintenance – assess the ease of installation and maintenance.
- Cost benefit analysis – compare the initial cost, installation and maintenance costs of different types of dead ends. Balance their performance and lifespan performance.
- Compliance – ensure the selected dead end complies with local electrical codes and regulations.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
Ensure the selected dead end complies with the regional and international standards related in the region. Each Southeast Asian country have their own set standards governing the electrical components and codes. The following are the common standards and certifications for slack span dead ends in Southeast Asia.

- IEC standards – this outlines the requirements for fittings and accessories used in overhead transmission and distribution lines.
- ASTM standards – this specifies requirements for concentric-lay-stranded aluminum conductors.
- ISO standards – these are quality management systems for manufacturers. They help to ensure consistent quality and compliance with standards.
- Environmental and safety standards – they should adhere to environmental and safety standards. This relates to materials, coatings and manufacturing processes.
- Local grid operator standards – they have specific standards and requirements for equipment used in their transmission and distribution systems.
- OHSAS 18001 – this is occupational health and safety management standards. They ensure the safety of workers during the manufacturing and installation of slack span dead ends.
Regional markets for slack span dead end in southeast Asia
There are various factors that influence the regional market for slack span dead end in Southeast Asia. These factors include infrastructure development, expansion of electricity transmission networks and environmental conditions. The need for reliable and efficient electrical systems also influences the market for slack span dead ends. The common markets for the dead ends include Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Philippines, Singapore and Laos among others. The following are the common factors that shape the regional market for slack span dead ends in Southeast Asia.

- Regional interconnections – the development of cross-border transmission projects to share electricity resources increase the use of electrical components. Slack span dead ends help ensure power reliability between the countries.
- Renewable energy projects – growth of projects such as wind farms and solar power plants require the integration of transmission lines. the dead ends contribute to the reliability of these renewable energy sources.
- Urbanization and infrastructure modernization – upgrades and modernization of electrical infrastructure includes the use of reliable slack span dead ends.
- Environmental considerations – presence of coastal areas and regions with high humidity are prone to corrosion. Slack span dead ends designed for corrosion resistance are in demand in these areas.
Frequently asked question
A slack span dead end is a component used in overhead transmission lines to accommodate thermal expansion. It also helps reduce mechanical stresses and enhance line reliability. Southeast Asian applications need to maintain transmission infrastructure by use of sack span dead end.
The dead end’s design provides flexibility and absorbs mechanical forces, reducing conductor vibrations and prevent galloping. These conditions threaten the integrity of the transmission lines.
The dead ends ensure the reliability and efficiency of cross-border power exchange and regional electrical grids.