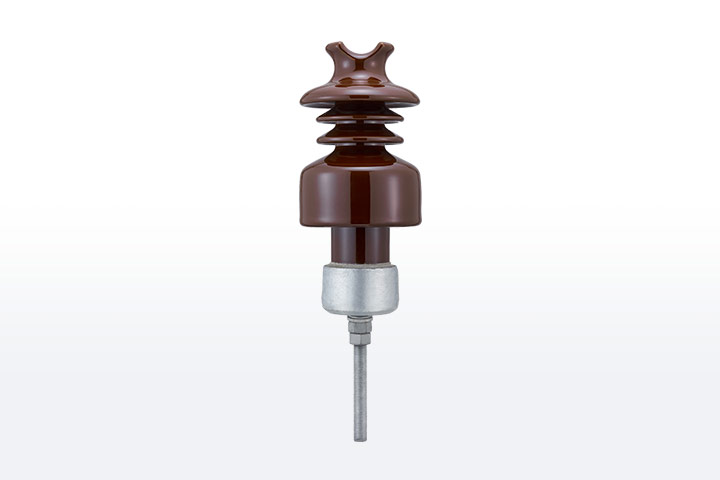

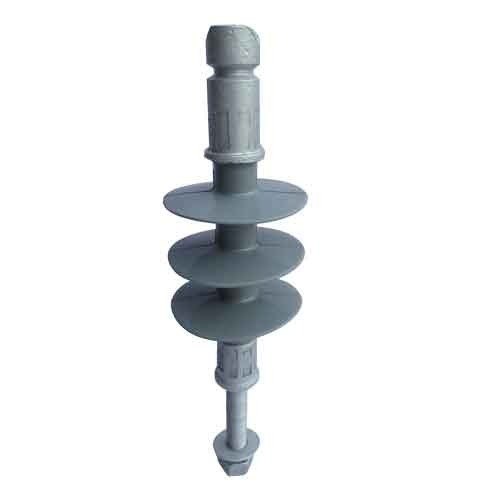
A pin insulator is a component used in overhead transmission lines to prevent electricity from flowing to unwanted areas. It helps to support and insulate the conductors from the support structures like poles. The pin insulator consists of a cylindrical body with a flange at one end and a groove at the other end. The flange end helps in attachment to the support structure while the groove end holds the conductor in place. Pin insulators are from materials that offer excellent insulating properties, durability and resistance. This material includes porcelain or glass. The main function is to prevent electrical current from escaping the transmission line and grounding. It ensures the electrical energy transmits along the conductor to its destination. Pin insulators are also able to withstand factors such as wind, rain, ice and UV radiation.
Components of the pin insulator
The pin insulator consists of several components working to provide efficiency in insulation. Each part of the pin insulator helps to fulfil specific functions in the application. The components helps to ensure safe and reliable operation of overhead transmission lines. the following are the common components of the pin insulator.
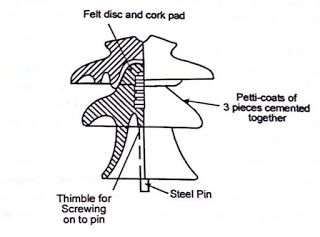
- Body – this is the main structure of the pin insulator in a cylindrical shape. It is from porcelain or glass materials. The body provides mechanical support and electrical insulation for the conductor.
- Metal pin – this is a metal rod or flange, disc-shaped to serve as the support for the insulating unit. It is from galvanized steel for corrosion resistance. The metal pin attaches to the supporting structure and provides mechanical strength to the insulator.
- Grooves – the other end of the pin insulator has a groove and petticoat. Grooves helps in distributing the mechanical load and provide extra insulation. This is by increasing the surface distance between the conductor and the supporting structure.
- Fittings – fittings secure the conductor to the pin type insulator. Such fittings include metal clamps, bolts, nuts and washers among others. They also ensure the reliable connection between the conductor and the insulator. This also helps to maintain the electrical continuity.
- Cement – this helps to secure the metal pin into the insulator body. This is to ensure the pin remains attached to the insulator and provide reliable mechanical support.
- Metal caps – some of the pin type insulators have a metal cap on top of the insulating component. The cap provides protection against environmental factors. They also help prevent moisture from entering the insulator.
- Grading rings – grading rings are optional components of the pin type insulator. They are conductive rings installed near the top of the insulator, designed to distribute the electrical field. They also reduce the concentration of electric stresses and help improve the voltage distribution along the insulator.
Types of pin insulator
There are several types of pin insulators designed for specific applications and operating conditions. Each type has specific characteristics depending on the specific requirements of the application. The following are the common types of insulator pin used in overhead transmission lines.
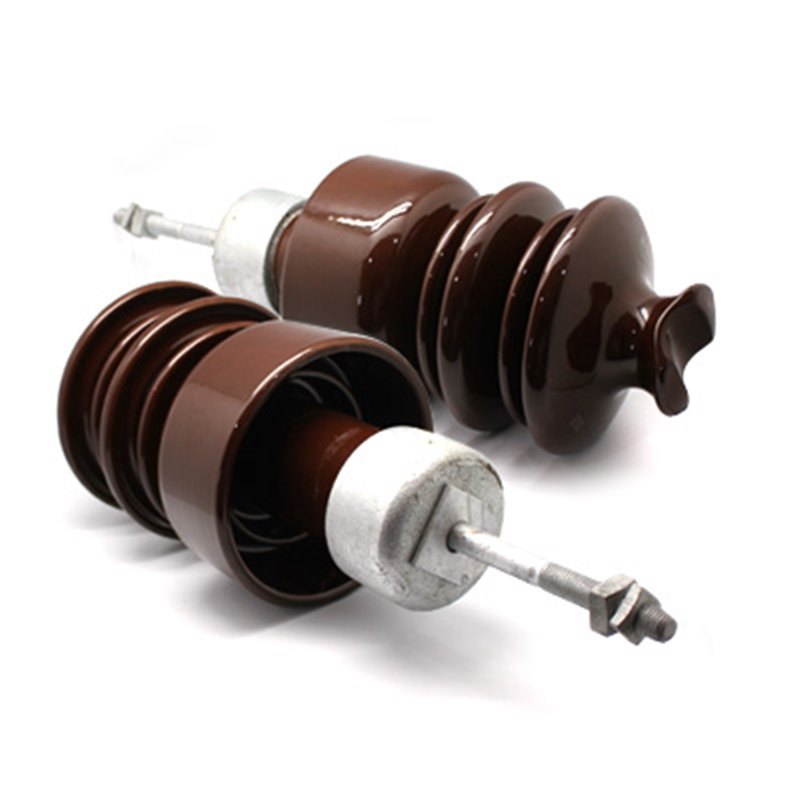

- Standard pin insulator – these are the most common types of pin insulators. They consist of a cylindrical body with a flange for mounting and groove for holding the conductor. They are suitable for applications in low to medium voltage transmission lines.
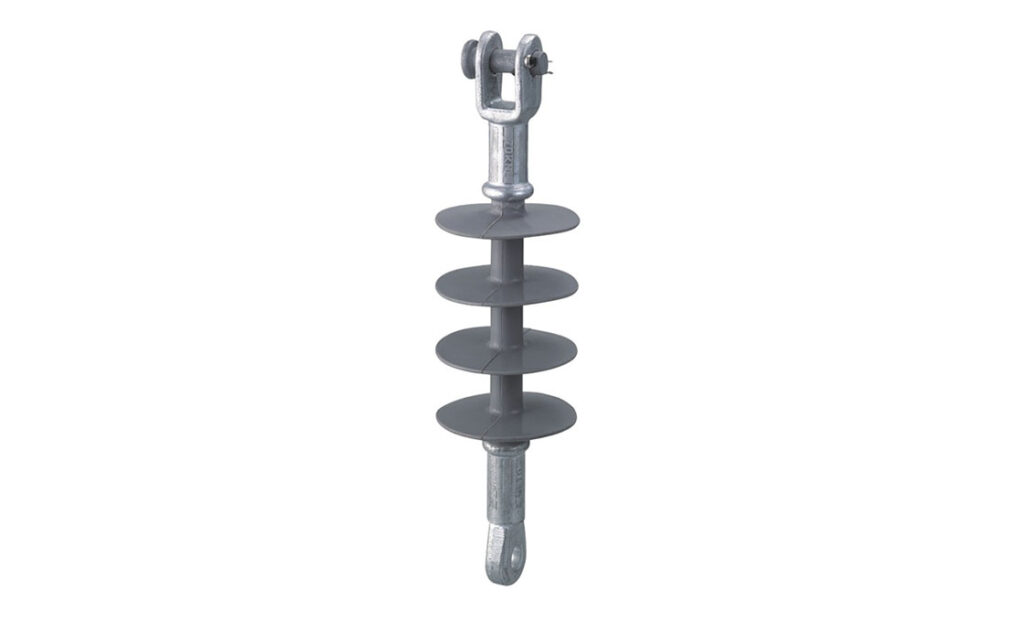
- Guy strain insulator – these help to insulate and support guy wires used to anchor poles or towers. Their design aims to withstand tension and mechanical loads on the overhead transmission lines. They have a disc shape and may be solid-core or multi-piece depending on the voltage requirements.
- Solid-core pin insulator – this is the most common type of pin insulator used for power transmission lines. it consists of a single solid porcelain or glass insulating component mounted on a metal pin. These types of pin insulators work in medium voltage applications. They provide good electrical insulation and mechanical strength.
- Composite pin insulator – these types of insulators are from a combination of polymer materials. This is including fiberglass reinforced with epoxy. They offer advantages like lighter weight, high strength and resistance to environmental conditions. They most work in areas with high pollution, coastal regions and areas susceptible to wreckage.
- Multi-piece insulator – the insulating component divides into several segments or shells stacked together. These insulators offer increased flexibility which allow for easier installation and replacement. They work in low to medium voltage applications.
- Long-rod insulator – long-rod insulators have designs for high voltage transmission lines. This consist of a series of porcelain of glass insulator disc connected by metal rods. The long rod design provides increased creepage distance. This distance allows for higher voltage ratings and better performance in polluted environments.
Differences between a pin insulator and an insulator pin
A pin insulator and insulator pin are both used to isolate the conductors on overhead transmission lines. a pin insulator is a complete insulating unit including the insulator body and the metal pin. The insulator pin is the metal component that secures the insulator to the support structure. The two components can lead to confusion and it is thus advisable to consult with experts. The following are the common differences between the insulator pin and the pin insulator.

- Pin insulators – this consists of a ceramic or glass insulator body with a metal pin inserted through its center. It mounts on a crossarm attached to the support structure like pole or tower. Its main function is to support and insulate the electrical conductor from the support structure.
- Insulator pins – this is a metal component that holds the insulator in place on the supporting structure. It inserts through the center of the insulator body and extends beyond both ends. The insulator pins serves as a mechanical anchor for attaching the insulator to the crossarm. It also provides a secure connection point for the insulator and ensures it remains in position.
Benefits of using the pin insulators
Use of pin insulator in overhead transmission lines offer several benefits. Pin insulators contribute to the safe, efficient and reliable operation of transmission lines. The following are the benefits the pin insulators offer to electrical applications.

- Electrical insulation – the insulators provide electrical insulation which prevents electrical current from flowing in unwanted areas.
- Durability – the insulators are from porcelain or glass materials that offer durability and resistance to various factors. This ensures the long-term performance and durability of the insulating system.
- Ease of installation – pin insulators are easy to install and maintain. They mount onto crossarms using insulator pins. They also have designs to withstand normal wear and tear.
- Versatility – pin insulators are available in different designs and configurations to hold different voltage levels and conductor sizes. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications in the systems.
- Mechanical support – the insulators support the weight of the conductors and help distribute mechanical stresses. They also provide a platform for the conductors reducing the risk of sagging or swinging.
- Resistance to pollution – the pin insulators are able to withstand pollution which can degrade insulating materials. Their shape helps to reduce the buildup of dirt, dust or pollutants. This is to maintain the insulating properties.
- Cost effectiveness – pin insulators are more cost effective which makes them a preferred choice for overhead transmission lines.
Limitations of pin insulators
Pin insulators work in medium to low voltage transmission lines and offer several benefits. They also face disadvantages and challenges during designing and operating overhead electrical systems. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with industry experts for guidance and insights. The following are the limitations of pin insulators.

- Voltage limitations – pin insulators work in medium to low voltage transmission lines. higher voltages need longer leakage distances to prevent arcing and flashovers.
- Leakage currents – accumulation of dust dirt and moisture can reduce its effectiveness and increase risk of electrical leakage. They thus need regular cleaning and maintenance to address such issues.
- Insulator failures – pin insulators experience failures due to factors such as manufacturing defects, mechanical damage and environmental degradation.
- Mechanical strength – the insulators may have lower mechanical strength which might lead to breakage. This can interrupt power transmission and need frequent maintenance.
- Space requirements – the insulators need enough space for mounting on crossarms or brackets attached.
- Costs – the initial installation and maintenance for pin insulators can be significant. Environmental conditions may also increase the total cost of ownership.
Frequently asked questions
A pin insulator is a type of insulator used to support and insulate conductors from the support structures.
Using pin insulators provides electrical insulation, mechanical support, durability, resistance to corrosion, ease of installations and cost effectiveness.
Pin insulators commonly work in overhead transmission and distribution lines for medium to voltage lines. They are also used in other electrical infrastructure in the industry.
Consider voltage rating, mechanical strength, environmental conditions, pollution levels, installation requirements and maintenance considerations.
Common components of the pin insulators include the body, flanges, grooves, cement, grading rings and metal caps.