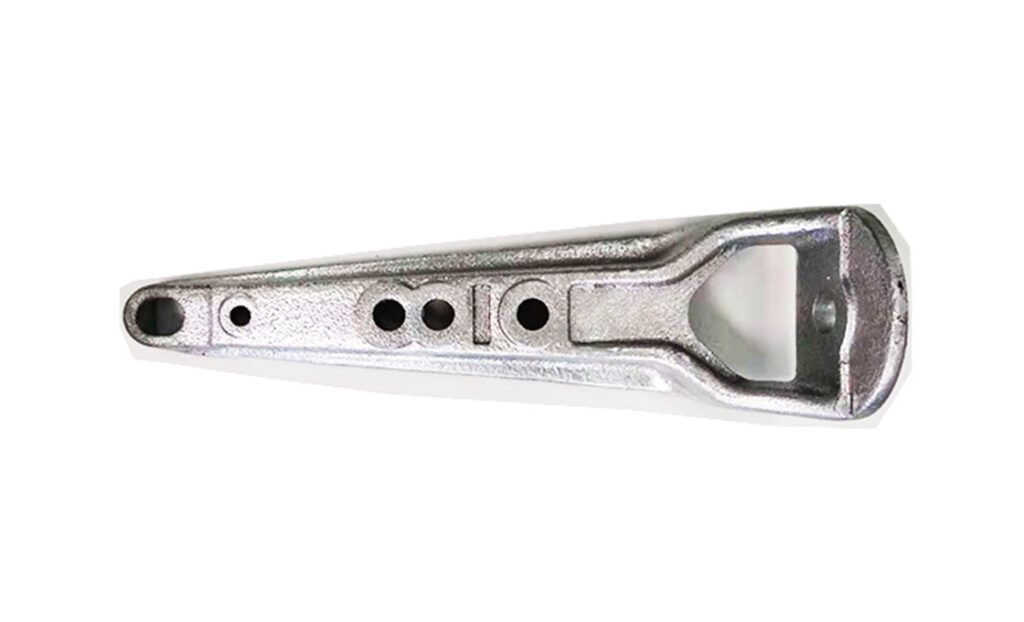

A pole top bracket is a device used to mount post insulators on transmission line poles. It also helps to provide extra space and support for various electrical equipment. A pole top bracket attaches to the top of utility poles through bolting, welding or other methods. It also helps to protect the post insulators from external damage. A pole top bracket is from durable materials such as steel or aluminum. These materials are able to to withstand outdoor environmental conditions. South American utilities require robust pole top brackets to meet the environmental conditions. This helps to ensure safe and reliable support for the electrical equipment. Common type includes crossarm pole top bracket, transformer bracket, lightning arrestors brackets and sign brackets. They find use in applications such as guy wire support, spacing and clearance, cable management, streetlight and bird diversion.
Key features of pole top bracket
Pole top brackets have various features that help them provide proper support to the electrical devices. The features vary depending on their specific design and intended application. The following are the key features of the pole top bracket.
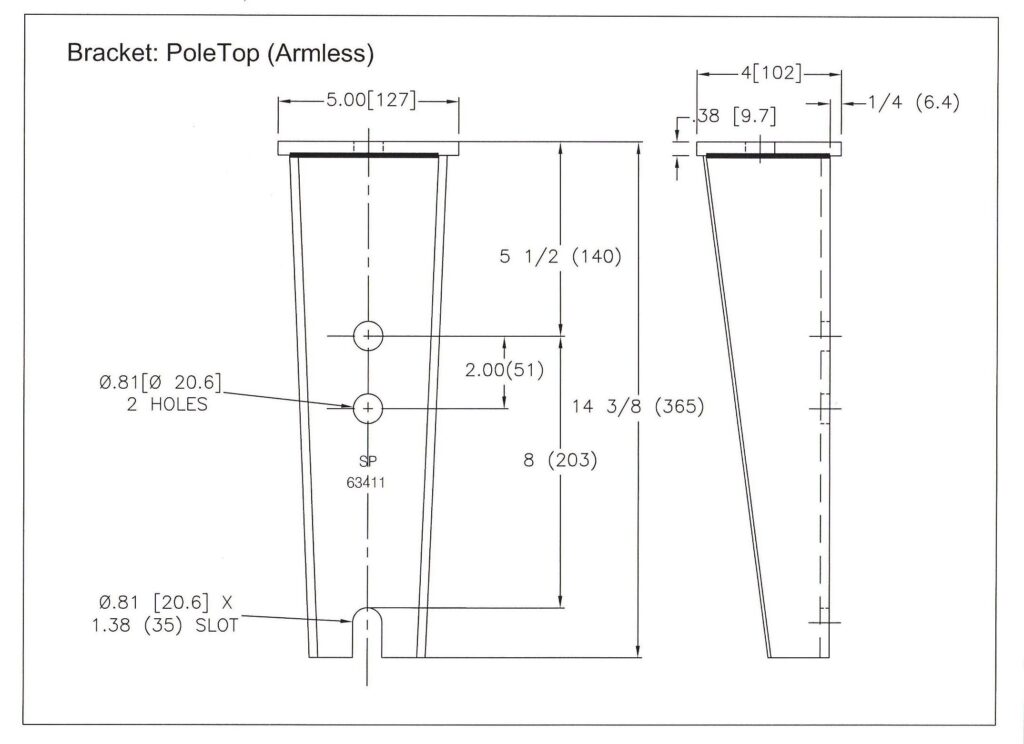
- Design – the pole top bracket design should align with the intended application. This is because there are various designs with different capabilities.
- Corrosion resistance – brackets should have corrosion resistance coatings or materials. This helps them to withstand the diverse environmental conditions.
- Material – they are from durable materials such as galvanized steel, aluminum or stainless steel.
- Load capacity – the brackets should also support various loads. This is including weight of equipment and environmental factors.
- Adjustability – this allows for fine-tuning of equipment positioning or alignment. This helps during installation or maintenance.
- Environmental considerations – the bracket should be able to withstand the various environmental conditions. These include resistance to UV radiation, extreme temperatures or exposure to salt in coastal areas.
- Versatility – some of the brackets can accommodate a range f equipment types and sizes. This helps to reduce the need for multiple bracket designs.
- Spacing and clearance – they also provide proper spacing and clearances for electrical equipment. This is to prevent electrical arcing, flashovers or interferences with adjacent structures.
Selection and installation of pole top bracket
The selection process includes careful consideration of various factors. This helps to ensure they meet the specific requirements. These factors include type of application, load requirements, environmental conditions, material, design, costs and warranty. The installation requires careful planning and adherence to safety standards. The following is a general guide for pole top bracket installation.

- Preparation – collect all the required tools and materials necessary for the installation. This includes pole top bracket, mounting hardware, safety equipment and a wrench. Ensure the workers use suitable personal protective equipment. This includes helmets, gloves and safety glasses.
- Site assessment – conduct a site assessment to determine the optimal location. Consider clearances, spacing and accessibility for maintenance.
- Pole preparation – clean the pole and ensure it is free from debris and other contaminants.
- Positioning the bracket – position the pole top at the desired location. Ensure proper aligning and levelling of the bracket.
- Mark mounting holes – mark the locations of the brackets mounting holes on the pole.
- Drilling – use a drill to create holes at he marked locations on the pole.
- Attachment – securely attach the pole top bracket to the pole using the mounting hardware. Tighten the bolts to the recommended torque specifications.
- Inspection – perform visual inspection of the bracket. Ensure that it is securely fastened, level and properly aligned with the pole.
- Attach electrical equipment – mount and secure the electrical equipment to the bracket.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the bracket installation. This is including specifications, load ratings, torque values and other adjustments made.
Maintenance and inspection of pole top brackets
Proper maintenance and inspection help to ensure the safety, reliability and longevity of electrical systems. It also helps to identify and address potential issues that may affect the electrical systems. This increases reliability and extends the lifespan of the infrastructure in South America. The frequency depends on the diverse weather conditions of the region. Also, ensure to perform a professional maintenance and inspection once in a while. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection in South America.

- Establish regular inspections of pole top brackets based on manufacturer specifications, environmental conditions and local regulations.
- Visually assess the condition of the pole top bracket and any attached equipment. Check for signs of damage, wear or corrosion.
- Confirm the clearances and spacing between the bracket, equipment and nearby structures.
- Perform electrical testing and measurements as required. This is to ensure proper functionality and insulation resistance.
- Evaluate the load-bearing capacity of the bracket. Confirm it can safely support the equipment without exceeding the rated capacity.
- Periodically clean the pole top brackets to remove dirt, dust and debris. This helps to prevent corrosion and ensures proper visibility during inspections.
- Inspect the brackets for signs of corrosion in regions with high humidity or coastal areas. Treat the corroded areas with suitable coatings to prevent further deterioration.
- Check the fasteners securing the bracket and ensure all connections are properly torqued.
- Verify that the pole top bracket is safely grounded to reduce the risk of electrical faults.
- Apply a fresh coat of corrosion resistant coating to maintain its protective properties.
- Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities. This is including dates, findings and any corrective actions taken.
Comparative analysis of pole top bracket in South America
A comparative analysis includes evaluating various factors that determine the most suitable applications. It includes assessing the different types, brands, manufacturer and sizes. This helps ensure the best selection of the pole top bracket for your application. Also, balance between cost, performance and compliance with safety and regulatory standards. The following are the key factors to include in a comparative analysis in South America.
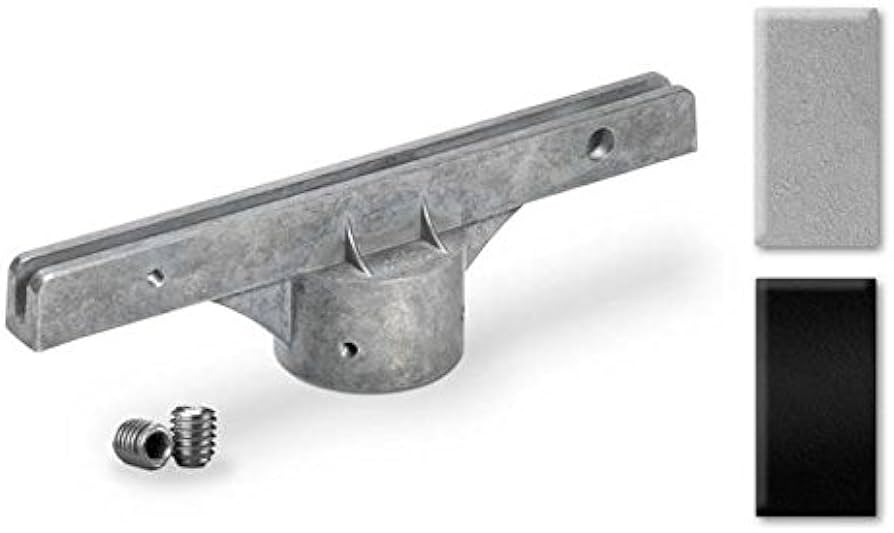

- Ensure the brackets provide proper clearances and spacing between equipment and other structures. This helps to comply with safety standards and prevent electrical arcing.
- Evaluate the safety features of the brackets like rounded edges and smooth surfaces.
- Consider the long-term maintenance requirements and factor in cost and effort.
- Check the materials used in pole top brackets. Consider corrosion resistance, strength and durability. Common materials include steel, aluminum or galvanized steel.
- Compare the load bearing capacities of the brackets. Ensure the selected one can support the weight of the intended equipment.
- Analyse the design and configuration of brackets to match the specific requirements of the equipment and application.
- Assess the resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
- Consider the adjustability to allow for adoption to unique project requirements.
- Compare the prices of different pole top brackets. Consider costs, maintenance requirements and expected lifespan.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are standards and certifications related to pole top bracket in South America. They help to ensure safety, quality and compliance with regulatory requirements. The standards also vary by country and some are international standards. The following are the standards and regulations in south America.
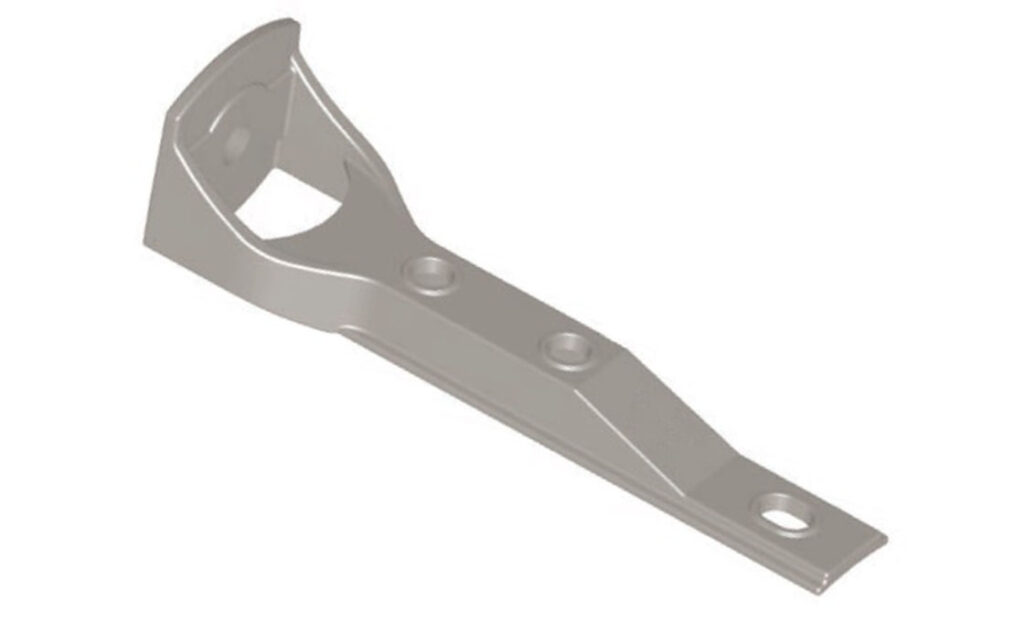

- IEC standards – this is an international standard that covers the requirements for metal supports used in overhead power lines. It includes specifications for materials, dimensions and mechanical electrical properties.
- ASTM standards – ASTM standards work as reference for materials and testing procedures.
- ISO certifications – this relates to materials, quality management and testing procedures for quality control.
- Regulatory authorities – these are responsible for the electric power sector. It helps to dictate the standards and certifications for pole top brackets.
- Local and regional regulations – these are standards and codes that apply to pole top brackets in the South American region.
Regional market for pole top bracket in South America
There are various market trends that affects and influence the regional market for pole top brackets in South America. The increased demand for reliable electricity leads to the increased demand for pole top brackets. The following are the factors that influence this regional market.

- Investment in smart grids – the increased investment in smart grid technology improves efficiency and reliability. This leads to the increased demand for pole top brackets for monitoring and control.
- Telecommunications – the growth of this sector impacts the demand for brackets accommodating both types of equipment.
- Urban and rural applications – pole top brackets find applications remote and rural regions to extend electrical access.
- Diverse geography and climate – the diverse geography in south America presents unique challenges for electrical infrastructure.
- Local manufacturing and suppliers – presence of local manufacturing industry influences the market dynamics and local availability.
- Maintenance and replacement – ongoing maintenance, repair and replacement of aging infrastructure contributes to demand for pole top brackets.
Frequently asked questions
A pole top bracket is a component used to support various equipment on transmission systems. It supports equipment such as transformers, insulators and crossarms. Its purpose is to provide structural support and spacing for the equipment on utility pole.
The frequency of inspection and maintenance varies depending on environmental conditions and regulatory requirements. It mostly occurs annually or semi-annually.