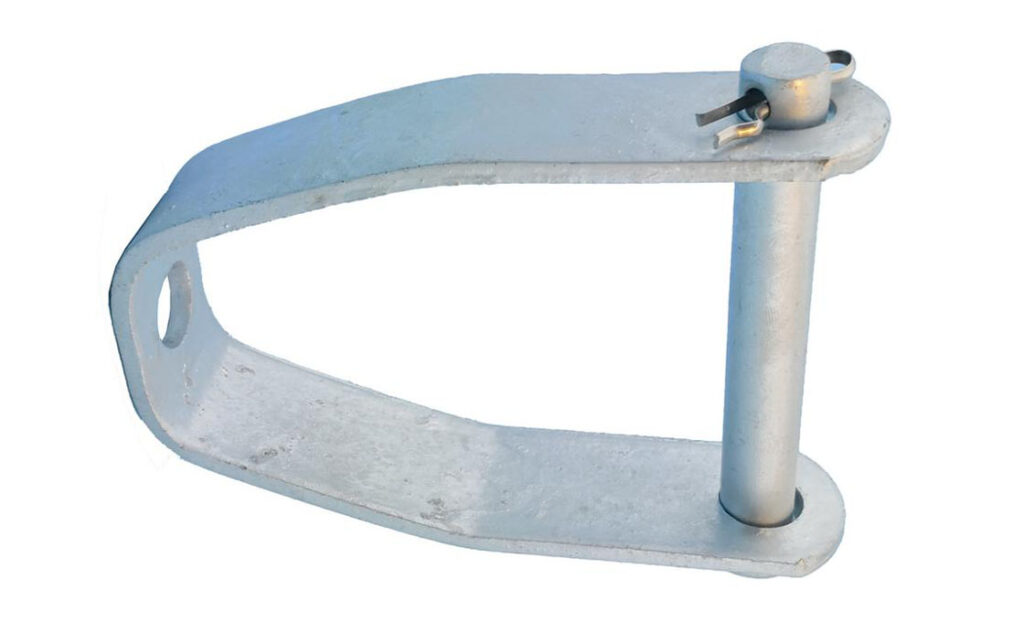

A secondary rack is a type of insulator cable support used to provide support either at the side or inside the power line pole. It is a U-shaped spool insulator cable that features a steel base foe connection. A secondary rack prevents the cable from sagging or swinging which cause damage to the cable. They are from materials such as aluminum or galvanized steel to prevent rust and corrosion. Secondary racks also provide electrical insulation between the cable and the pole. They are mainly used in power transmission and telecommunications lines to prevent sag and provide cable support.
Components of secondary rack
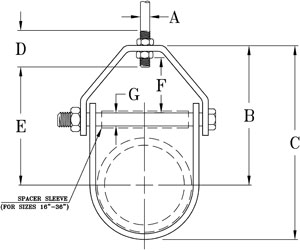
A secondary rack has several components working together to enhance reliability and safety. The exact components vary depending on the specific manufacturer, region or power system requirements. The following are the key components of a secondary rack.

- U-shaped spool insulator – this is a key component that provides support and insulation for the cable on the overhead pole line. The design allows the cable to wrap around the rack and prevent sagging.
- Steel base – the base provides stability and strength to the rack and allows secure attachment to the power line pole.
- Mounting holes – these holes enable the rack to attach to the power line pole using fasteners. They also offer flexibility in positioning and allow for adjustable placement of the rack.
- Nuts and bolts – these fasteners secure the secondary rack to the power line pole through mounting holes.
Common types of secondary racks
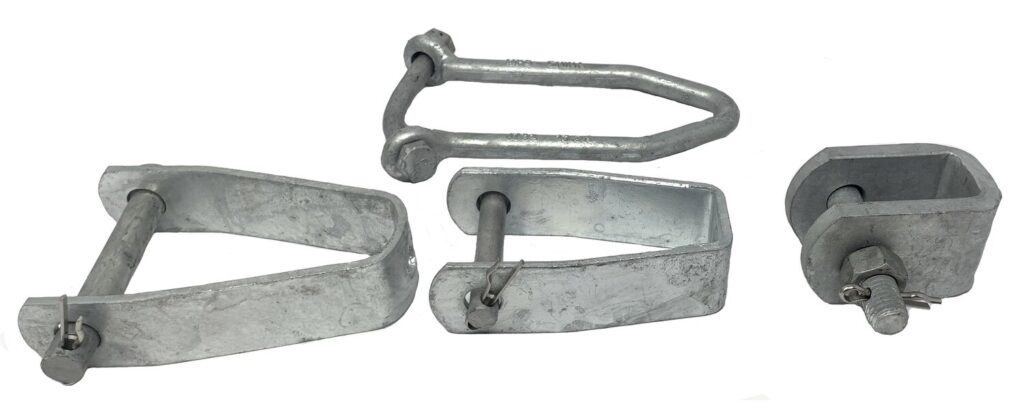
There are various types of secondary racks available each with a design that meets different applications and requirements. The selection of a secondary rack depends on various factors. These factors include specific application, load requirements, attachment method and adjustability needs. Also, consider the design specifications and recommendations from the manufacturer. This is when choosing the right secondary rack for a particular application. The following are the common types of secondary racks.

U-bolt secondary rack – this rack features a U-shaped spool insulator with a steel base that attaches to the power line pole. This type of secondary rack offers easy installation and adjustment.
Adjustable secondary rack – these type offers flexibility in positioning and height adjustment. They have an adjustable mounting mechanism that allows for fine tuning the position of the U-shaped spool insulator.
Band secondary rack – this type consists of a band-shaped metal bracket that wraps around the power line pole. The U-shaped spool insulator attaches to the band which provides support and insulation for the cable.
Welded secondary rack – these form by welding the U-shaped spool insulator directly onto a metal bracket. The bracket is then welded to the power line pole to ensure a robust and durable attachment.
Clevis secondary rack – this type utilizes a clevis-style attachment mechanism to provide a secure and reliable connection. They are simple and easy to install.
Applications of secondary racks
Secondary racks find use in various applications in the industry depending on the application. Secondary racks work in various applications such as power transmission systems, telecommunication lines and electrical systems. Their uses vary depending on the type of application and the specific requirements. Additionally, you should consult with industry experts for guidance on the type of rack that best suits your application. The following are the common application areas of secondary racks.

- Oil and gas industry – secondary racks support power cables and ensure uninterrupted power supply to critical equipment and facilities in oil and gas industry.
- Rural electrification – secondary racks support and insulate cables. This ensures safe and reliable power supply to rural communities.
- Renewable energy – secondary racks work in wind farms and solar power plants to support and manage electrical cables. These cables transmit power generated from these sources.
- Electrical utilities – secondary racks work in electrical utility companies.
- Telecommunications – the racks support and manage power cables that supply power to communication towers and infrastructure.
- Industrial power distribution – secondary racks provide support to cables used in industrial systems. They also ensure reliable power supply to equipment and machinery.
Installation guide for secondary racks on transmission lines
Installation process of secondary racks vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer’s instructions. It should follow all the relevant industry standards and enhance safety protocols. Some manufacturers offer installation guidelines for secondary racks and the components involved. Additionally, it is advisable to seek professional assistance whenever in doubt. The following is a basic installation guide for the secondary rack.
- Prepare the installation area by ensuring the area is clear of any obstacles. Remove any debris or obstructions that may interfere with the installation and performance.
- Position the secondary rack on the power line pole. Consider factors such as cable alignment, clearance requirements and accessibility for maintenance.
- Use a marker or pencil to mark the positions of the mounting holes on the power line pole.
- Drill the mounting holes using the suitable tools to create the necessary mounting holes at the marked positions.
- Align the mounting holes of the secondary rack with the drilled holes. Insert the appropriate bolts or fasteners and tighten them.
- Double check the secondary racks’ stability and alignment and ensure it is securely fastened to the power line pole.
- Route the cables along the U-shaped spool insulator of the rack. Ensure the cables are properly supported and spaced to prevent sagging.
- Inspect the installation checking for any loose fasteners and ensure the cables are properly positioned and secured on the rack.
Selecting the best secondary rack for your application
There are several styles and designs of the secondary rack to select from for your application. the selection process can sometimes be tedious as it should meet the specific requirements of the application. The selected secondary rack should provide reliable cable support, durability and comply with industry standards. Also, it is advisable to consult with experts in the industry to offer guidance on the most appropriate secondary rack for your application. It therefore involves several factors to consider as discussed below.

- Check the cost effectiveness of secondary rack by comparing prices from different manufacturers. Consider durability, quality and performance of the rack.
- Ensure the selected secondary rack complies with the industry standards, codes and regulations to meet the specific performance and safety requirements.
- Determine the specific application requirements of the power transmission system. Consider factors such as voltage level, cable size, load capacity, environmental conditions and clearance requirements.
- Evaluate the load capacity of the secondary rack. Ensure it can handle the expected weight and mechanical forces exerted by the cables.
- Select from materials that ensure durability and corrosion resistance such as steel or aluminum. Consider environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, UV radiation and chemical contaminants.
- Ensure the secondary rack is compatible with the power line pole, cable type and size.
- Assess the design features and mounting options of the secondary rack. Consider factors such as adjustability, ease of installation accessibility for maintenance and available mounting methods.
- Select secondary racks from reputable manufacturers. Check the product specifications, installation guidelines and quality of the products.
Frequently asked questions
A secondary rack is a type of insulator cable support that provides support at the power line pole. Secondary racks prevent the cable from sagging or swinging.
Secondary racks provide insulated support to overhead cables which make them useful in various applications. These applications include electrical systems, telecommunication lines, rural electrification, oil and gas companies, renewable energy and industrial power distribution.
Secondary racks improve cable support, sag control, mechanical protection, electrical insulation and organized cable management. Other benefits include durability, flexibility and versatility. These contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability and safety of the power transmission infrastructure.
There are various limitations associated with using secondary racks. These include limited load capacity, design limitations, installation consideration, regular maintenance and inspection and limitations in cable management. Addressing these limitations ensures the reliable and safe operation of the infrastructure.