A side tie is a way of securing a conductor to an insulator on a utility pole. It wraps around the conductor and insulator to avoid slippage or displacement. A side tie maintains a firm grasp on transmission wires, ensuring their stability and safety. A side tie’s basic components are the conductor, insulator, and tie wire. The tie wire wraps around the conductor and insulator in a specified arrangement, which varies based on the type of tie and the transmission line’s specifications. In telecommunications and electrical networks, side ties serve to link ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) and OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) cables to support structures, giving both mechanical and stability.
Components of the side tie
Several components operate along with the side tie to secure ADSS and OPGW cables. These components vary depending on the type of cable and the installation requirements, with each performing a unique role in ensuring the cable system’s integrity and performance. The side tie assembly for ADSS and OPGW cables typically consists of the following components.
- Insulator for ADSS – these are from porcelain, glass or composite polymers. They provide insulation to provide electrical interference and mechanical support for the cable. They feature a groove to support the cable and ease secure attachment by the tie wire.
- Cable support hardware – these distribute the cable’s weight and reduce mechanical stress over long spans. The hardware includes suspension clamps and dead end clamps.
- Tie wire or rod – Side ties for ADSS cables consist of high-strength polymers or plastic. These non-conductive compounds serve to reduce electrical interference and maintain the dielectric qualities of the ADSS cable. They provide a secure connection point, ensuring the cable’s integrity and performance. Side ties for OPGW cables are from aluminum or galvanized steel. These conductive materials provide a secure attachment while maintaining the cable’s grounding function.
- Protective coverings for ADSS – helical armor rods wrap around the cable to provide extra mechanical protection. Cover the cable to prevent damage from abrasion or external impacts.
- Vibration dampers – spiral dampers wrap around the cable to reduce vibration and mechanical stress. They also attach to the cable and help dissipate vibrational energy to reduce wear and tear.
- Pole or tower attachment points – attach the tie wire to the pole or tower using bolts and clamps. Mounting brackets have designs to fit specific pole or tower configurations. This is to provide a secure attachment point for side ties.
The elements of the side tie
Side ties have a range of attributes that ensure their stability, durability, and the effective operation of overhead transmission systems. These features highlight their design, material properties, and functionality. Below are the key characteristics of side ties.
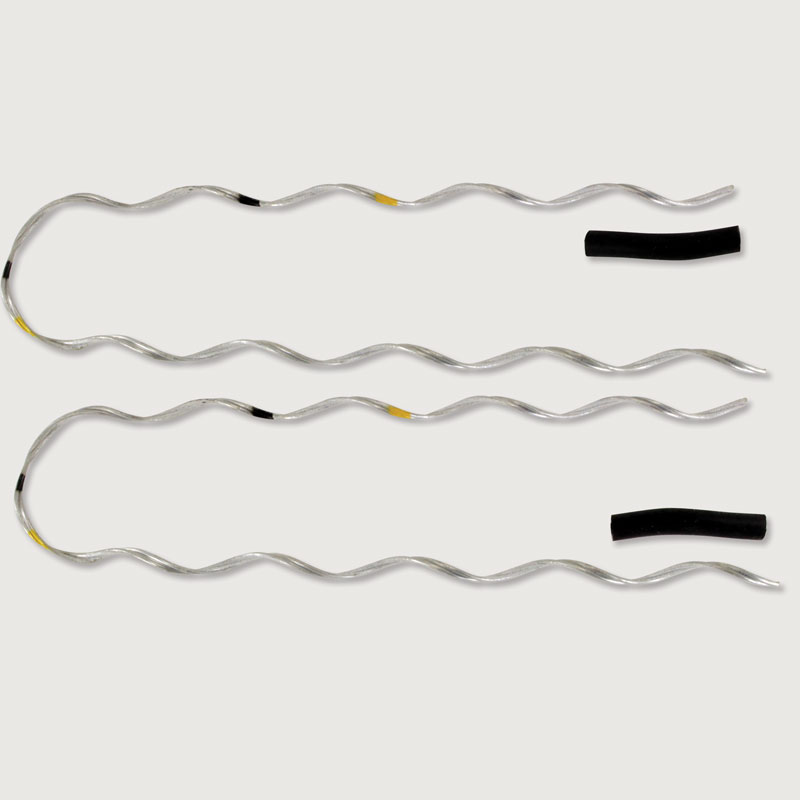

- Preformed design – preformed ties have designs to fit specific cable sizes and shapes to offer a uniform and secure fit. They also help reduce the time and skill required for installation.
- Mechanical strength and flexibility – side ties have designs to withstand high mechanical loads. The materials are also flexible to allow the cable to absorb and dissipate dynamic loads caused by environmental factors.
- Material composition – they are from materials with dielectric properties like high-strength polymers. These materials prevent electrical interference.
- Corrosion resistance – materials like aluminum, galvanized steel and high strength polymers offer their resistance to corrosion. They also have coatings that enhance their resistance to rust and chemical degradation.
- Environmental resilience – non-metallic ties are resistant to ultraviolet radiation. They help to prevent degradation and maintain their mechanical properties. Side ties have designs to operate across a wide range of temperatures.
- Vibration dampening – some of the side ties have designs to absorb and dampen vibrations to reduce wear on the cables. side ties help extend the lifespan of both the cable on the side tie itself.
- Compatibility with insulators – side ties are compatible with a variety of insulator types. This include insulators from materials like porcelain, glass and composite materials. They are available in many sizes and configurations to match specific installation needs.
- Secure and stable attachment – the design ensures the cable stays in place to prevent any movement. Side ties maintain their grip and alignment in challenging conditions.
- Ease of maintenance and inspection – side ties have designs to easily inspect and maintain and ease routine checks.
Checking conductor compatibility for side ties
Side ties that are compatible with conductors can help ensure a secure and stable cable attachment to support structures. This requires matching the side ties to the precise types of conductors used in overhead wires. Right side tie selection not only improves stability, but also allows a strong, long-lasting, and efficient system. The following are the main features of conductor-compatible side ties:
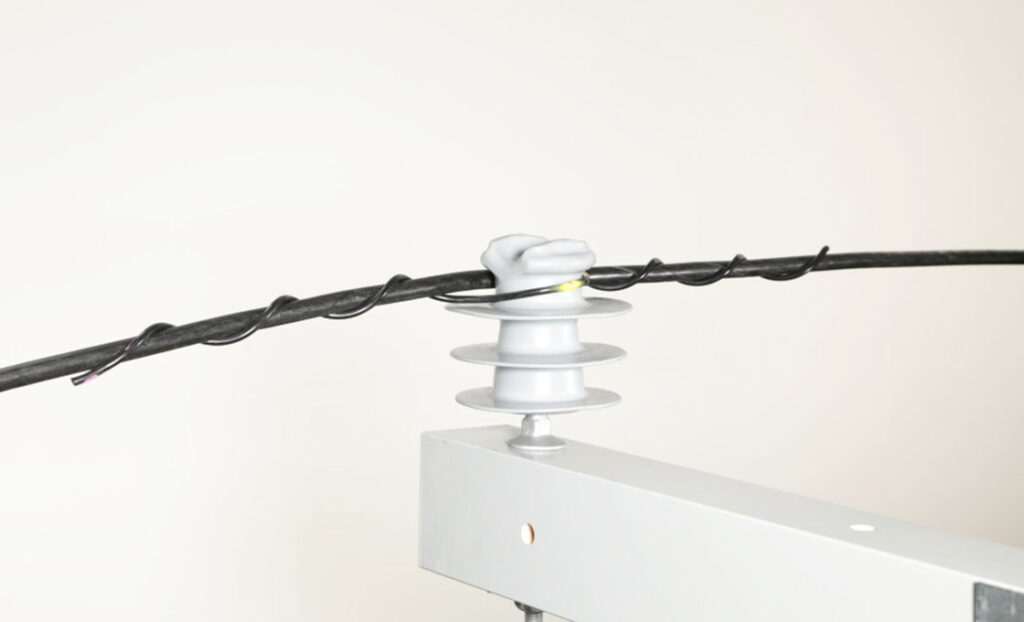

- Mechanical strength and load bearing – Use side ties that can withstand the weight and tension of the cable without breaking. The ties should be able to withstand dynamic loads such as wind, ice, and temperature fluctuations. To enable secure attachment and performance, OPGW cables must have side ties that match their tensile strength.
- Diameter and size compatibility – side ties must fit the specific diameter of the conductor they are securing. This ensures a firm grip and reduces the risk of slippage or excessive movement. They are available in various sizes to accommodate different conductor diameters.
- Vibration and fatigue resistance – the ties should be able to reduce vibrations from wind or mechanical forces. They should also withstand repeated stress cycles without degradation.
- Material compatibility – to prevent electrical interference, ADSS cables’ side ties must be non-conductive. High-strength polymers and composites are excellent for these applications. For OPGW cables, side ties should be from conductive materials. This is to ensure correct electrical conductivity and allow grounding.
- Environmental and operational conditions – for ADSS cables, the side ties need to withstand environmental conditions. This is including UV radiation and temperature extremes. They must accommodate the thermal expansion and contraction of the cable without causing damage. For OPGW cables, side ties must resist corrosion to maintain their strength and function.
Side ties used for ADSS cables
Side ties for ADSS cables keep the cables securely linked to supporting structures. The type of side ties used for ADSS cables varies depending on the dielectric and nonmetallic characteristics of the cables. Choosing the right side ties for ADSS cables is critical for ensuring cable stability and protection. The features of ADSS cable side ties are as described below.

- High strength and flexibility – side ties need to support the weight of the ADSS cable and withstand dynamic loads from wind and ice. The materials used provide enough flexibility to absorb movement and vibration.
- Corrosion resistance – ADSS installations face extreme weather conditions. This is including rain, snow and UV exposure. Non-metallic materials do not corrode which enhances durability.
- Non-conductive materials – ADSS cables work in conditions where electrical conductivity needs a reduction. Side ties for ADSS cables are from non-conductive materials to avoid electrical interference.
- Compatibility with cable diameter and insulator type – the side tie should match the specific diameters of ADSS cables. This is to ensure a precise fit that provides secure attachment without damage.
- UV and weather resistance – side ties for ADSS cables must be resistant to UV exposure to prevent deterioration. They should also perform well under a wide range of weather conditions.
- Secure attachment and cable protection – the design of the side ties ensures a secure grip on the cable to prevent slippage. The materials should reduce abrasion and mechanical stress on the cable.
Side ties used for the OPGW cables
Side ties attach OPGW cables to structures such as towers and poles. These cables have two functions: they serve as ground wires and they house optical fibers for telecommunications. Choosing the right side ties is critical for ensuring that your application systems remain stable and perform well over time. The following are the major qualities of OPGW cable side ties.

- Electrical conductivity – side ties are from conductive metals that help maintain the integrity of the electrical grounding path.
- Material composition – side ties for OPGW cables are from conductive metals to contribute to the electrical grounding functionality. They also provide protection against rust and corrosion.
- High mechanical strength – side ties must be capable of withstanding high tensile loads to support the weight of the OPGW cable.
- Vibration dampening – side ties have designs to absorb and dampen vibrations caused by environmental factors.
- Compatibility with OPGW cable diameter – side ties are available in sizes that match the diameters of different OPGW cables.
Frequently asked questions
Key characteristics of side ties include non-conductive materials, high strength, UV and weather resistance, and ease of installation.
OPGW wires need conductive side ties to ensure correct electrical grounding. These materials protect the electrical path via the cable system, increasing safety and performance.
Side ties attach cables to support structures and ensure electrical integrity to enhance the system’s reliability. They reduce the risk of cable damage, electrical interference and operational disruptions.