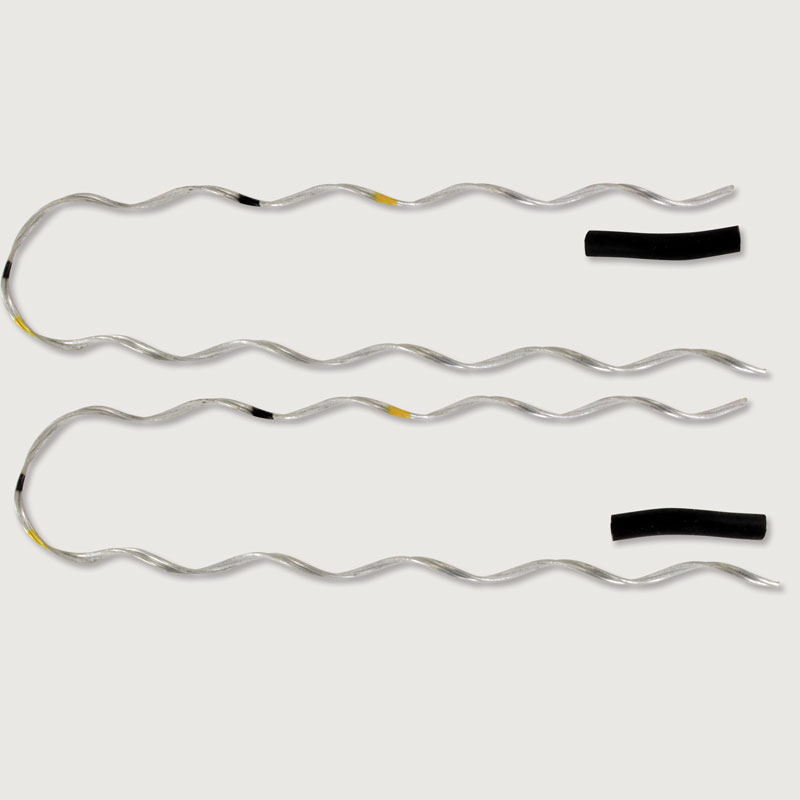
A side tie refers to a type of hardware used to secure conductors to insulators to provide a reliable and stable connection. It may also refer to a conductor or set of conductors that connect two or more transmission lines at the side. Side ties help to prevent conductors from chafing against the insulator and provides extra support for the conductor. They also balance the currents flowing through each line. This is crucial to maintain stable voltage levels and prevent excessive stress. Side ties are from materials such as aluminum-clad steel wire. In South America, side ties create a web of connectivity that enhances the stability and efficiency of networks. Types include spacer dampers, jumper cables, preformed side ties, ball side tie, single side tie and double side tie. They find use in applications such as load balancing, mitigation of imbalances, electromagnetic field control, grounding.
Key features of side tie
Side ties have various features that set them apart and make them a popular choice in the various applications. These features also help in the selection process for the side tie. The following are the key features of the side ties.
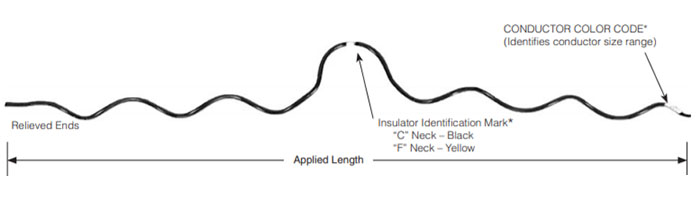
- Load distribution – side ties allow the distribution of electrical load across multiple lines. They also help to prevent overloading on specific sections of the transmission network.
- Vibration and oscillation control – the ties also help to control vibrations and oscillations in conductor. This is important to maintain the structural integrity of the transmission lines.
- Bird collision prevention – bird flight diverters act as side ties to reduce the electromagnetic interference and corona discharge. This is to ensure the efficient and safe operation of the transmission system.
- Connectivity – side ties help to provide a means of connecting two or more transmission lines. This is to enhance the stability and reliability of the power grid.
- Redundancy – they also create redundancy to ensure the electricity transmits through the alternative routes.
- Aeolian vibration reduction – Stockbridge dampers are able to reduce the aeolian vibrations. This helps to enhance the lifespan and reliability of the transmission lines.
- Grounding – downleads provide a safe path for fault currents to dissipate into the ground. It also protects the transmission system from damage.
Selection and installation of side tie
The selection process of the side ties depends on various factors related to the specific requirements of the system. These factors include voltage levels, environmental conditions, type of conductor, transmission line configurations and bird presence among others. The installation process varies depending on the type of side tie used. The following is a general installation process for various side ties.

- Preparation – select the side ties that best suits your application needs. Wear suitable personal protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Conductor preparation – clean the conductor and insulator’s surface to remove any dirt or grease.
- Side tie threading – this may include different installation processes for the different types of side ties used.
- Thread the loop of the double side tie through the groove in the insulator.
- Pass the loop of the side tie through the groove in the insulator and wrap around the conductor
- Insert the ball-shaped end of the tie into the corresponding socket on the insulator.
- Position the pre-shaped preformed tie around the conductor and insulator.
- Position the padded side of the tie against the conductor.
- Side tie tightening – use a special tool such as the twisting pliers or a side tie tool to tighten the wire around the conductor. Tighten and twist according to the various types of side ties used and ensure there is no overtightening.
- Installation inspection – conduct visual inspections of the side tie to ensure they are properly seated in the groove of the insulator. Ensure the side tie is tight enough to prevent the conductor from moving.
- Documentation – keep proper records of the installation. This is including the dates, types and locations of the installation.
Maintenance and inspection of side tie
Proper maintenance and inspection of side ties help to ensure the continued reliability and performance of power systems. The specific maintenance procedures vary depending on the type of side tie used. Additionally, it helps to identify and address potential issues that may cause failures and accidents. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection of side ties in South America.
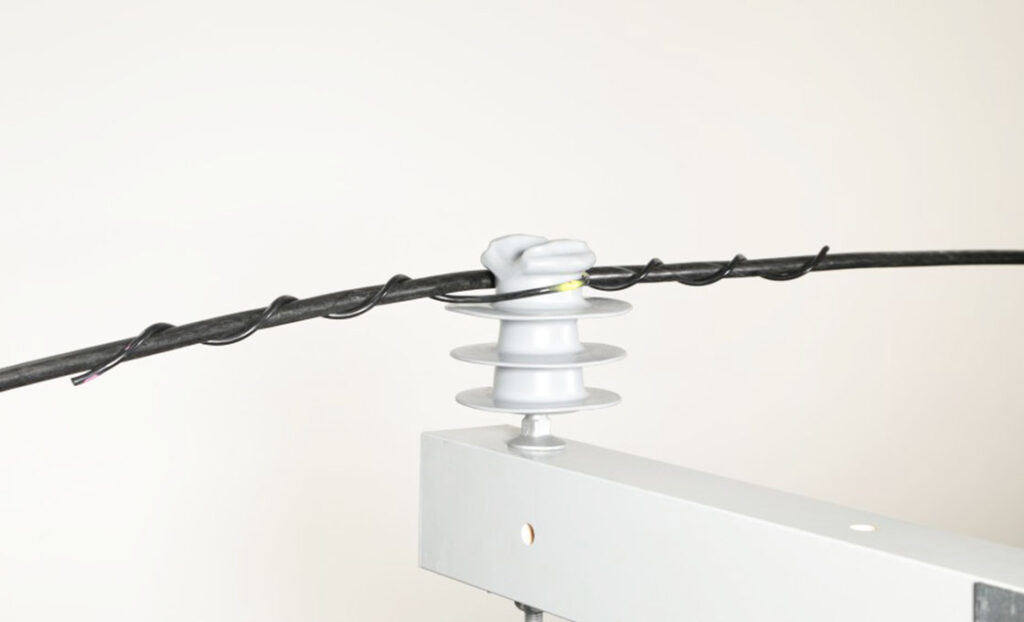

- Perform regular inspections of the side ties for any signs of damage, corrosion or wear. Check the wire for breakage, cracks or tightness.
- Perform ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects in the side ties and insulators.
- Periodically check and adjust the tension of the side ties to ensure their effectiveness in reducing vibrations.
- Clean the side ties to remove debris to ensure they are free from contaminants that may influence their performance.
- Apply protective coatings or use corrosion resistant materials to ensure they are free from corrosion.
- Apply lubrication to side ties that can reduce friction and wear to extend their lifespan. This is relevant in areas with high temperatures and humidity.
- Re-tighten the loose side ties to ensure they maintain proper tension and prevent conductor movement.
- Replace any damaged or worn-out side ties to avoid potential failures and safety hazards. This is especially in areas with extreme weather events like storms and hurricanes.
- Keep detailed records of the maintenance and inspection activities. This includes the dates, repairs and adjustments made to the side ties.
Comparative analysis of side ties in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis for side ties includes assessing and evaluating various factors. Some of these factors include types, designs, sizes, brands and availability. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with industry professionals for guidance in the best side ties for your specific application. The fooling are the factors to include in a comparative analysis in South America.

- Environmental conditions – consider the diverse climates and topographies across South America.
- Transmission line configurations – evaluate the variability in the transmission line configurations.
- Bird collision risk – implement effective bird flight diverters as side ties may be more critical in regions with biodiversity hotspots.
- Budget – assess the economic considerations and budget constraints in different countries. The availability of financial resources may influence the selection and implementation of side ties.
- Technological advancements – investigate the adoption rates of new and advanced side tie technologies in the region.
- Expansion plans – consider the future plans for expanding the power transmission infrastructure in each country.
- Seismic activity – assess the seismic activity in certain regions and in areas along the tectonic plate boundaries.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various certifications and standards that govern the use of side ties in South America. Many other South American countries adopt the various international standards for side ties. Also, it is important to adhere to the specific standards and regulations of the country you intend to install side ties. The following are the key certifications and standards in South America.
- IEC standards – this provides international standards for electrical, electronic and related technologies for side ties.
- ANSI standards – this provides standards for design, testing and performance of various electrical equipment.
- IEEE standards – this develops standards for various aspects of the electrical power industry. It also provides guidelines for the design, testing and application of side ties.
- ISO certifications – this develops international standards for various industries and standards related to materials and coatings for side ties.
- National standards – each south American country may have its own national standards and certifications for power transmission equipment.
- IEC 61400-24 – this standard is specifically to addresses the reduction of mechanical loads through aerodynamic devices.
Regional market for side ties in South America
There are various factors that influence the regional market and demand for side ties in South America. These factors may include brands, manufacturer reputation, supplier availability for spare parts. Additionally, it is crucial to observe the market trends and market dynamics that may influence the regional market. The following are the factors that shape the market in South America.
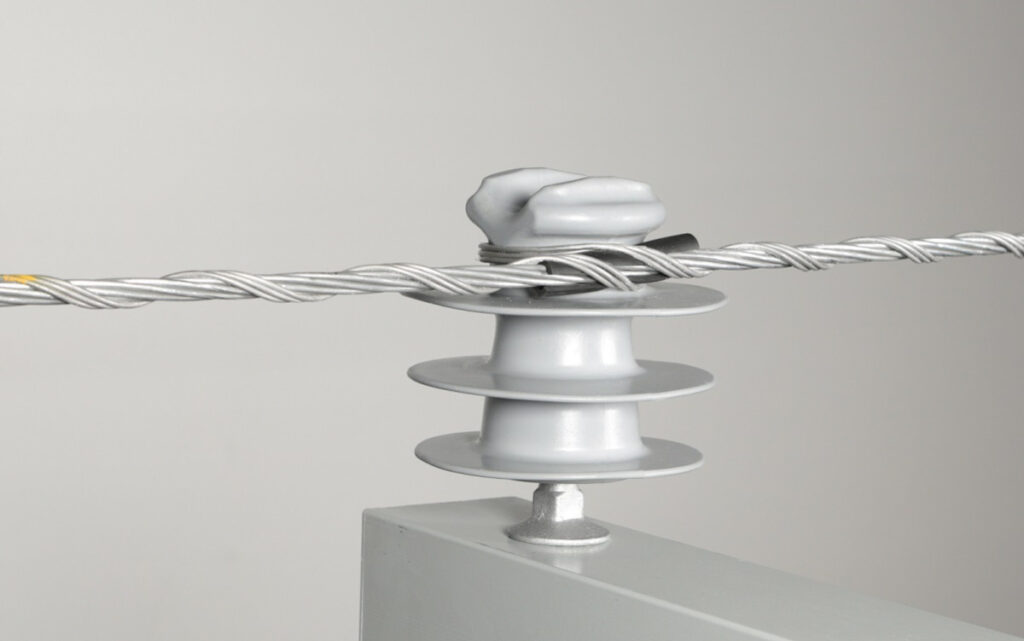

- Technological advancements – advancements in side ties technologies provide better performance, durability and efficiency.
- Market competition – the presence of local and international manufacturers and suppliers in the market can affect competition and pricing.
- Economic factors – economic stability and investment in the power sector influence the market for transmission equipment.
- Environmental conditions – South American region has various weather conditions that may influence the demand for specific types of side ties.
- Renewable energy integration – the integration of renewable energy sources involves the installation of new transmission lines. This includes the use of side ties to ensure the stability and reliability.
Frequently asked questions
The most common types of side ties used in South America include double side ties, ball eye side ties, preformed side ties and padded side ties.
The inspection and maintenance frequency for side ties depends on factors like environmental conditions, line voltage and accessibility.
Common problems include loosening, corrosion and damage.