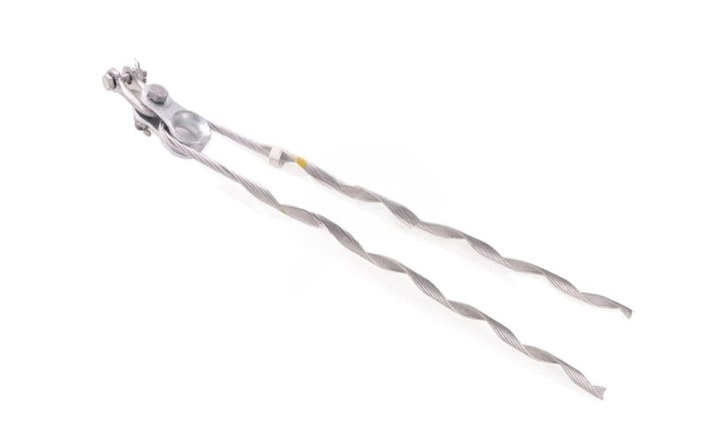
A slack span dead end is a transmission line segment designed to have lower stress than the main spans. It has a special function in the structural and operational integrity of the system. The slack span dead end helps to regulate the system’s mechanical and environmental stressors. They also provide decreased tension, which promotes flexibility and movement. It also functions as a buffer, absorbing loads and vibrations to cut excessive stress on the major components. The slack span dead ends are compatible with a variety of components. This is including insulators, clamps, connectors, and dead ends. Slack span dead ends serve at terminal points, directional changes, and crossing applications.
Choosing the right slack span dead end
There are many slack span dead ends on the market that fulfill various functions. When selecting dead ends, many factors need consideration. These elements ensure that the transmission line systems work optimally, safely, and reliably. The following are common aspects to consider while choosing slack span dead ends.

- Environmental conditions – consider the impact of temperature fluctuations, wind speeds and ice accumulation. The selected dead end should accommodate ground movement and reduce stress.
- Geographical factors – check the terrain of the installation area to determine the necessary adjustments for the dead end.
- Mechanical load and tension needs – check the mechanical load that the slack span dead end must support. This includes the weight of the conductors, insulators and any extra hardware. Determine the suitable tension level to ensure the slack span can handle the forces.
- Conductor and hardware specifications – select the suitable conductor based on their electrical and mechanical properties. Select insulators and hardware that can withstand the lower tension of the slack span.
- Electrical load and voltage – ensure the slack span dead end can handle the specific voltage level of the transmission line. Assess the current carrying capacity of the conductors to avoid overheating.
- Structural support and stability – identify suitable anchor points that can hold the slack span dead end. Ensure the design of the towers can support the slack span dead end.
- Future expansion and scalability – the design of the slack span dead end should allow for upgrades or changes.
- Costs – consider the cost of materials for slack span dead end including conductors, insulators and hardware. Check the long term costs associated with installation and maintenance.
Installation process for slack span dead end
Installing slack span dead ends necessitates detailed planning and execution to assure the system’s safety and reliability. Also, it is advisable to follow the guidelines provided by the manufacturer. The following is a step-by-step installation tutorial.

- Planning and preparation – conduct a thorough site survey to understand the terrain and environmental conditions. Develop a safety plan including hazard assessments and emergency procedures.
- Materials and tools preparation – gather all the necessary materials used with the dead end. These include conductors, insulators and fittings. Inspect all materials to ensure they are in good condition.
- Site preparation – clear the installation site of any vegetation that could interfere with the installation process. Install any temporary supports needed to secure conductors during installation.
- Anchor and support installation – identify and prepare anchor points for the slack span dead end. Install the anchors and ensure they are well aligned and capable of handling the mechanical loads.
- Conductor preparation and installation – unroll and inspect the conductors for any damage and position them in place. Apply tension to the conductors to remove any slack suing tension meters to achieve the specified tension level.
- Install insulators and hardware – attach insulators to the conductors and support structures. Attach dead end fittings such as clamps or connectors
- Final tensioning and adjustment – apply the final tension to the conductors and ensure they meet the specified tension levels. Make adjustments to the conductors and fittings to ensure proper sag and alignment.
- Inspection and testing – conduct a thorough visual inspection of the installation. Perform electrical tests to ensure proper conductivity and insulation.
- Documentation – keep a record of the installation process. This is including any adjustments, procedures followed and recommendations for maintenance.
Maintenance and inspection for the dead ends
Regular maintenance and inspections of the slack span dead end maintain its dependability and safety. It also aids in the early detection and resolution of issues, hence preventing failures. Additionally, it contributes to the reliability of the power transmission network. The following is a simple maintenance and inspection guidance for slack span dead ends.
- Remove dirt, debris and bird droppings from conductors and insulators. This is to prevent electrical leakage and corrosion. Apply lubricants to moving parts and hardware to ensure smooth operation.
- Use tension meters to check the tension in the conductors and adjust as necessary. This is to maintain specified tension levels. Ensure the slack span dead ends maintain the correct sag to prevent excess stress.
- Perform visual inspection checking for signs of wear, corrosion or damage. Inspect for cracks, chips or contamination that could affect performance.
- Replace any damaged insulators to maintain electrical integrity. Upgrade hardware components such as clamps or connectors.
- Inspect anchor points for signs of movement, corrosion or wear. Repair anchor points if they show signs of instability.
- Use thermal imaging to detect hot spots showing issues with electrical conductivity or insulation. Scan the slack span dead end components with a thermal camera to identify any unusual heat patterns.
- Measure the insulation resistance to ensure there are no leaks in the electrical insulation. Check the electrical continuity of the conductors and connections.
- Check for signs of corrosion or rust on metal components such as hardware, conductors and support structures. Apply corrosion resistant coatings to replace affected parts to prevent degradation.
- Keep detailed records of all inspections including findings, maintenance actions taken and any issues detected.
Troubleshooting steps for dead ends
Troubleshooting a slack span dead end entails recognizing, diagnosing and resolving issues that could influence its performance. It ensures correct handling of the problems and decreases downtime and prevent potential failures. The following is a troubleshooting process for the slack span dead ends.

- Initial assessment – conduct a visual inspection to check for sagging, fraying or breaks in the conductors. Check for chips, cracks or contamination.
- Identification of issues – regular inspections can identify early sings of problems. This is including unusual sagging, corrosion or damage to components. Use real-time monitoring systems to detect anomalies in tension, temperature or electrical conductivity.
- Diagnosis and analysis – categorize the issues by symptoms such as mechanical, electrical or environmental problems. Determine the potential causes of the issues . This could include excess tension, sagging, corrosion, or conductor damage.
- Root cause analysis – isolate the specific component causing the issue. Consider environmental and operational factors that might contribute to the problem.
- Corrective actions – based on the root cause analysis, develop suitable corrective actions. Adjust tension in the conductors to the specified levels. Carry out repairs as needed to ensure all work meets safety and operational standards.
- Preventive measures – check existing maintenance practices and update them based on the troubleshooting findings to prevent future issues. Provide training for maintenance personnel on identifying and addressing specific issues.
- Verification – conduct detailed inspections to verify that the repairs have resolved the issue. Perform electrical and mechanical tests to ensure the slack span dead ends operates correctly.
- Documentation – prepare a comprehensive report documenting the troubleshooting process. Describe the initial symptoms, analysis, repairs, and provide test results.
Community forums and discussions for Slack span dead ends.
Several community forums and platforms host conversations on slack span dead ends. Participating in such forums can help you network, share your knowledge, and gain new insights. The following are the most popular community forums and discussion settings for slack span dead ends.

- T&D world community – this is a platform that provides news, articles and forums related to transmission and distribution systems.
- Eng-Tips forums – this is an online community for engineers across various disciplines including electrical and power engineering. It provides forums where professionals discuss technical issues and share solutions.
- Reddit – Reddit hosts subreddits where professionals and enthusiasts discuss electrical engineering topics.
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library and communities – these offer a digital library with extensive research papers, articles and conference proceedings on electrical engineering.
- LinkedIn groups – these groups provide a platform where professionals discuss industry trends, share insights and seek advice on topics related to transmission systems.
- GlobalSpec – this provides forums and resources for professionals in various engineering fields. The electrical engineering community provides discussions on topics like transmission lines and slack span dead ends.
Frequently asked questions
Key components include conductors, insulators, dead end clamps, tensioning and anchor points. Each of these components help in maintaining the integrity and stability of the transmission line.
Documentation entails keeping thorough records of inspections, maintenance activities, repairs, and component specifications. It includes checklists, photographs, test results, and reports that detail the situation and actions performed.
Environmental conditions such as wind, ice, temperature variations, and corrosive atmospheres can all have an affect on slack span dead ends. Regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to mitigate the impacts.