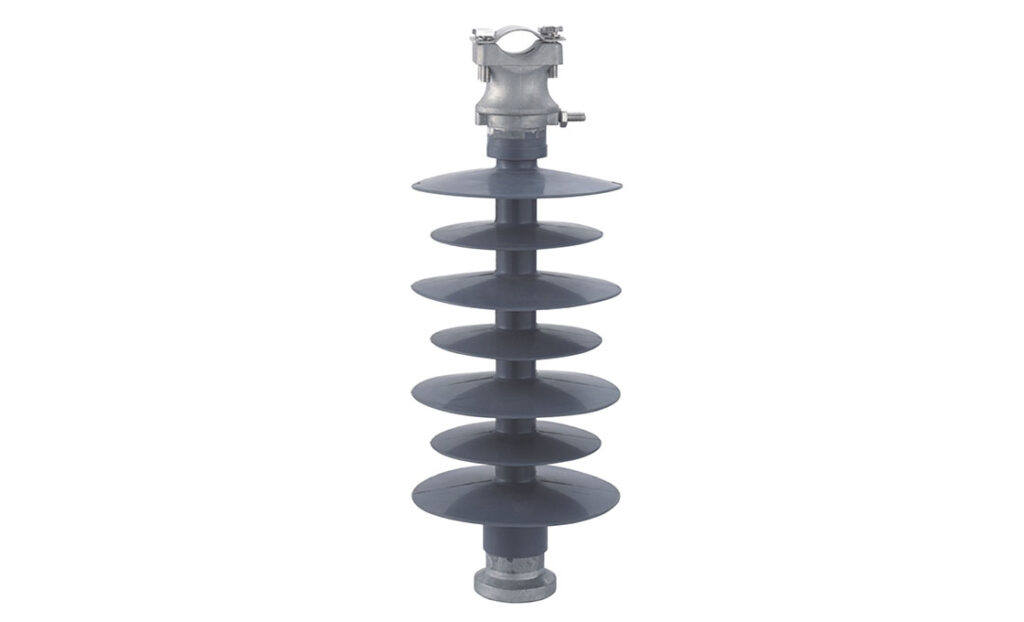

A post insulator is a component used to support and insulate conductors from the supporting structures. The main function is to prevent the flow of electrical current along the supporting structure. It also helps to ensure the safe and efficient transmission of electricity across regions. It is also known as a post-type insulator. A post insulator has distinctive design with a cylindrical shape. It mounts vertically on the supporting structure to provide electrical insulation. The insulator ensures the stability and durability through withstanding mechanical loads and stresses. Post insulators safeguard power infrastructure ensuring reliable electricity transmission across diverse terrains in South America. Types includes pin type post insulator, guy strain insulator, station post insulator and cap and pin insulator. They find use in applications such as distribution lines, transmission lines, guyed structures and industrial applications.
Key features of post insulator
Post insulators have various features that help to ensure the safety and reliability of the structures. They also help to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support. The following are the key features of post insulators.
- Design – they have a distinguishing design with a cylindrical shape. This is to provide sufficient creepage distance. It also helps to maintain electrical isolation between the conductor and supporting structure.
- Voltage rating – they are available in various voltage ratings to accommodate different applications and voltage levels.
- Leakage distance – the design of the post insulators includes a specific leakage distance. This is crucial for preventing flashovers. This is the distance along the insulator’s surface that electricity must travel to reach the supporting structure.
- Thermal stability – post insulators should be able to withstand temperature variations. They do this without significant changes in their electrical properties.
- Ease of installation – the insulators design allows for efficient deployment in power systems. This includes features such as standardized mounting arrangements.
- Material – the post insulators are from materials such as porcelain, glass or composite materials. They help to determine the electrical and mechanical properties.
- Mounting configuration – they mount vertically on the top of poles, towers or other support structures. They secure in place using a variety of mounting arrangements such as caps, pins or flanges.
- Mechanical strength – they are also designed to withstand mechanical loads and stresses. This is including wind, ice and the weight of conductors.
Selection and installation of post insulator
Proper selection of post insulators involves considering several factors to ensure their suitability for specific applications. The factors include voltage rating, environmental conditions, mechanical strength, leakage distance, material, corrosion resistance and ease of installation. The installation is a critical process that requires careful attention to detail. The following is a general installation process of the post insulator.

- Preparation – ensure all the necessary safety equipment and personal protective gear are available for the installation crew. Inspect the insulators for any visible damage before installation. The insulators should match the specified voltage rating.
- Safety procedures – ensure you follow all the safety protocols established by relevant industry standards and local regulations.
- Mounting arrangement – confirm the correct mounting arrangement for the specific type of post insulator to install. Ensure it is compatible with the supporting structure and the mounting hardware.
- Lifting and handling – use suitable lifting equipment to handle and position has the post insulator safely.
- Alignment – align the insulator with the mounting structure. Ensure the insulator is level and perpendicular to the conductor.
- Installation on the structure – attach the post insulator to the supporting structure. This is using the designated mounting hardware.
- Conductor attachment – ensure the conductor is correctly attached according to the insulators design.
- Grounding – install the grounding following manufacturers guidelines for proper grounding procedures.
- Final inspection – conduct final visual inspection of the installed post insulator. This is to verify its alignment, attachment and overall condition.
- Documentation -maintain detailed records of the installation. This is including insulator specifications, installation date and any observations during the process.
Maintenance and inspection of post insulator
Proper maintenance and inspection of post insulators in overhead and distribution systems. This is to ensure their ongoing reliability and performance of the post insulator. Additionally, regular inspections help identify potential issues early allow for timely intervention. It also allows for timely intervention and preventing unexpected failures. The following is a basic maintenance and inspection guide for post insulator in South America.

- Perform regular visual inspections of post insulators to identify any visible signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, chips or other surface irregularities.
- Evaluate the extent of contamination in the insulator surfaces in areas with high pollution.
- Verify that the leakage distance along the insulator surfaces is free from any foreign material. This is to ensure the specified creepage distance is properly maintained.
- Inspect the mechanical components of the post insulator. This is including mounting hardware and fittings for signs of corrosion or wear.
- Check the integrity of the grounding system to ensure the grounding connection are secure and conductive. This is to provide a reliable path for fault current.
- Periodically use thermal imaging to identify any abnormal temperature variations on the insulator surfaces.
- Apply corrosion resistant coatings to protect against environmental corrosion.
- Maintain detailed records of inspection dates, observations and any maintenance activities.
Comparative analysis of post insulator in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis of post insulators involves assessing various factors. These factors influence their performance, reliability and suitability for different applications. It also considers a combination of technical specifications, environmental factors, industry practices and market dynamics. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with industry standards. This is to ensure proper selection of the post insulator. The following are the factors to include in a comparative analysis in South America.

- Material selection – compare the performance of different materials used in post insulators. This includes porcelain, glass and composite materials. Consider factors such as mechanical strength, resistance to pollution and longevity.
- Mechanical strength – compare the mechanical strength of post insulators. Consider factors like wind and ice loads.
- Performance in pollution – check the performance of post insulators in areas with different pollution levels.
- Manufacturers and suppliers – identify and compare manufacturers and suppliers of post insulators in South America. Assess their reputation, product quality and market presence.
- Environmental condition – check the impact of diverse environmental condition in south America. This includes pollution levels, humidity and temperature variations.
- Voltage ratings – analyse the voltage ratings of post insulators and their durability. Check their and their suitability for the varying voltage levels.
- Corrosion resistance – assess the corrosion resistance of metal components in post insulators. This is especially in areas where corrosion risks may be higher.
- Installation practices – compare installation practices and standards across different regions. Conduct installation practices contributing to the overall reliability of post insulators.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various standards and certifications regulating the use of post insulators in South America. The standards provide guidelines for design, testing, performance and other characteristics of post insulators. Additionally, adhering to these standards helps to ensure the reliability, safety and compatibility of post insulators. The following are the common standards and certifications in South America.

- International standards – this standard provides specifications for porcelain insulators for overhead power lines. They also specify the requirements and tests for insulating materials of electric and optic cables.
- American national standards – this is a series of standards that cover various aspects of porcelain and ceramic insulators for overhead power lines.
- European standards – this specifies the requirements for composite station post insulators for indoor and outdoor electrical installations.
- ABNT standards – this issues standard which covers porcelain insulators for overhead power lines.
Regional market for post insulators in South America
There are various factors that influence the regional market for post insulators in south America. This is including the region’s economic growth, infrastructure development and the expansion of the power transmission networks. Additionally, it is advisable to consult industry reports and market analyses specific to the current date. The following are the main factors that influence the regional market in South America.

- Industrial growth – this manufacturing facilities may lead to increased demand for electrical infrastructure.
- Urbanization and electrification – these projects contribute to the expansion and modernization of electrical grids. This is driving the demand for reliable insulators like post insulators.
- Infrastructure development – the increased demand for post insulators tie to infrastructure development. This includes construction of new power transmission and distribution lines.
- Urbanization and electrification – development of projects contribute to the expansion and modernization of electrical grids.
- Government initiatives – the availability of initiatives aim to improve energy infrastructure ensures access to electricity in rural areas.
Frequently asked questions
A post insulator is a crucial component in high-voltage power transmission systems. Its high strength, non-conductive support structure that isolates electrical conductors from the ground and other structures.
Environmental conditions such as pollution, humidity and salt spray impact the performance of the post insulators in transmission lines. It requires maintenance and inspections to ensure the reliability and efficiency of power transmission systems.