
A crossarm brace is a component used on pole line hardware. It helps to provide extra support to electrical crossarm, insulators and other hardware. It plays the important role of stabilizing the crossarms that hold electrical conductors. The crossarm brace helps to enhance the stability of crossarms, prevent sagging and resist wind loads. Crossarm brace is available in different types and designs depending on application. They are from materials such as steel, wood and aluminum alloys. Hot dip galvanized finish adds an extra coat that resist rust and corrosion. The use of high-quality crossarm braces helps to resist wind forces and prevent conductor staffing. Common types include single crossarm braces, double, triangular and adjustable crossarm braces. They find use in applications such as preventing sag, maintaining alignment, enhancing system safety and supporting hardware.
Key features of crossarm braces
It is important to consider the specific features of the crossarm brace. These features help to select the best type of crossarm brace that suits your application. The specific features also help provide reliability and safety of transmission lines. The following are the main features of the crossarm brace.
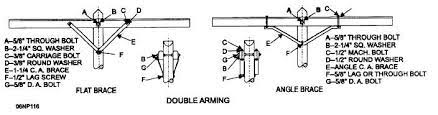
- Design – crossarms consists of diagonal members that connect the crossarm to the pole. This may include a single diagonal member, double diagonal members forming an “X” shape or triangular configurations.
- Size and length – they are available in different lengths and sizes. This helps them to accommodate different configurations.
- Load capacity – crossarm braces are ale to support specific loads. This is including weight of the conductors, insulators and hardware.
- Material – they are from durable and corrosion resistant materials that offer durability. These include steel, galvanized steel or aluminum.
- Adjustability – this allows for precise tensioning and alignment of crossarm.
- Corrosion resistance – the braces may have coatings or materials that resist corrosion. This helps to provide a longer serviceable life.
- Ease of installation – the braces have attachment points that secure it to the crossarm.
- Safety – they also provide safety of overhead electrical systems by preventing conductor sag. It also helps maintain clearance and reduce the risk of electrical faults.
Selection and installation of crossarm braces
Proper selection of the crossarm brace involves considering several factors. These factors include load requirements, environmental factors, right material, adjustability, durability, cost effectiveness and installation. The installation process should ensure structural support and stability to the crossarms. The following is a step-by-step guide to installing crossarm brace.

- Preparation – gather all the required tools and equipment before the installation. These include crossarm brace, fasteners, wrenches, safety equipment, ladders, tape measures, levels and manuals.
- Crossarm inspection – check the crossarm brace to ensure it is in good condition.
- Positioning – determine the proper location of the crossarm brace. This is depending on project specifications, engineering plans and load requirements.
- Brace orientation – orient the brace correctly to provide the intended support and stability. Ensure the attachment points align with the crossarm and utility pole.
- Attachment points – attach one end of the crossarm brace to the crossarm. This is using suitable fasteners like bolts, nuts and washers.
- Utility pole attachment – attach one end of the crossarm brace to the utility pole. This is using the designated attachment points.
- Alignment and leveling – use a level and tape measure to check the alignment and levelness.
- Tightening bolts – tighten all nuts and bolts using wrenches or a torque wrench.
- Inspection – conduct a visual inspection of the installation. This is to ensure proper positioning, attachment and aligned as needed.
- Documentation – keep comprehensive records of the installation. This is including the date, location, torque values and any other information.
Maintenance and inspection of crossarm brace
Periodic maintenance and inspection of crossarm brace ensures safety and reliability. It also helps to identify and address potential issues that could lead to accidents. Additionally, addressing the issues early can help extend the life of the infrastructure. It also helps prevent costly downtime and repairs. The following is a basic guide of maintenance and inspection of crossarm brace.

- Conduct regular inspections to examine the crossarm braces. check for cracks, fractures, rust, corrosion, loose fasteners, deformation and alignment issues.
- Maintain clearance between conductors, insulators and other hardware components.
- Check for safety hazards such as loose hardware, loose conductors or damages insulators.
- Clean to remove dirt, debris or any vegetation accumulated on the crossarm braces.
- Inspect the braces for signs of corrosion and apply corrosion resistant coatings.
- Check the tightness of the bolts and nuts and tighten any loose connection. Loose fasteners can compromise the integrity of the crossarm brace.
- Confirm the proper alignment and level as misalignment can affect the stability.
- Regularly assess the load-bearing capacity of the crossarm braces. Ensure they can handle increased loads.
- Replace any crossarm brace that have corroded, damaged or structurally compromised.
- Maintain detailed records of the inspection findings. This is incuding dates, location and any identified issues.
Comparative analysis for crossarm brace in south America
A comparative analysis involves assessing and evaluating different factors. These are factors that influence the use of crossarm braces. These include material, design, performance and suitability to the regions needs. These factors influence the demand and choice of a particular type of crossarm brace. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with experts for guidance on the selection. The following are the key factors to include in a comparative analysis in South America.
- Material – crossarm braces are from different materials that provide durability and excellent load-bearing capacities. Consider the corrosion resistance of each material. This is judging by the diverse weather conditions in South America. The common materials used for crossarm brace include steel, aluminum and galvanized steel.
- Design – there are different designs of the crossarm brace available in the market. These include single crossarm brace, double crossarm brace and triangular crossarm brace. Consider the load-bearing capacity of each design and the benefits of each. This helps to decide the best type to select for a specific application.
- Corrosion resistance – the availability of corrosion resistant coatings helps to protect against rust and corrosion. This also helps ensure longevity of the braces in humid or coastal regions. They also need regular inspections and maintenance. This helps to monitor the condition of the coatings.
- Customization – there may be custom made crossarm brace according to the manufacturer. This allows for tailored solutions based on specific load, size or configuration needs.
- Environmental conditions – South America has a diverse range of climate conditions. Regions with salt exposure may require use of corrosion resistant materials or coatings.
- Regulatory compliance – there are various standards and regulations in South America. The selected crossarm brace should follow the international and regional standards.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various certifications and standards that govern the use of crossarm braces. However, they may range or vary depending on country within the region. Some of the countries take after the international standards. This is to ensure the safety and reliability of the electrical infrastructure. The following are the certifications and standards in South America.

- IEC standards – this provides guidelines for the design, testing and performance of overhead line fittings.
- ANSI standards – these provide specifications for crossarm braces used in overhead line construction.
- Local and national standards – some of the countries have their own national standards and regulations. These standards relate to electrical infrastructure components like crossarm braces.
- ISO certifications – these offer quality control in regards to materials and coatings. It ensures that the material and manufacturing processes meet international quality standards.
- ASTM standards – these relate to galvanization for corrosion resistant coatings on crossarm brace.
- Quality assurance and certification – manufacturers should provide certification and documentation to confirm that their products meet relevant standards.
Regional market for crossarm brace in South America
There are various factors that influence the regional market for crossarm brace in South America. These factors include energy demand, renewable energy projects and environmental conditions. They influence the regional demand and availability of crossarm braces in the region. These factors are as detailed below.

- Competition – there is more competition from local and international manufacturers in the market.
- Infrastructure resilience – susceptibility to natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes influence the need for crossarm braces.
- Corrosion resistance – crossarm braces are able to withstand the salt exposure of the region.
- Maintenance and retrofitting – crossarm braces are easy to replace which enhances the reliability of the grid.
- Infrastructure development – the braces hep in the construction and upgrading of new infrastructure in the region.
Frequently asked questions
A crossover clamp is a component used to support and stabilize overhead electrical transmission and distribution. It helps maintain the integrity and reliability of the electrical infrastructure in South America.
Crossover are mainly from materials such as steel, aluminum or galvanized steel. The selection depends on factors such as load-bearing requirements, environmental conditions and weight considerations.
Consider design, material, corrosion resistance, load baring capacity, alignment and adjustability. These helps ensure the clamps stability for the region’s conditions.