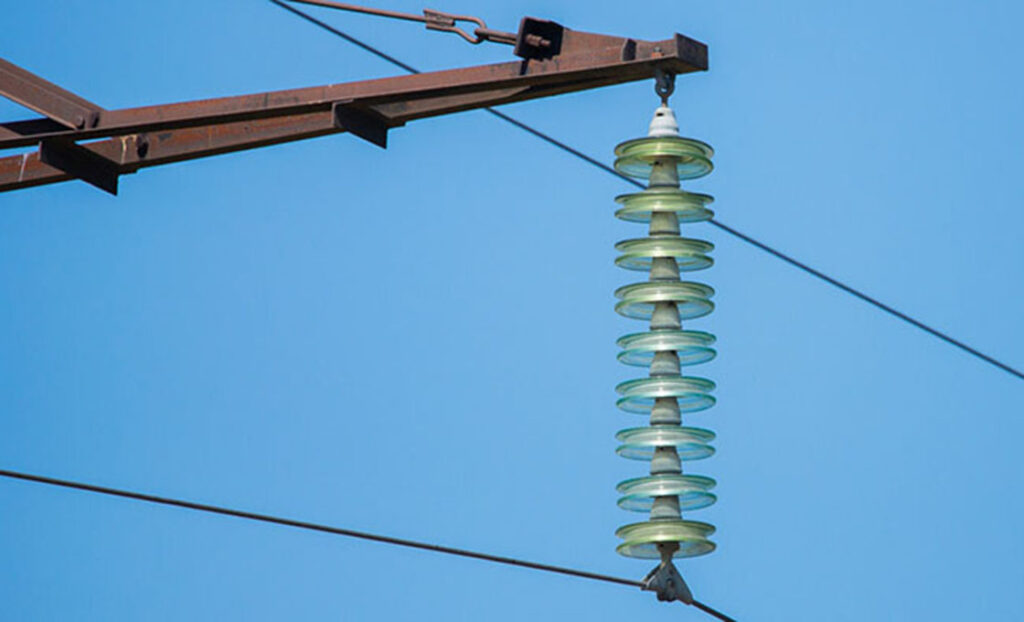

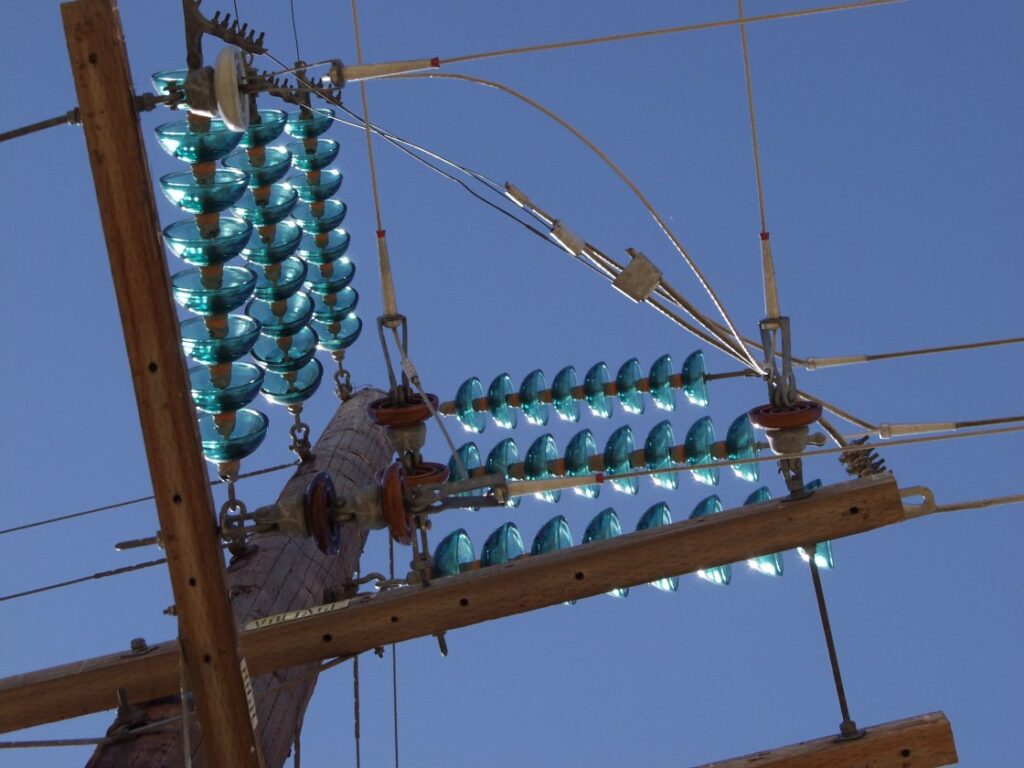
A suspension insulator is one of the electrical insulators used on the transmission and telecommunication lines. Suspension insulators are vital to use to ensure the stability and proper functioning of the overhead cables. They also contribute to the reliable and efficient operation of electrical and telecommunications systems. Suspension insulators are also known as disc insulators or porcelain insulators. They help to suspend and support the overhead cables securely in place. Suspension insulators help to provide mechanical stability. They also hold the cables securely in place while allowing them to maintain the desired tension. It has a metal or composite body with various components like bolts, fasteners and gripping elements. The gripping elements secure the cables by applying pressure or creating a clamping mechanism that prevents them from slipping or sagging.
Components of the suspension insulators
There are different designs of the suspension insulators used in the market for proper energy transmission. The designs also vary depending on the specific application and cable type. They help to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support to overhead conductors. To achieve this, they have different features to support the operability. The components are as discussed below.
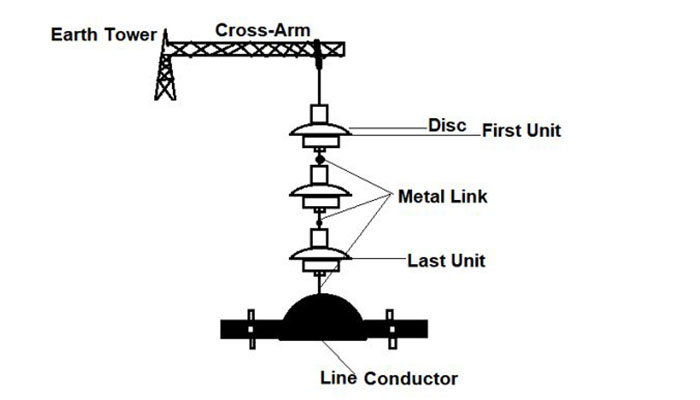
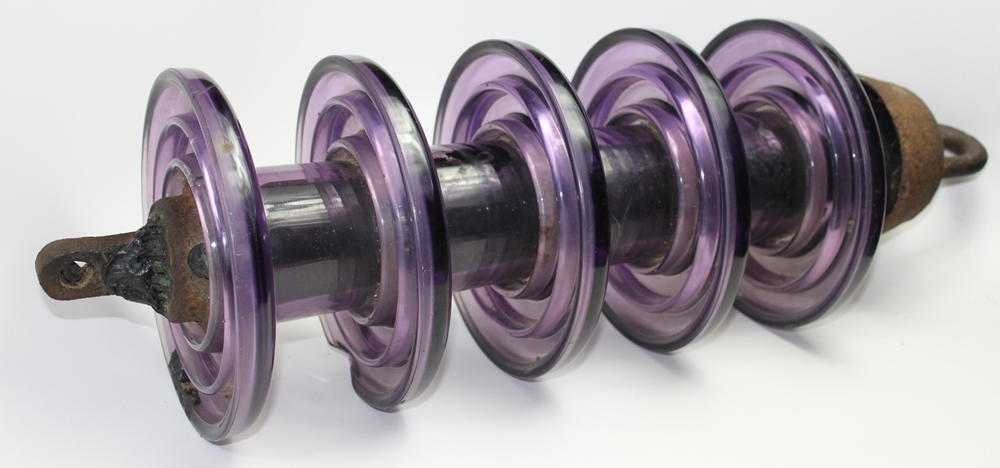
- Insulator disc – these are the main components of the suspension insulator made of porcelain, glass or polymer materials with high dielectric strength. They work in a series and stacked vertically forming a string. The number of strings used depends on the system voltage and the required electrical insulation level.
- Metal fittings – the insulators have metal caps at the end of each string to provide a means to attach the insulator to the supporting structure.
- Cement – cement applies between the discs to ensure a strong bond and preventing moisture from entering. This prevents the insulator discs from moving or separating under various conditions.
- Fastening devices – suspension insulators use the fastening devices like bolts, nuts and washers. They help to secure the discs, fittings and cement together. They ensure a firm and reliable connection between the various parts of the insulator.
- Shed – each disc has a shed surrounding it designed to provide extra leakage path for surface water or contaminants. This helps to improve the performance of the insulator under wet polluted conditions.
- Suspension assembly – these consists of a metal or composite bracket, a hanger and a connecting link. This provides a means to attach the insulator string to the overhead conductor. This allows the insulator to hang in a suspended manner.
Types of the suspension insulator
Suspension insulators are from different material for different specifications in the applications. There are various types of suspension insulators used in transmission and distribution systems. The selection of the insulators depends on factors such as voltage levels, pollution levels, mechanical loads and environmental conditions. The following are the common types of insulators used on the overhead lines.

- Interphase spacer suspension insulator – these insulators work in three-phase transmission lines. They provide the required separation between conductors. They entail multiple insulator strings connected with metal fittings. This helps create a spacing arrangement between the conductors.
- Pin type suspension insulator – this entails a series of porcelain or composite discs stacked vertically then mounted on a pin. The pin is the attached to a cross arm or tower. These types of insulators mainly work in medium voltage distribution systems.
- Pollution-resistant suspension insulator – -pollution-resistant insulators manufactured to withstand heavy contamination or pollution levels. This reduces the damages to the insulating properties of traditional insulators. They feature surface coatings, hydrophobic properties or improved shed designs. This helps to repel contaminants and maintain effective insulation.
- Toughened glass suspension insulator – these suspension insulators are from toughened glass materials instead of porcelain or glass. They offer enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to breakage. This makes them suitable for areas with high mechanical loads.
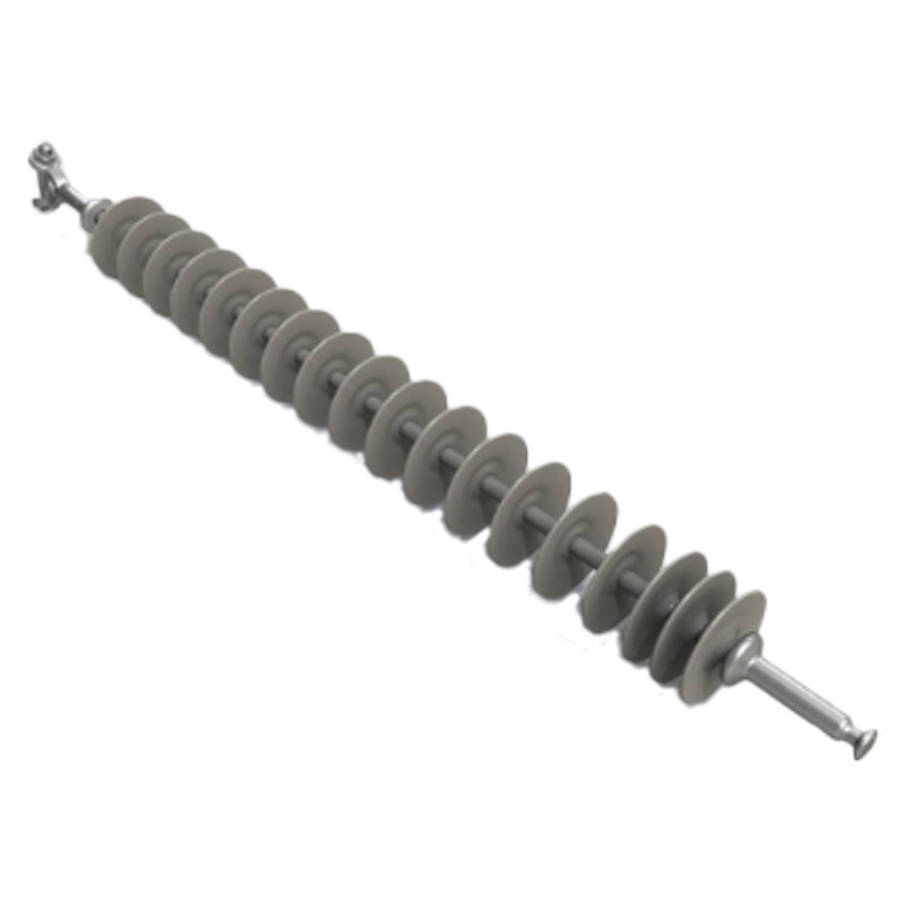
- Long rod suspension insulator – long rod suspension insulators have longer porcelain or composite insulator strings. They have a design that enables them to withstand higher systems. They also provide increased creepage distance and improved electrical performance.
- Composite suspension insulator – composite suspension insulators are from non ceramic materials. These materials offer benefits like light weight, high mechanical strength and resistance to pollution and vandalism. They are mostly used in areas with high pollution levels or corrosive environments.
Applications of the suspension insulator
Suspension insulators are widely used in electrical power systems to support overhead power transmission and distribution lines. They are mainly from porcelain or composite materials. These materials helps them withstand mechanical stresses, electrical voltage and environmental conditions. The following are the main areas of applications for the suspension insulators.

- Railway electrification – suspension insulators in railway systems provide insulation and support to the overhead wires that supply power to electric trains. This ensures safe and efficient transmission of electricity.
- Distribution lines – the insulators also work in medium voltage distribution lines to support and insulate the conductors. They are mostly used in urban and rural areas to deliver electricity from substations to residential, commercial and industrial areas.
- River crossings – suspension insulators work where power lines need support over water bodies and valleys. This ensures the safe and reliable transmission of electricity across the challenging terrains.
- High voltage power transmission lines – these insulators support the high voltage power transmission lines and keep the conductors at a safe distance from the supporting towers and the ground.
- Substations – such insulators support bus bars, transformers and other equipment. They also provide isolation, ensuring the current flows only through the desired paths. This also helps prevent the unwanted leakage.
- Heavy industrial applications – suspension insulators apply in heavy industrial settings such as steel plants, refineries and mining operations. They support the lines in areas where mechanical stresses and environmental conditions are more demanding.
- Extreme weather conditions – suspension insulators can withstand adverse weather conditions like strong winds, ice and heavy snow.
Installation process of suspension insulators
The installation process varies depending on the type of suspension insulator, the power line configuration and local regulations. You should consult experienced professionals whenever in doubt. Some manufacturers also provide installation instructions and guidelines for their suspension insulators. The installation process ensures proper positioning, attachment and electrical insulation. Below is a general step by step process of installing suspension insulators.

- Follow safety precautions and ensure that the work area is safe and clear of any hazards.
- Prepare the tower or the supporting structure by cleaning, checking for damage or corrosion and ensuring it is structurally sound.
- Determine the appropriate positions for the suspension insulators along the power line. The spacing should depends on electrical voltage and mechanical requirements of the line.
- Attach the suspension insulators to the tower or cross arm using suitable hardware and fittings. This involves using metal fittings like bolts, clamps and brackets to secure the insulator.
- Install the conductor onto the groove or shed of the insulators and secured with conductor fittings or clamps.
- Apply pre-tension to the conductors to ensure proper sag and tension levels. This by using appropriate tensioning devices following manufacturers guidelines.
- Conduct inspection and testing after installation to ensure proper installation and functionality.
Selecting the best suspension insulator for your application
Since there are various manufacturers and suppliers in the market, it may be hard deciding who to buy from. The selected suspension clamps should meet the specific requirements of your power system. There are various factors that help select the best as discussed below.

- Determine the voltage rating required for the application to accommodate various voltage levels.
- Consider the mechanical strength of the insulator which should be able to withstand the mechanical stresses from various conditions.
- Evaluate the pollution performance requirements of the installation location. This ensures the insulators have designs and coatings that reduce the accumulation of pollutants and maintain insulation performance.
- Evaluate the environmental conditions of the installation area such as humidity, UV exposure and corrosive atmospheres.
- Ensure that the selected insulators comply with relevant industry standards and regulations.
- Consider the reptation and track record of the manufacturer or supplier. They should have a record for delivering high quality products and after sales services.
- Compare the cost of different suspension insulators while considering their performance and durability.
Frequently asked questions
Suspension insulators are device used to support transmission lines on steel towers and isolate the lines from the tower.
The main functions of the suspension insulator include mechanical support, electrical insulation, prevent currenting leakage and pollution control.
Suspension insulators are cheaper in cost as compared to the other types of insulators used in high voltages.They also have an increased insulation strength.
Suspension insulators have various limitations which include voltage limitations, complex installation, high initial cost, environmental conditions and pollution levels.