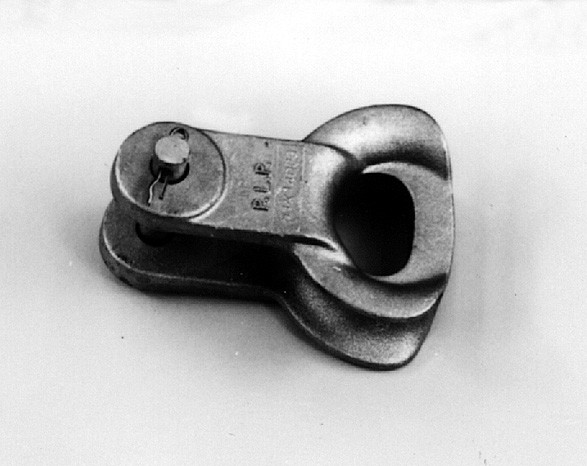

A thimble clevis is a component used in overhead transmission lines to connect insulators to ends of conductors. It provides mechanical support and helps maintain the integrity of power lines. Its designs help to attach to the end of a conductor and hold it securely in place. The design has a thimble-shaped opening or eye that allows the attachment of various hardware components. It is from materials that are durable and corrosion resistant. This ensures the longevity and reliability in South American applications. The thimble clevis also helps to distribute mechanical loads along the conductor. Thimble clevises contribute to the control of tension in the transmission line. This is by securely holding the conductor. Common types include standard thimble clevis, detachable clevis, ball and socket thimble clevis. They find use in applications such as conductor attachment, insulator attachment, tension control and transmission towers.
Key features of thimble clevis
Thimble clevis has various features that help them provide a secure and stable connection. They ensure stability between conductors and various hardware. They also contribute to their functionality and effectiveness in power transmission systems. The following are the key features of thimble clevis.
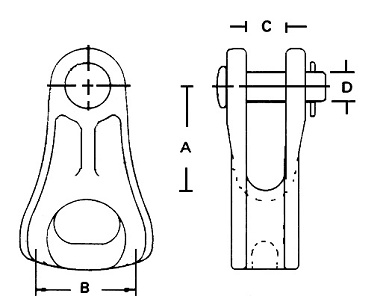
- Thimble-shaped opening – this opening serve as the attachment point for the conductor. This allows for a secure connection to other line hardware.
- Versatility – their designs allow them to accommodate a range of conductor sizes and applications. This also allows for their use in various configurations and transmission line setups.
- Secure attachment – they also provide a secure attachment point for conductors to ensure they remain firmly in place.
- Compatibility – this allows for a secure attachment of insulating components to conductors. This helps in electrical insulation and prevents flashovers.
- Resistance to twisting – they resists twisting to enhance stability and prevent unwanted movement.
- Durability – they are also built to withstand harsh environmental conditions. This is including exposure to UV radiation and varying temperatures.
- Material – the thimbles are from durable and corrosion resistant materials. The materials help ensure reliability in outdoor conditions. These materials include hot dip galvanized steel or aluminum.
- Adjustability – they are also adjustable to accommodate different conductor sizes.
- Ease of installation – they feature standard bolted connections or other fastening mechanisms. This facilitates efficient installation during construction and maintenance.
Selection and installation of thimble clevis
Proper selection of thimble clevis is vital in designing and maintaining transmission lines. The proper selection ensures the integrity, reliability and safety of power transmission systems. It includes considering factors such as conductor size, material, load rating, corrosion resistance, ease of installation and insulator attachment. The installation process should ensure the stability, reliability and safety of the power transmission system. The following is a step-by-step guide for thimble clevis installation.
- Thimbles clevis inspection – inspect each thimble to ensure it is free from damage or defects. Check for proper sizing and compatibility with the conductor.
- Conductor end preparation – ensure the end of the conductor is clean and free from burrs, dirt or contaminants. This is to ensure a secure and stable connection.
- Hardware selection – select the suitable bolts, nuts and cotter pins for the thimble clevis installation.
- Thimble clevis securing – insert the bolts through the holes in the thimble clevis and the conductor. Tighten the nuts securely using wrenches.
- Torque bolts to specifications – tighten the bolts following the manufacturers torque specifications. Over-tightening and under-tightening can affect the stability of the thimble clevis.
- Cotter pin installation – insert the cotter pins through the holes in the bolts and bend them to secure the nuts. This is to prevent the nuts from loosening due to vibrations and other factors.
- Extra hardware installation – follow the installation procedures for other components. These components include insulators and vibration dampers.
- Inspection – double check the installation to ensure the thimble clevis is securely attached. It also ensures the hardware properly fastened.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the thimble clevis installation. This is including the date, location and any specific considerations.
Maintenance and inspection of thimble clevis
Regular maintenance and inspection of thimble clevises ensures the continued reliability and safety of transmission lines. It also helps to identify and address potential issues that could lead to failures and accidents. The frequency of this activity depends on the environmental conditions of the installation areas. Also, it is advisable to conduct professional inspections once in a while. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection of thimble clevises.
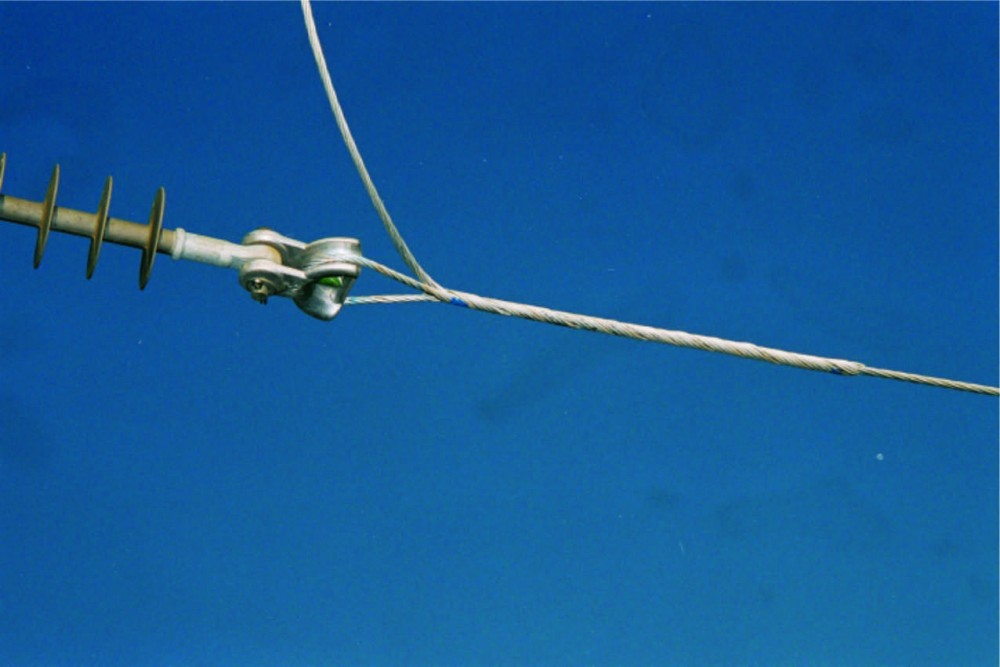

- Establish a routine maintenance schedule for thimble clevises depending on the environmental conditions.
- Conduct visual inspections of each thimble clevis looking for signs of wear, corrosion or damage.
- Ensure the thimble clevises are free from dirt, debris or contaminants and clean them to maintain performance.
- Check the torque of bolts to ensure they are tight to the manufacturers specifications to enhance the stability of the clevis.
- Inspect the cotter pins for signs of damage and replace any cotter pins if necessary.
- Confirm the alignment of the thimble clevis with the conductor and attached hardware.
- Inspect the insulator attachment points to ensure the insulators are securely connected and free from damage.
- Inspect the thimble clevis looking for cracks or signs of metal fatigue.
- Examine the bolts and nuts for wear, corrosion or damage and ensure the threads are in good condition.
- Inspect the cotter pins for proper installation and signs of wear or corrosion. Replace any cotter pins with signs of deterioration.
- Assess the thimble clevises for exposure to harsh environmental conditions. This is including UV radiation, moisture and salt.
- Conduct functional tests to simulate the conditions where the thimble clevises operate. It also involves applying controlled loads to verify their performance under stress.
- Maintain detailed records of each inspection and note any observations, repairs or replacements.
Comparative analysis of thimble clevis in South America
This process involves assessing various types or brands of thimble clevises depending on specific criteria. Thie is to determine their suitability for different applications. It also involves considering other factors such as designs, types and load specifications of the thimble clevis. The following are the factors to include in the comparative analysis for thimble clevises.

- Design – assess the design of the thimble-shaped opening and its compatibility with various conductor sizes. Also, compare the designs for versatility in accommodating different conductor sizes.
- Insulator attachment – test the compatibility of the thimble clevises with the insulators.
- Ease of installation – check the ease of installation for different thimble clevis types. Consider quick-release designs for efficiency.
- Cost – compare the costs of different thimble clevis types considering factors such as material quality, load capacity and extra features.
- Innovation and technology – explore innovation in various features of the thimble clevis. This is to ensure their performance, durability and installation efficiency.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various certifications and standards that govern the use of thimble clevises in South America. The standards also govern the use electrical equipment including components used in power systems. They help to ensure the compliance and quality, performance and reliability of the thimble clevis. Additionally, it is advisable to consult local regulations to help ensure compliance to local and international standards. The following are the common certifications and standards in South America.

- IEC standards – these are standards that ensure the quality and performance of electrical equipment including thimble clevis.
- National standards – each south American country have their own national standards for electrical equipment.
- Industry standards – this includes ANSI standards that provide standards for various electrical components.
- ISO certifications – this attest to the quality management systems and processes for thimble clevises are in place.
- Local regulations – it is important to consult with local electrical regulations and safety standards.
Regional market for thimble clevises in South America.
Various factors and conditions influence the demand, availability and supply of thimble clevises in South America. These factors include market dynamics, trends and economic conditions. Additionally, it is advisable to consult industry reports, market research studies and experts in the sector. The following are the factors that shape the regional market for thimble clevis in South America.

- Regulatory environment – changes in standards, regulations and compliance requirements impact the demand for thimble clevis.
- Technological advancements – there are new advanced technologies that impact the performance of thimble clevises. Their adoption could drive the market growth in this sector.
- Economic factors – growth of the economy impacts the pace and scale of projects requiring corona rings.
- Market competition – availability of local and international manufacturers and suppliers also impact the market for thimble clevises.
- Infrastructure development – ongoing and planned developments in power infrastructure increase the demand for thimble clevises.
Frequently asked questions
A thimble clevis is a component used to connect conductors to hardware like insulators or vibration dampers. It provides a secure attachment point and helps maintain the structural integrity of the power line.
Thimble clevises should comply with relevant international and national standards such as IEC standards. They should also present certifications from recognized bodies to ensure adherence to quality and safety standards.