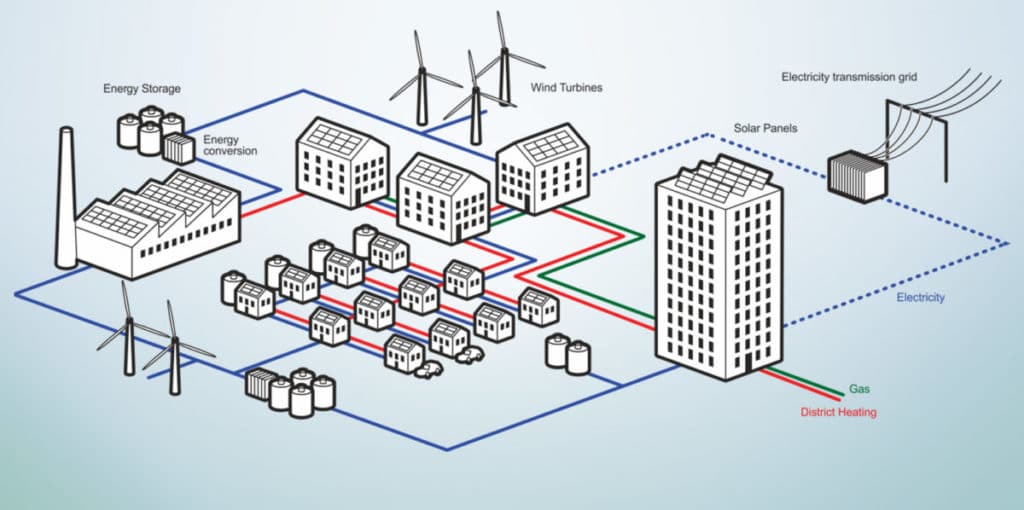
· Decentralized energy systems ensure that energy produced is also consumed within the region.
Using such systems ensure proper energy control and management from producers to consumers.
· The systems ensure there is integration of artificial intelligence and Internet of Things.
Energy is a vital factor in the modern day to day life where most of the industries need fuel to run. Oftentimes, the energy demand is higher than the energy production. This may be from factors such as power outages or grid failures. To ensure the consistent flow and supply of energy, we need to adapt to energy systems. This is because our energy consumption is growing and the use of renewables isn’t enough. Decentralized energy systems are very popular as it generates off the main grid. The system includes micro-renewables, heating and cooling systems. A decentralized energy system contains energy from combined heat and power and biomass. Decentralized energy systems are more resilient, reliable and efficient.
Utility fasteners help secure other gadgets used on the transmission lines. They ensure the there are no loose connections on the lines to reduce electric shocks. Utility fasteners serve as non-permanent joints that reduce abrasion and other damages. Abrasion is from vibrations from strong winds. they include devices such as bolts, nuts, washers and screws. Decentralized energy systems allow use of renewable energy to reduce fossil fuel use.
Types of energy storage
Energy for the decentralized energy systems may be from various energy sources. These sources include waste, biomass, geothermal, solar power and combined heat and power. Energy sources may be renewable or non-renewable and supply the energy to the main grid. Decentralized energy systems aim to reduce the effects of climate change from gas emissions. Utility fasteners are from materials that resist rust and corrosion. This property gives them a longer serviceable life. The various types or examples of decentralized energy systems are as discussed below:
· Combines heat and power technology.
This is a power plant that include renewables and thermal power technology. It generates electricity and heat combined with very high efficiency rates. Heat distributes to residential developments, desalination plants or manufacturers. These systems operate on a municipal level.
· District heating and cooling
This system uses the infrastructure interconnecting buildings within a city. Such facilities help to supply heating and cooling with water as the transport medium. This heat and cooling meets demand for space heating and cooling and refrigeration. It is also water for domestic and industrial use. They aim at enhancing a comfortable working and living space for everyone.
· Biomass energy systems
Biomass is energy generated from living or non-living things organisms such as plants. The energy from these materials burn to create heat which converts to electricity.
· Geothermal heating and cooling
This is where the earth’s heat generates electricity. Ground source heat pumps and direct use geothermal are some examples of geothermal harnessing. It is also in deep and enhanced geothermal systems. This energy is applicable in households and the excess supplies to the main grid.

Advantages of energy systems
Decentralized energy systems reduce the bridge between energy producers and consumers. This is by the use of microgrids to allow for more use of the renewable energy. Energy systems help to meet the climate goals which aims to reduce the carbon emissions. Utility fasteners work with other devices to ensure the secure connections. The various advantages of the decentralized energy systems are as discussed below.
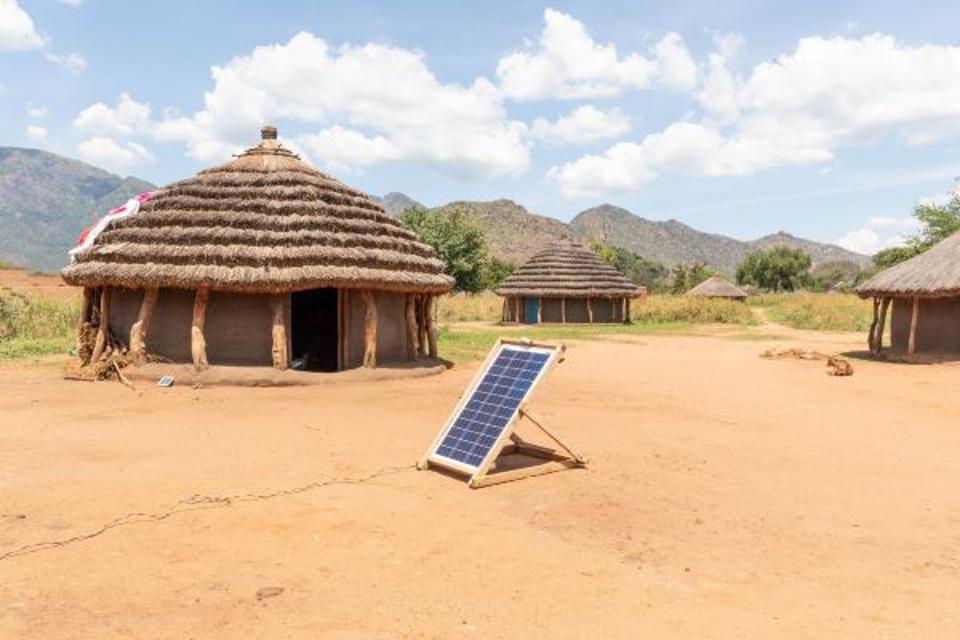
· Rural electrification
Power plants are set up in the rural areas to provide efficient power supply. These systems also provide cost effective power distribution to the rural areas.
· Reduced technical losses
This is from the lengthy distribution lines used to connect the supply and demand. Decentralized energy systems ensure the energy suppliers enjoy the reduced lines.
· Lower capital costs
These power plants costs less to set up, control and manage compared to larger power plants.
· Planning flexibilities
The grid operators and energy suppliers are able to make better decisions. these decisions are not conformed to the centralized energy systems.
· Better technical relationships
This is the relationships between the energy retailers and energy consumers. Such relations are from the adoption of the smart grids. It is also supported by the Internet of Things into electrical systems.