
A washer is a thin, flat and circular-shaped disk with a hole in the center. It works in various applications to distribute the load of a threaded fastener. Washers prevent damage to the surface of the materials fastened. This improves stability and reliability of the joint. A washer helps in load distribution and electrically isolate the fastener. The demand for washers in southeast Asian countries growing int he coming years. This is due to the increasing construction and manufacturing activities. Washers are from materials such as plastic, metal and rubber. These materials ensure durability of the materials. They work in applications such as construction, automotive industry and industrial machinery.
Components of the washer
The components of the washer vary depending on its type and intended use. There are two main components of the washer discussed below. Some washers may have extra components such as the in helical cuts, concave shapes and conical shapes. The components are as discussed below.

- Body – this is the main component of the washer that is a flat, circular-shaped disk. This components comes into contact with the surface of the material fastened.
- Hole – the hole in the center allows the fasteners such as bolts or nuts to pass through.
Types of washers
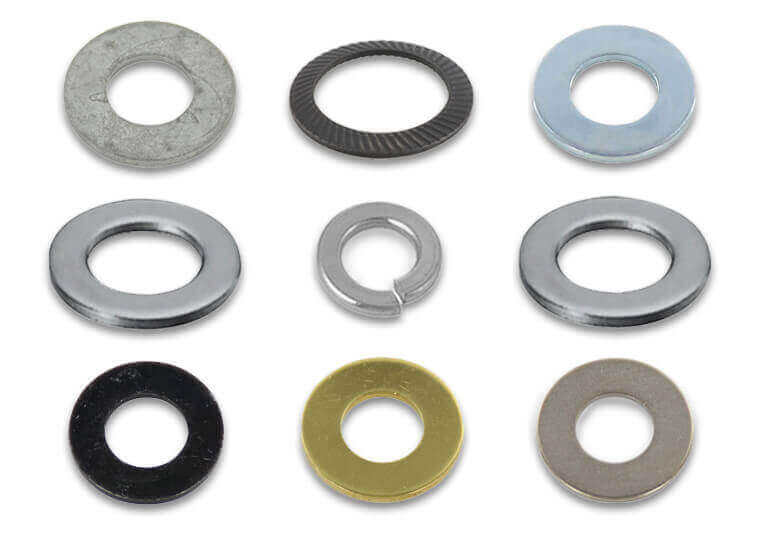
There are different types and configurations of the washers to select from. The specific type of washer used in a particular application depends on various factors such as application requirements and materials. The following are the common types of the washers.

- Flat washers – this is the most common type of the washer with a hole in the center. It helps to distribute the load and provide a smooth surface between the fastener and the materials used.
- Lock washers – lock washers have a split design that adds tension when compressed. This helps prevent the fastener from loosening due to vibrations or forces.
- Spring washers – these have a design that provides a spring-like action. This helps maintain tension in the joint and compensating for thermal expansion or contraction.
- Fender washers – these are large-diameter flat washers used in automotive and construction applications. They provide a larger load-bearing surface.
Application areas of a washer
Washers find use in various applications in the industry for fastening. Washers play a vital role in ensuring proper functioning and longevity of mechanical assemblies and fastening systems in various industries. Additionally, it is advisable to consult industry professionals for guidance on the best washer to use for the specific needs of your application. the following are the common application areas of the washers.
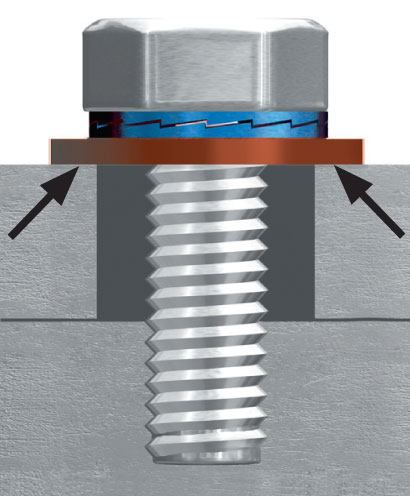
- Electrical installations – washers secure electrical boxes, switches and outlets to walls in electrical installations.
- HVAC systems – washers help in heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. This is to secure ductwork and other components in place.
- Industrial machinery – the fasteners secure components, reduce friction and provide stability in rotating parts such as bearings and gears.
- Plumbing – washers work in plumbing installations to create watertight seals in pipe components from the pressure of fasteners.
- Automotive industry – they also help in automotive manufacturing and maintenance. This is to secure bolts and nuts in various components such as engines, chassis and suspension systems.
- Construction – washers help to distribute the load and prevent damage when fastening bolts or nuts to structural elements.
- Marine applications – washers prevent corrosion and create a secure seal when fastening components in boats and ships.
- Metal fabrication – washers provide stability and distribute loads in welding and assembly applications.
Installation guide for washers
Installing a washer is a simple process which works with the use of fasteners such as bolts or nuts. The installation process of the washers should ensure safe connections for best results. Proper installation of the washers help distribute the load and prevent damage to the surface of the material or components fastened. This enhances the stability and reliability of the joint which makes it less prone to loosening or failure. Additionally, ensure you follow manufacturer’s installation instructions to ensure safety. The following are the basic steps used in the installation process.
- Choose the suitable washer size and type for your application and ensure the washer has a hole diameter that matches the bolt or nut used.
- Place the washer over the bolt or under the nut and ensure the washer’s flat surface is in contact with the material or component you are using.
- Insert the bolt or threaded end of the fastener through the hole in the washer and align it with the hole in the material you are using.
- Tighten the bolt or nut until comfortable and do not overtighten to prevent damages to the material.
- Ensure the washer is properly aligned with the fastener and the material for tightening.
- Conduct visual inspections to ensure the washer is providing a smooth surface between the fastener and the material.
Selecting the best washers for your application
Selection process of the washer involves several factors to consider. This helps to ensure it meets the requirements of your specific application. This consideration ensures secure and reliable fastening solution. Also, it is advisable to consult with professionals in the industry for guidance on the best washers depending on your application needs. The following are the factors to consider when selecting washers.

- Consider the cost-effectiveness of the washer and balance between the cost and the quality.
- Ensure the washer material is electrically insulating to prevent any unwanted electrical conductivity.
- Choose the type of washer that suits the specific needs of your application. These include lock washers, flat washers, spring washers or fender washers.
- Evaluate the environment in which the washer will work on and choose a material that resists corrosion and rust.
- Ensure that the washer matches the diameter of the bolt or nut used to fit the fastener comfortably.
- Select a washer material that is compatible with materials to fasten and offers the necessary properties such as strength, corrosion resistance and insulation.
- Consider the load-bearing requirements of your application and ensure that the washer can handle the expected load without deforming.
Frequently asked questions
A washer is a flat, curved disc with a hole in the center used to distribute the load of a fastener evenly and prevents the fastener from damaging the object fastened.
The washer has two main components working together to provide stability and secure connections. These include the body and the hole. Other components of the washer include the edges, a lip, raised center and coating.
Washers offer several benefits in various fastening and assembly applications to ensure proper functioning and reliability of mechanical assemblies. These include ease of use, versatility, corrosion resistance, stability enhancement, vibration dampening, insulation, load distribution and surface protection.
Washers have various limitations to consider when selecting for a particular application. These include environmental compatibility, proper sizing and matching, electrical conductivity, thermal expansion, additional cost, space constraints and surface damage.