
A ground rod is also known as earthing rod that installs in the ground to create a safe path for electrical current to dissipate into the earth. It is a long metal rod that works in various applications like residential, commercial and industrial buildings. The main purpose of the ground rod is to protect people an electrical equipment from the dangers of electric shock and electrical faults. They also provide a low resistance path for electrical current to flow into the ground. Additionally, it is from copper or steel and it drive vertically into the ground until it reaches a depth where the soil provides sufficient conductivity. The ground rod should have good contact with the surrounding soil to ensure effective grounding. Grounding rod, also, helps to stabilize voltage levels and protect against electrical surges caused by lightning strikes or power outages.
Components of a ground rod
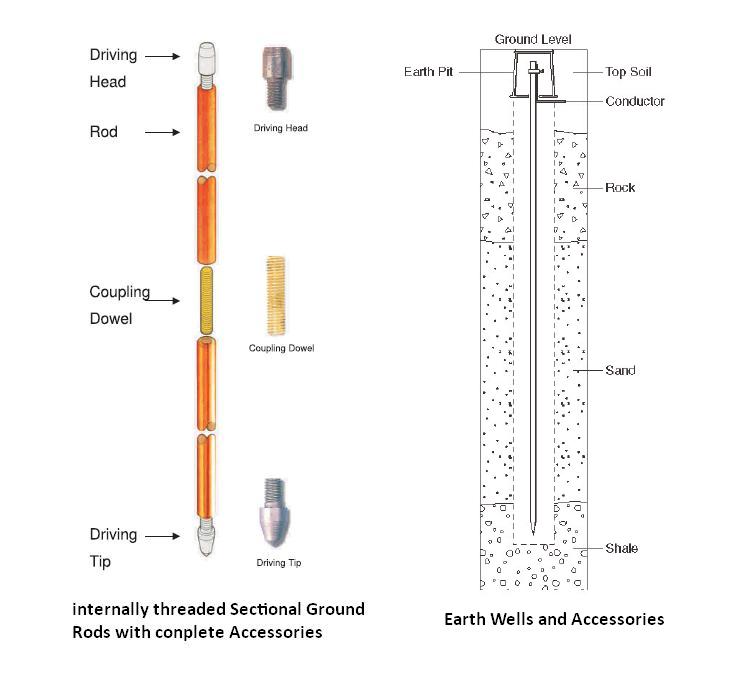
There are various components making up the ground rod used in power and distribution systems. The main component used is the rod itself made from copper or steel and has a design that is resistant to corrosion and provide good electrical conductivity. The rod has a cylindrical shape and a pointed end for easier installation into the ground. The other components of the grounding system are as discussed below.
- Grounding conductor – this is a copper wire or conductor that connects the ground rod to the electrical system. It provides a low-resistance path for fault currents into the ground.
- Grounding clamp – the grounding clamp or connector attaches the grounding conductor securely to the ground rod.
- Grounding electrode conductor – the grounding electrode conductor is a larger-sized copper wire that connects the ground rod to the main grounding busbar or panel. It transmits fault currents from the ground rod to the main electrical systems grounding point.
- Grounding busbar – this is a metal bar or panel that aids as a central point for connecting multiple grounding conductors. Also, they provide a common connection point for all grounding components.
Types of grounding rods

Various types of rods work in various applications that ensures a safe path for electrical current to pass. They types vary depending on factors such as specific application, soil conditions, corrosion risk and local regulations. The following are the common types of ground rods used on the power transmission and distribution systems.
Copper-clad ground rods – these types of ground rods involve a steel core with a thick copper coating to provide strength and durability. They are commonly used in applications like residential, commercial and industrial settings.
Solid copper ground rods – these are entirely from copper for excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. They work in areas where corrosion is a concern such as coastal areas or soil with high moisture content.
Galvanized steel ground rods – these are from steel coated with a layer of zinc that provides corrosion resistance. This makes them suitable for areas with moderate to high risk of corrosion.
Stainless steel ground rods – stainless steel ground rods are from highly resistant materials that make them suitable for harsh or corrosive environments. They are mostly used in industrial and marine applications where the ground is prone to chemicals, saltwater or other corrosive substances.
Solid bronze ground rods – these rods offer good conductivity and corrosion resistance and are mostly used in harsh environment conditions.
Applications of ground rods
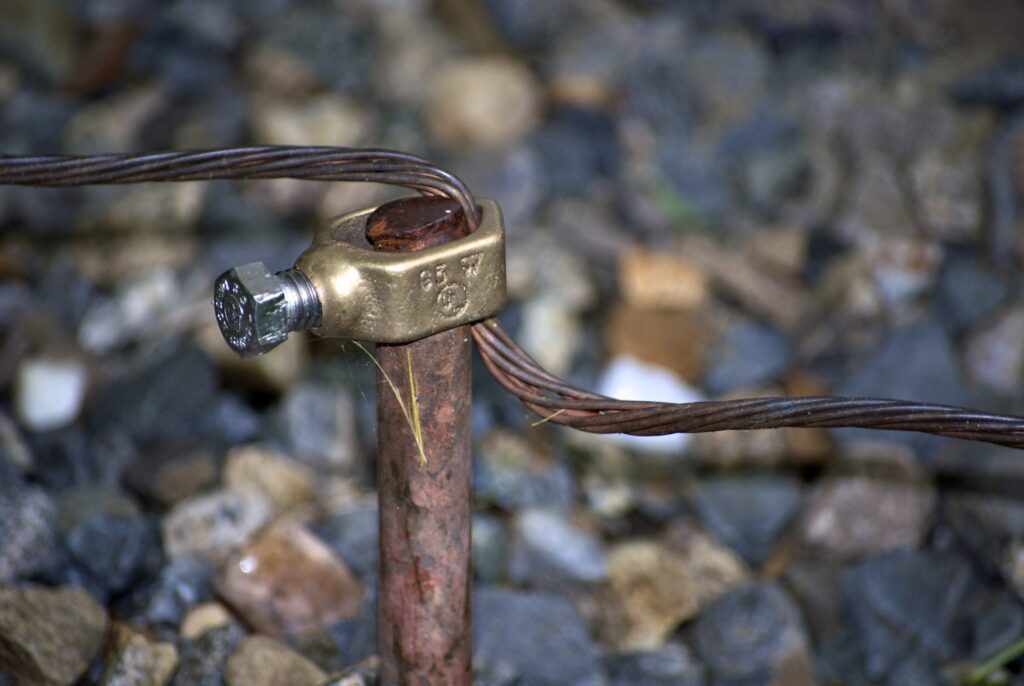

The primary purpose of the ground rods is to provide a safe and effective grounding system for your project. They also ensure the faulty current transmits to the ground for safety of the system and workers. The following are the major application areas of the ground rod.
Residential electrical systems – The ground rods are essential components of any residential electrical system to ensure the safe dissipation of fault currents. They ground electrical panels, outlets and other electrical equipment and protect against electrical shocks.
Commercial and industrial buildings – Ground rods play a vital role in commercial and industrial buildings to ensure electrical safety. They ground electrical distribution systems, machinery, equipment and other electrical systems.
Lightning protection systems – The rods are an integral part of lightning protection systems as they provide a path of least resistance for lightning strikes. This allows the electrical energy to safely dissipate to the ground.
Telecommunication systems – Ground rods in telecommunication systems provide a solid grounding connection by preventing electrical interference, protect against power surges and ensure the proper functioning of the telecommunication equipment.
Power transmission and distribution systems – The ground rods work in these systems to ground transformers, substations, transmission lines and other equipment. Additionally, they stabilize voltage levels, provide fault current paths and protect equipment from electrical surges.
Renewable energy systems – The rods also work in renewable energy systems such as solar and wind power installations to provide a path for fault currents and help protect the electrical components of the system.
Cathodic protection systems – In cathodic systems, ground rods protect the underground metal structures such as pipelines and storage tanks from corrosion. The ground serves as an anode or reference electrode in the cathodic protection system.
Installation process of the ground rods
The installation process may vary based on the specific requirements for your grounding system, local electrical codes and manufacturer’s instructions. It is advisable to consult experts in the industry for guidance and assistance with the installation process to ensure compliance and electrical safety. The following is the basic steps involved in the installation of the grounding rods.
- Determine the location for the ground rod installation which should be in close proximity to the electrical system that requires grounding. Consider factors such as accessibility, soil conditions and proximity to the grounding components.
- Ensure the grounding system design allows for installation. Determine the size of the grounding conductor, select the appropriate grounding clamp and prepare the grounding electrode conductor if required.
- Gather the necessary tools and equipment for the installation process which include hammers, mallets, grounding clamp, grounding conductor and wrench or pliers.
- Drive the ground rod vertically into the ground using a hammer. Apply firm and consistent force to ensure it reaches the recommended depth. The depth varies depending on local electrical codes and soil conditions.
- Attach the grounding clamp to the rod and ensure a tight and secure connection between the rod and the clamp. The grounding clamp should be compatible to the grounding conductor.
- Connect the grounding conductor to the grounding clamp using wire cutters to remove the appropriate length of insulation from the grounding conductor. This ensures a tight and reliable connection.
- Connect the grounding electrode conductor if needed by securing it to the grounding clamp and connecting the other end to the designated terminal on the main grounding system.
- Test and verify the effectiveness of the grounding system using the appropriate tools such as resistance testers or multimeters to measure the resistance between the ground rod and the grounding system.
Selecting the best ground rod for your project
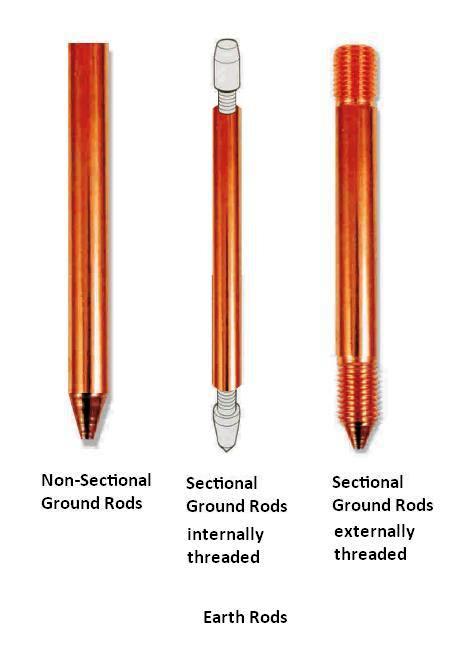

The requirements for a ground rod depend on the unique project and local regulations. You should seek advice of a qualified professional to ensure that you select the most suitable ground rod for your specific needs. Below are some key factors to consider when selecting the ground rods for your application.
- Consider the material of the ground rod which plays a crucial role in performance and longevity. Common materials include copper, copper-clad steel, galvanized steel, stainless steel and bronze. Consider the environmental conditions, soil composition and corrosion risk to determine the most fit material.
- Evaluate the corrosion resistance depending on the area in which the ground rod will install. Check the moisture level, soil composition and the chemical exposure of the area.
- Chose the length and diameter of the rod based on the specific requirements of your grounding system and local electrical codes. Consider the recommended burial dept for effective grounding and choose a length that meets those requirements.
- Ensure that the chosen ground rod provides adequate conductivity for your specific requirements for grounding systems. This includes the type of rod, minimum diameter and resistance values.
- Consider you budget when selecting a ground rod while balancing the desired performance and durability.
- Choose the ground rods from a reputable manufacturer with track record of producing high quality products. Review customers feedback to ensure reliability and durability of the chosen ground rod.
Frequently Asked Questions
A ground rod is a long metal rod installed in the ground to create a safe path for electrical currents to dissipate into the earth. They are mostly used in residential, commercial and industrial buildings.
Copper-clad ground rods
Solid copper ground rods
Galvanized steel ground rods
Stainless steel ground rods
Solid bronze ground rods
Electrical safety
Protection against electrical faults
Lightning protection
Voltage stabilization
Protection against electrical surges
Compliance with electrical codes
Improved equipment performance
Soil conditions limitations
High resistance
Corrosion resistance
Ground faults in isolated systems
Limited area of protection
Maintenance and inspection