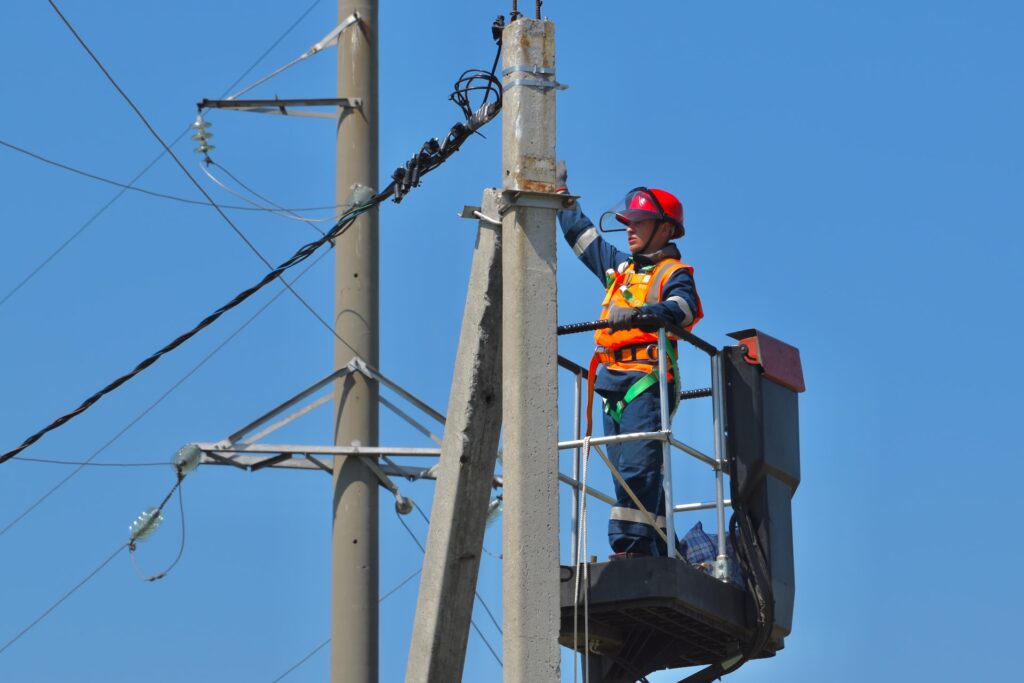
Power line insulator is a critical component in overhead electrical transmission systems. They prevent electric current leakage from the overhead conductors on power towers, poles, or other structures to the surroundings. Our insulator products include corona ring, pin insulator, post insulator, shackle insulator, stay insulator, suspension insulator and more.
Table of Contents
- What is Corona ring?
- Features
- What is a pin insulator?
- Mounting position of pin insulator
- How to use a porcelain pin insulator?
- Features of pin insulators
- What is a post insulator, and what is it used for?
- What applications do post insulators have?
- Features of post insulators
- What is a shackle insulator?
- Features of shackle insulator
- What is a stay insulator, and what is it used for?
- What is the best way to use a stay insulator?
- Features of stay insulators
- What is a Suspension Insulator?
- Features
- Notes:
- How Suspension Insulators Work
- How are Suspension Insulators installed?
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is Corona ring?
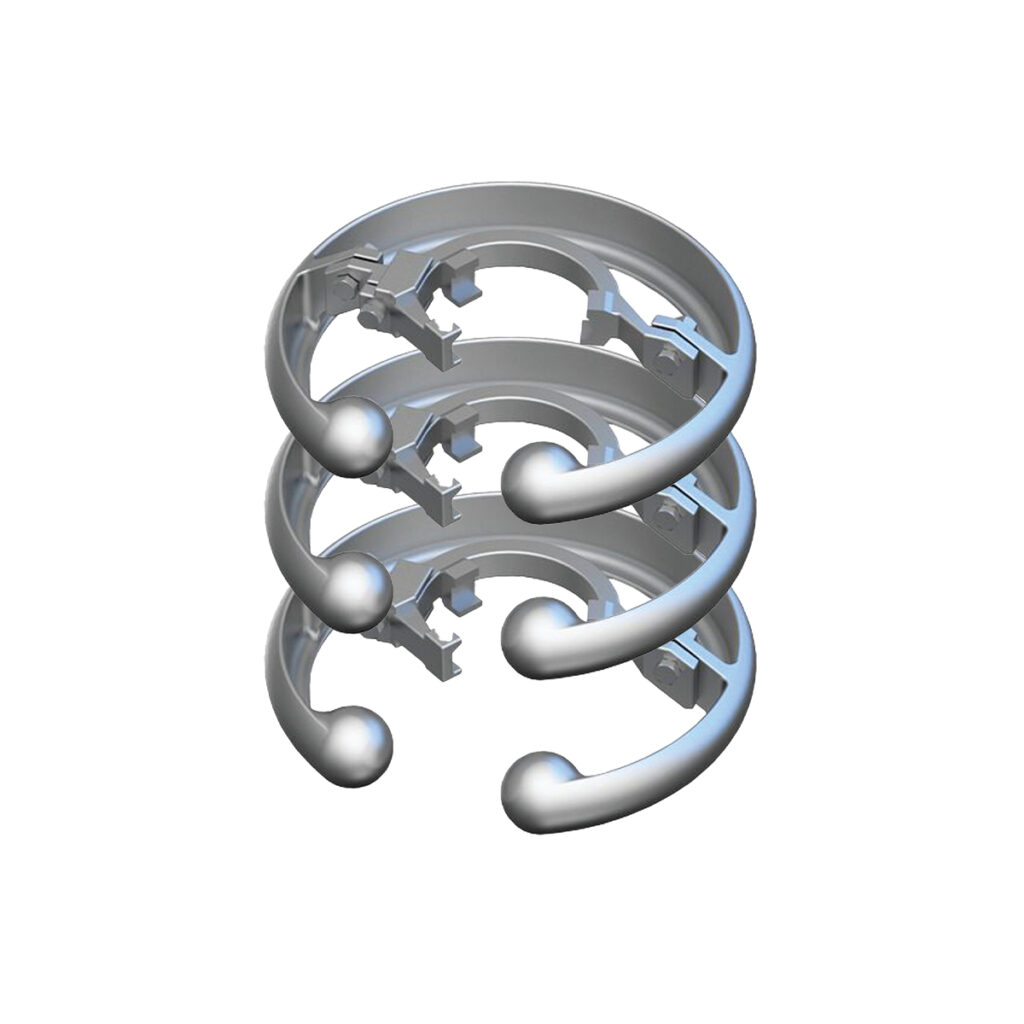
The Corona ring is intended to reduce the noise generated by corona voltage. It is made up of rings that are attached to the insulators’ ends and bushings that are also attached to other transmission line fittings. Corona discharge is also prevented at these sites of installation.
Corona discharge occurs at the curvatures of most transmission line installations. The corona rings are put in this exact location. They encircle such places and are also connected to the conductors of the transmission line. Additionally, enclosing the insulators helps to lessen the potential gradient within the insulators’ specific spots.
The corona rings’ ring-like structure helps to distribute the electrical discharge from a localized area to a large area. This ensures that the charges will not build up to the point where they will trigger a discharge.
Corona rings are comprised of aluminum metal rings that can resist 230V voltages. They also come in a variety of diameters, with the diameter you choose based on the voltage passing through the transmission line. They are effective enough to keep the insulators from breaking down.
Features
- It can be installed in any direction as it’s unidirectional.
- Ideal for voltages over than 230V
- Various ring diameters
What is a pin insulator?
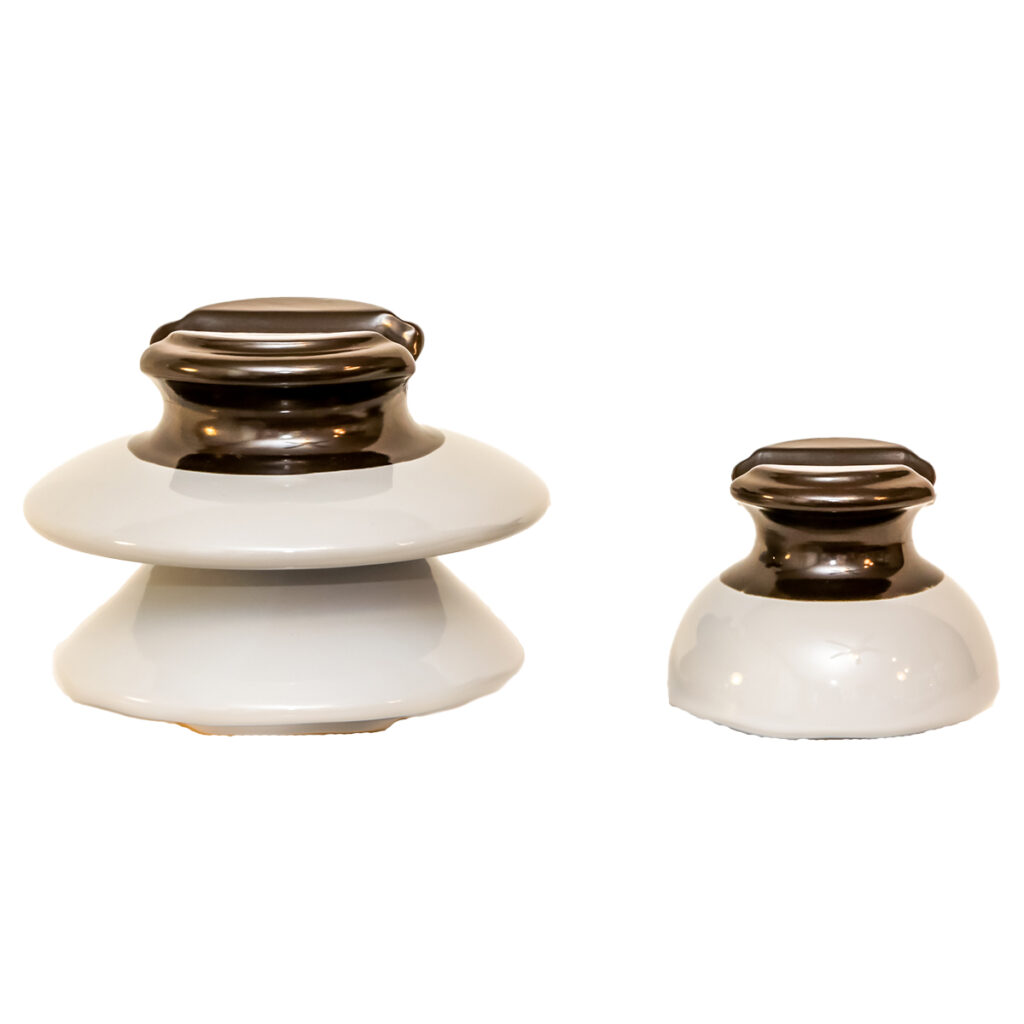

The pin insulator is a type of low voltage insulator that is used in power transmission and distribution lines with voltage ratings ranging from 11 kV to 33 kV.
The insulator is held in place by a pole top pin and grips the pin, therefore the name pin insulator.
Pin insulators are available in a variety of materials, including porcelain, ceramic, silicon rubber, and polymer. A pin insulator is typically mounted on a telephone pole, utility pole, or tower, with cables and wires dressed to the top. It is built in the shape of an umbrella or an upside-down bowl to cover the inside parts from the rain and keep them insulated.
Mounting position of pin insulator
The pin insulator can be held in a vertical or horizontal position by the pole top pin, which is normally made of galvanized steel. It should be long enough to withstand the conductor’s high voltage and high stress.
The price of a pin insulator is rather modest when compared to other electrical insulators, notably conventional porcelain types. TTF is a pin insulator manufacturer with a wide range of designs, materials, and standard criteria to choose from.
How to use a porcelain pin insulator?
The porcelain pin insulator is made up of two parts: the porcelain section and a steel pole top pin. The conductor is attached to the insulator on the top groove of a pin insulator, which is mounted on the cross arm of a utility pole or tower.
Features of pin insulators
- High mechanical strength.
- Proper creepage distance
- Modest price
- It can be used vertically or horizontally
- Simple construction
- Easy maintenance.
What is a post insulator, and what is it used for?
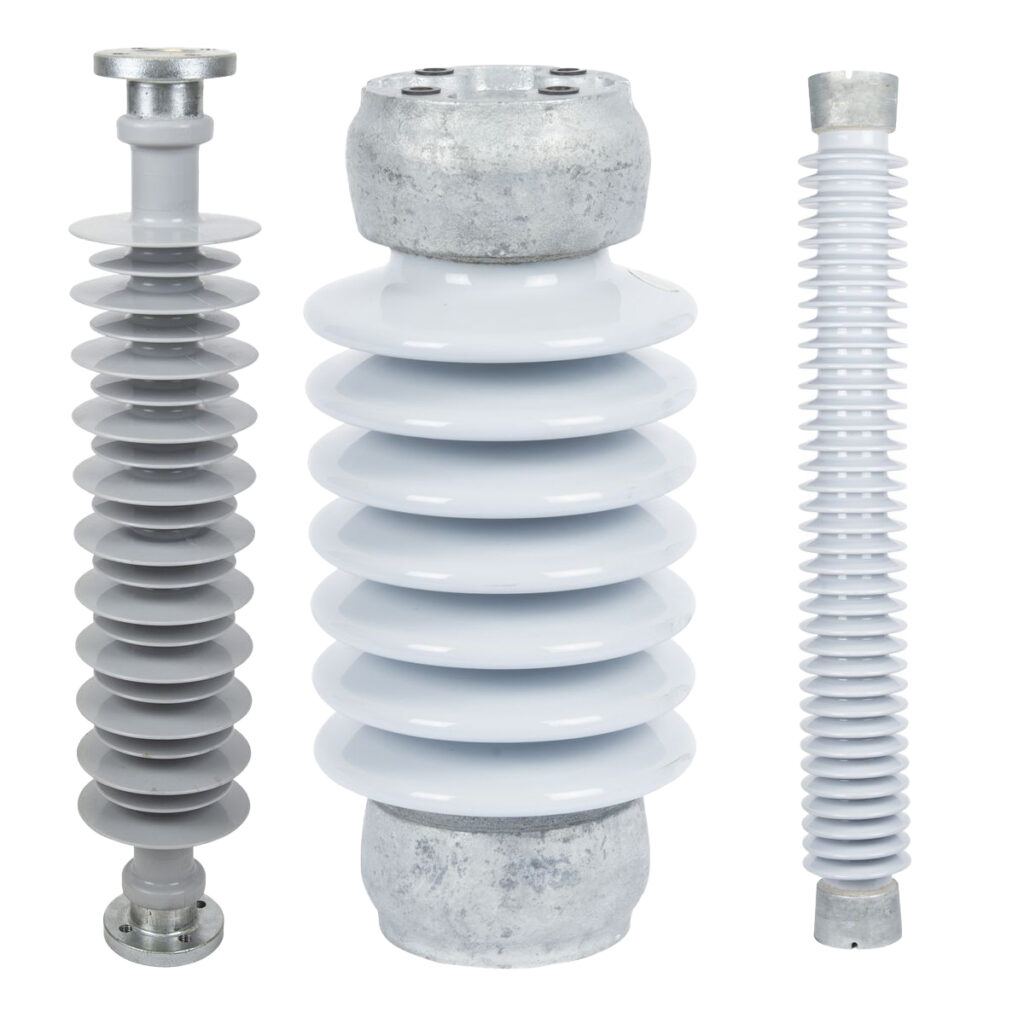

Post insulators are commonly applied in low to high voltage systems, and there are line post insulators and station post insulators for diverse applications.
Line post insulators are installed on the transmission line’s electrical pole. Line post insulators are classified into various varieties based on their intended use and positioning on the pole: Tie Top Line Post Insulators, Horizontal and Vertical Line Post Insulators, Under Arm Line Post Insulators, and Clamp Top Line Post Insulators are all available.
In electric power plants, transmission and distribution substations, and other electrical facilities with voltages up to 1100kV, station post insulators provide insulation and structural support for the poles.
Post insulators can be manufactured of porcelain or silicone polymer. They’re made to standard dimensions and designed for specific markets, so they can meet the electrical and mechanical requirements of IEC, ANSI standards, and customer specifications.
What applications do post insulators have?
Up to 1100 kV, the post insulator can be applied in transmission lines, distribution plants, and switchgear systems.
Features of post insulators
Post insulators provide the following characteristics: Excellent creepage distances between 1 and 1100 KV Multiple insulators can be connected for higher voltage applications.
What is a shackle insulator?
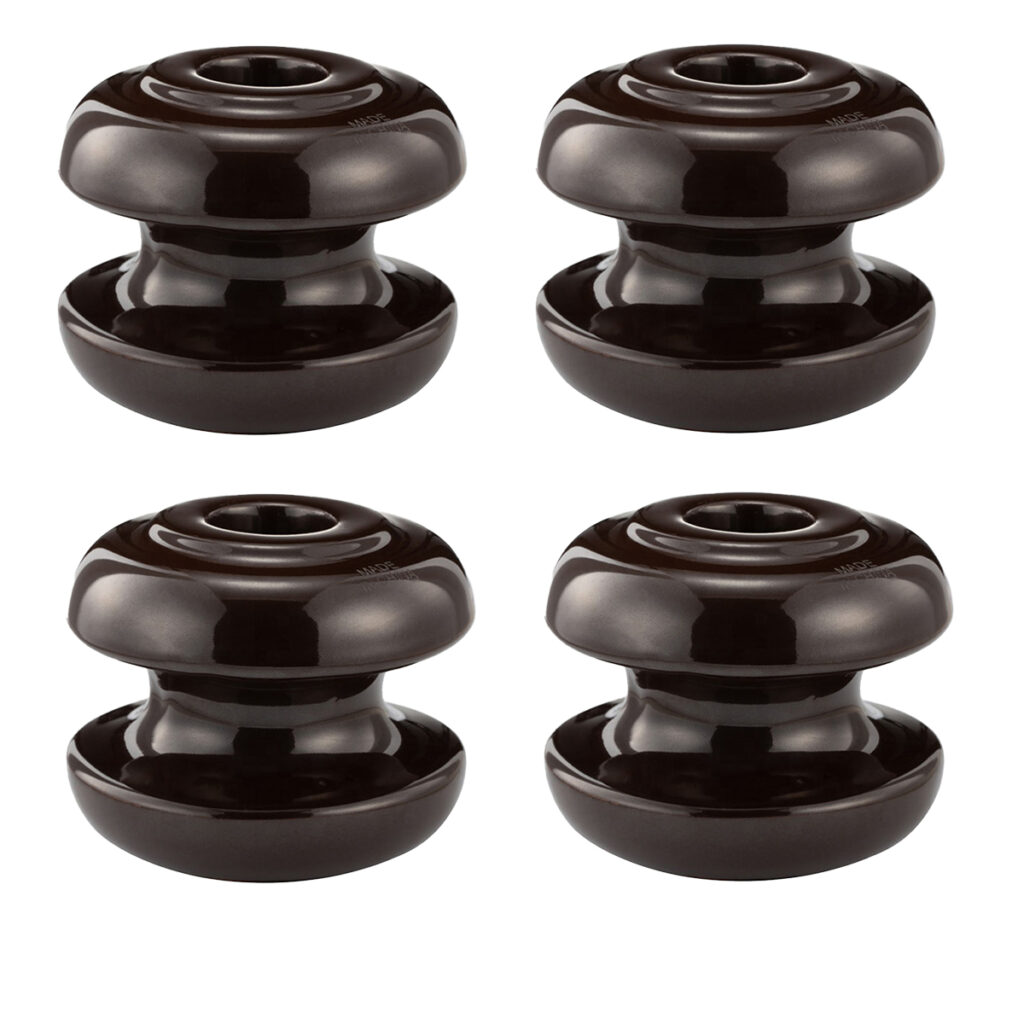

Shackle insulator, also known as spool insulator or butterfly insulator, is a type of insulator that is commonly used on low-voltage transmission and distribution lines.
Designed to insulate and support secondary wires, these shackle insulators can be fastened to the pole directly with a bolt or to the electrical cross arm, or with the addition of D-iron brackets or secondary racks to provide additional support and insulation. They can be mounted either horizontally or vertically.
All of the shackle insulators from TTF are designed, manufactured, and tested in accordance with international standards such as GB, IEC, AS, BS, ANSI, and others.
According to customer requirements, we can also provide Shackle Insulators with varied specifications, such as different kV of systems, types, colors, sizes, measurements, and, of course, different pricing.
Features of shackle insulator
- High impact resistance
- Both vertical and horizontal positions
- For low voltage distribution networks only
- Easy replacement for porcelain
What is a stay insulator, and what is it used for?
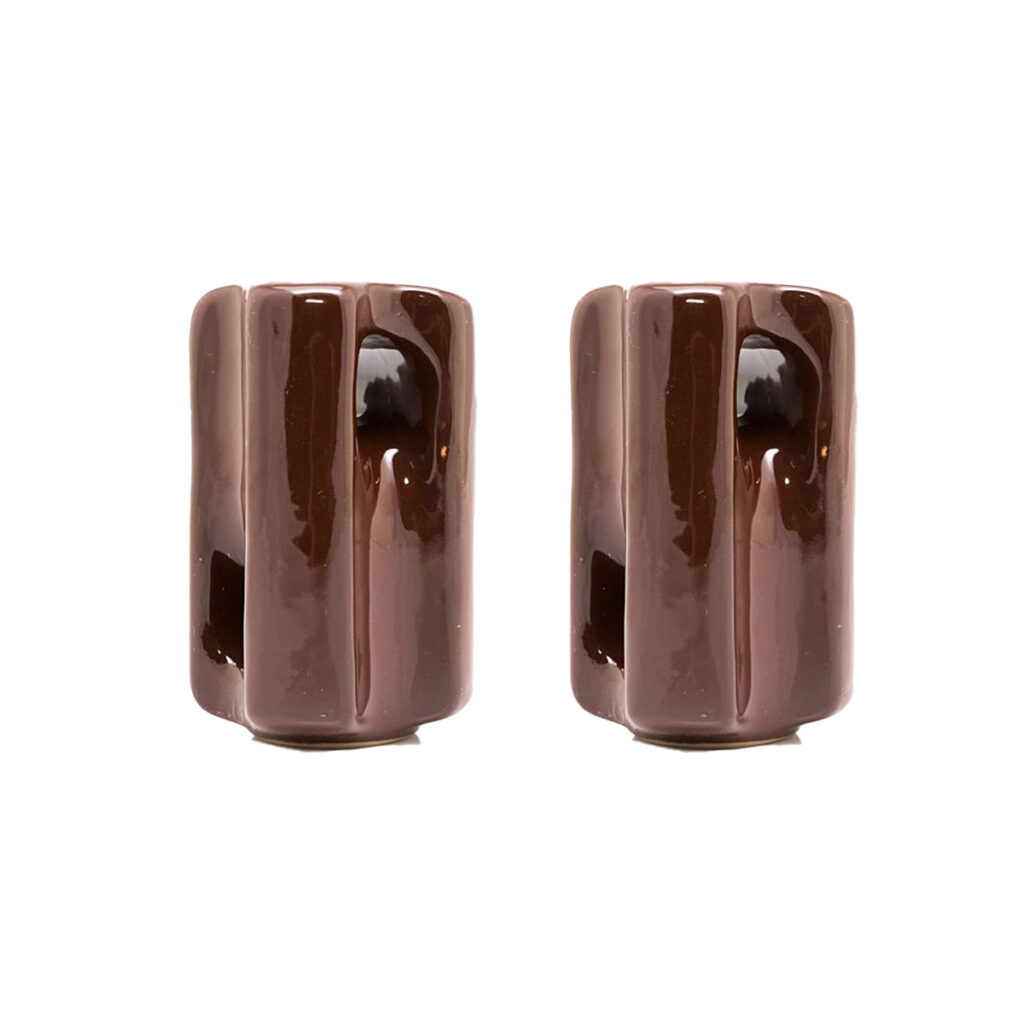

Stay insulators are a type of strain insulator that is frequently used in rural and railway medium and low voltage lines. The stay insulator is also known as the egg insulator or the guy insulator.
The stay insulator is typically installed in the middle of a stay wire or guy wire, and it can provide sufficient insulation for the utility pole and stay clamp.
The insulator should be comprised of compressive-strength materials, such as high-quality porcelain in TTF’s stay insulator.
What is the best way to use a stay insulator?
The porcelain stay insulator is installed in the middle of the stay wire, which connects the utility pole to the ground at both ends. It acts as a barrier between the two components.
Features of stay insulators
- It used for low voltage Stay system structures
- Despite its small size, it has a high tensile strength.
- Material: porcelain or ceramic
What is a Suspension Insulator?
Suspension insulators are rugged, high-resistance insulators that are well suited to endure higher voltage loads in a variety of electrical systems working under a wide range of environmental circumstances.
The suspension insulator is made of a string of insulator discs placed onto a malleable rod and is made of waterproof, robust materials. This flexible design allows for swing movement in inclement weather, reducing pressure on the insulator and extending its service life.
Furthermore, the suspension insulator’s ingenious design allows you to add or replace insulator discs as needed, saving you the time, cost, and risk of changing the entire insulator. This model is also compatible with a wide selection of accessories, such as insulator string, corona rings, and end fittings, making it a popular choice in a variety of sectors!
Features
- Time and cost-effective
- Adaptable construction
- High voltage resistivity
- Accessory compatible
- Minimal maintenance
- Flexible string design
- Versatile application
- Replaceable discs
- Weather-resistant
- Durable materials
Notes:
To minimize unsafe conditions, the assembly, installation, and maintenance of suspension insulators must always be done with the help of competent personnel.
Before installing an insulator, make sure it’s suitable with the electrical circuit.
How Suspension Insulators Work
Suspension insulators are used to restrict the flow of electricity to certain zones of an electrical circuit as an insulator. This voltage distribution regulation, which works in tandem with conductors (which assist electrical flow), ensures that the circuit operates safely and efficiently.
Suspension insulators are made out of a flexible metal rod with a string of insulator discs attached to it. Each disc has a low voltage capacity, which allows the stress of a high voltage load to be dispersed over the discs and reduces the possibility of overloading. The insulator’s compartmentalized architecture also ensures that if one disc fails, the integrity of the remaining insulator discs is not jeopardized.
The insulator is strung at the end of a length of insulator string that is attached to the pole or tower when it is installed. The cross arms assist the insulator clamp in keeping the insulator in the proper position.
How are Suspension Insulators installed?
Suspension insulator installation should always be done by trained specialists who have all of the appropriate safety equipment.
The following are the fundamental procedures in installing a suspension insulator after these are in place:
Clearing the site of any debris and setting the insulator pieces on a protective covering are the first steps in the process.
Insulator Assembly: Thread the desired number of discs onto the insulator rod and secure the necessary connection hardware.
Hoisting Into Position: The assembled insulator is then slowly raised to the desired location using a pulley; Mounting Insulator: The insulator is then aligned into position using the cross arms and insulator clamp. End fittings and corona rings can be used to fix the insulator even more.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What does electrical insulator include?
Our insulator products include corona ring, pin insulator, post insulator, shackle insulator, stay insulator, suspension insulator and more.
What is the definition of electrical insulator?
Power line insulator is a critical component in overhead electrical transmission systems. They prevent electric current leakage from the overhead conductors on power towers, poles, or other structures to the surroundings.
